|
78th Parallel North
The 78th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 78 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane, in the Arctic. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, Europe, Asia, the Arctic Ocean and North America. It is the southernmost integral parallel north that does not pass through any continental mainland (being slightly to the north of Cape Chelyuskin). At this latitude the sun is visible for 24 hours, 0 minutes during the summer solstice and nautical twilight during the winter solstice. Around the world Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastwards, the parallel 78° north passes through: : See also * 77th parallel north *79th parallel north The 79th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 79 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane, in the Arctic. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, Europe, Asia, the Arctic Ocean and North America. At this latitude the sun is visible for ... {{geographical coordinates, state=collapsed n78 Geography of the Arctic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle Of Latitude
A circle of latitude or line of latitude on Earth is an abstract east–west small circle connecting all locations around Earth (ignoring elevation) at a given latitude coordinate line. Circles of latitude are often called parallels because they are Parallel (geometry), parallel to each other; that is, planes that contain any of these circles never Intersection, intersect each other. A location's position along a circle of latitude is given by its longitude. Circles of latitude are unlike circles of longitude, which are all great circles with the centre of Earth in the middle, as the circles of latitude get smaller as the distance from the Equator increases. Their length can be calculated by a common sine or cosine function. The 60th parallel north or 60th parallel south, south is half as long as the Equator (disregarding Earth's minor flattening by 0.335%). On the Mercator projection or on the Gall-Peters projection, a circle of latitude is perpendicular to all meridian (geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in place. Res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mackenzie King Island
Mackenzie King Island is one of the uninhabited Queen Elizabeth Islands in northern Canada. It lies north of Melville Island and south of Borden Island, and like them is divided when it comes to administration. Most of the island is in Northwest Territories, while its easternmost portion lies in Nunavut. The border runs along the 110th meridian west. Mackenzie King has an area of , long in northeast or in southeast and wide, making it the 116th largest island in the world, and Canada's 26th largest island. History The first known visit to the island was by Vilhjalmur Stefansson in 1915, and it was later named for William Lyon Mackenzie King William Lyon Mackenzie King (December 17, 1874 – July 22, 1950) was a Canadian statesman and politician who served as the tenth prime minister of Canada for three non-consecutive terms from 1921 to 1926, 1926 to 1930, and 1935 to 1948. A Li .... References Further reading * Vilks, G. ''Foraminiferal Study of East Bay, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilkins Strait (Canada)
Wilkins Strait () is a natural waterway through the central Canadian Arctic Archipelago. It is mostly in the Northwest Territories, although its eastern extremity is in Nunavut. It separates Borden Island (to the north) from Brock Island (to the south-west) and Mackenzie King Island Mackenzie King Island is one of the uninhabited Queen Elizabeth Islands in northern Canada. It lies north of Melville Island and south of Borden Island, and like them is divided when it comes to administration. Most of the island is in Northwes ... (to the south). Straits of the Northwest Territories Straits of Qikiqtaaluk Region {{NorthwestTerritories-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brock Island
Brock Island is one of the uninhabited members of the Queen Elizabeth Islands of the Arctic Archipelago located in the Northwest Territories, Canada. Located at 77°51'N 114°27'W, it measures in size and lies close to Mackenzie King Island. The first known sighting of the island by a European was by Vilhjalmur Stefansson in 1915 and it was later named for Reginald W. Brock, Dean of Applied Science at the University of British Columbia. References External linksBrock Island in the Atlas of Canada - Toporama; Natural Resources Canada Islands of the Queen Elizabeth Islands Uninhabited islands of the Northwest Territories {{NorthwestTerritories-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2016 census population of 41,790, it is the second-largest and the most populous of the three territories in Northern Canada. Its estimated population as of 2022 is 45,605. Yellowknife is the capital, most populous community, and only city in the territory; its population was 19,569 as of the 2016 census. It became the territorial capital in 1967, following recommendations by the Carrothers Commission. The Northwest Territories, a portion of the old North-Western Territory, entered the Canadian Confederation on July 15, 1870. Since then, the territory has been divided four times to create new provinces and territories or enlarge existing ones. Its current borders date from April 1, 1999, when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
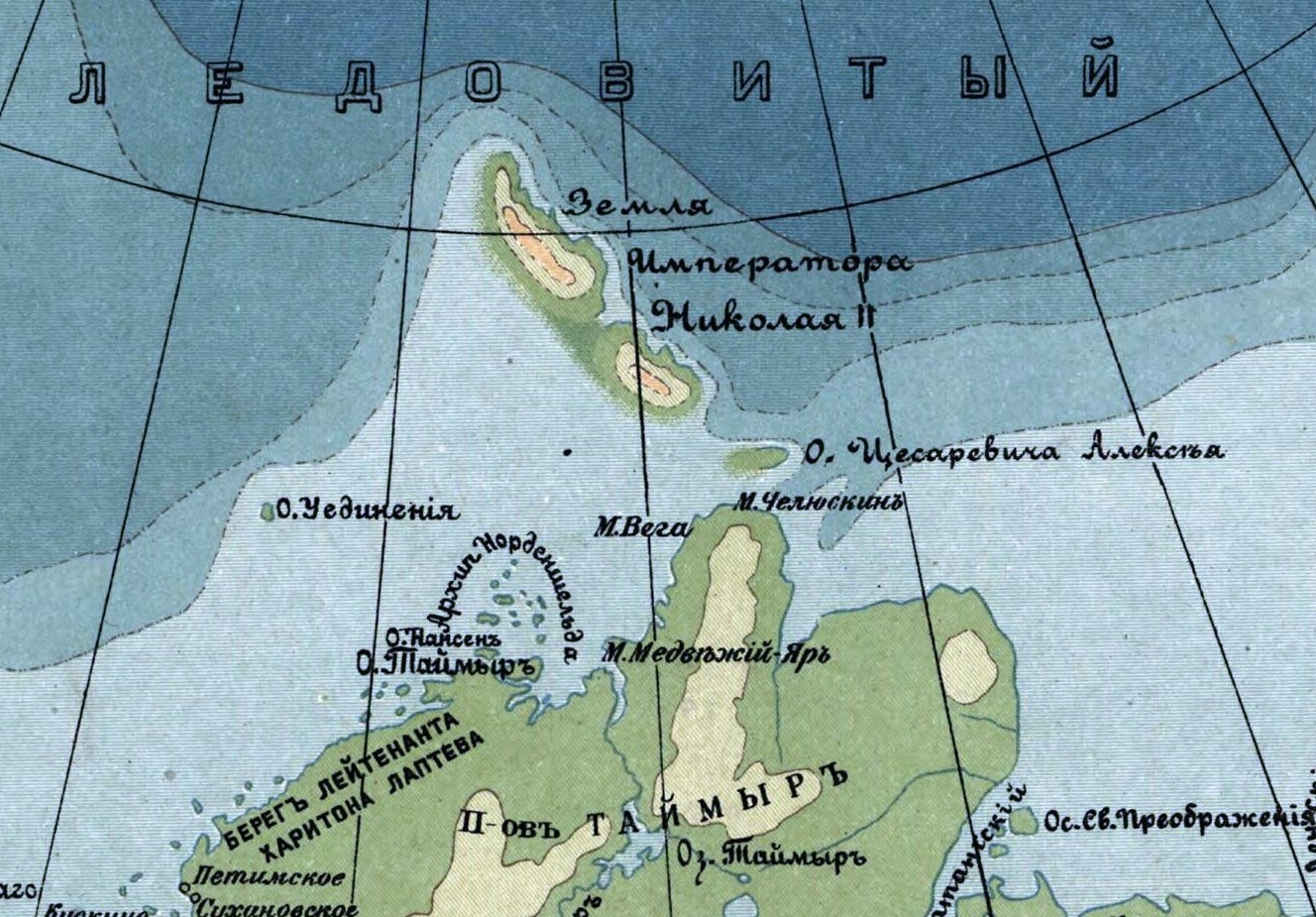
Maly Taymyr Island
Maly Taymyr Island (russian: Малый Таймыр, or Little Taymyr Island) is an island in the Laptev Sea, Russian Arctic. Geography It is located off the southeastern end of the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago and northeast of the Taymyr Peninsula and has a smaller island, Starokadomsky Island, close by on its northwestern side. The area of Maly Taymyr Island is and its location is . The Vilkitsky Strait runs south of Maly Taymyr Island and its waters, as well as the waters surrounding the two islands, are covered with pack ice during the long and bitter winters. There are many ice floes even in the short summer, between June and September. Maly Taymyr Island belongs to the Krasnoyarsk Krai administrative division of the Russian Federation and is part of the Great Arctic State Nature Reserve – the largest nature reserve of Russia and one of the biggest in the world. On the northern shores of Maly Taymyr there is a small island named Ostrov Oktyabrenok. History The island wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laptev Sea
The Laptev Sea ( rus, мо́ре Ла́птевых, r=more Laptevykh; sah, Лаптевтар байҕаллара, translit=Laptevtar baỹğallara) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy Cape. The Kara Sea lies to the west, the East Siberian Sea to the east. The sea is named after the Russian explorers Dmitry Laptev and Khariton Laptev; formerly, it had been known under various names, the last being Nordenskiöld Sea (russian: link=no, мо́ре Норденшёльда), after explorer Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld. The sea has a severe climate with temperatures below 0 °C (32 °F) over more than nine months per year, low water salinity, scarcity of flora, fauna and human population, and low depths (mostly less than 50 meters) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolshevik Island
__NOTOC__ Bolshevik Island (russian: о́стров Большеви́к, ) is an island in Severnaya Zemlya, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russian Arctic. The island is named after the political faction of the same name. History The island, together with the eastern coast of what was named Emperor Nicholas II Land, was discovered by Boris Vilkitsky at the time of the 1913 Arctic Ocean Hydrographic Expedition. Its insularity, however, wasn't proven until 1931, when Georgy Ushakov and Nikolay Urvantsev charted the archipelago during their 1930–32 expedition. Prima Polar Station, currently the only Polar station operating in Severnaya Zemlya, is located in this island near Cape Baranov. Geography It is the southernmost island and the second largest island in the group. The area of this island has been estimated at . The island is mountainous reaching a height of 935 m. About 31% of Bolshevik Island, totaling over , is covered by glaciers, the largest are Leningrad Glacier, Semyonov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severnaya Zemlya
Severnaya Zemlya (russian: link=no, Сéверная Земля́ (Northern Land), ) is a archipelago in the Russian high Arctic. It lies off Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula, separated from the mainland by the Vilkitsky Strait. This archipelago separates two marginal seas of the Arctic Ocean, the Kara Sea in the west and the Laptev Sea in the east. Severnaya Zemlya was first noted in 1913 and first charted in 1930–32, making it the last sizeable archipelago on Earth to be explored. Administratively, the islands form part of Russia's Krasnoyarsk Krai. In Soviet times there were a number of research stations in different locations, but currently there are no human inhabitants in Severnaya Zemlya, except for the Prima Polar Station near Cape Baranov. The largest glacier in the Russian Federation, the Academy of Sciences Glacier, is located in Severnaya Zemlya. The archipelago is notable as well in connection with the ongoing multiyear Arctic sea ice decline. Until recently, ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kara Sea
The Kara Sea (russian: Ка́рское мо́ре, ''Karskoye more'') is a marginal sea, separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and from the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago. Ultimately the Kara, Barents and Laptev Seas are all extensions of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. The Kara Sea's northern limit is marked geographically by a line running from Cape Kohlsaat in Graham Bell Island, Franz Josef Land, to Cape Molotov (Arctic Cape), the northernmost point of Komsomolets Island in Severnaya Zemlya. The Kara Sea is roughly long and wide with an area of around and a mean depth of . Its main ports are Novy Port and Dikson and it is important as a fishing ground although the sea is ice-bound for all but two months of the year. The Kara Sea contains the East-Prinovozemelsky field (an extension of the West Siberian Oil Basin), containing significant undeveloped petroleum and natural gas. In 2014, US gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territorial waters.World Wildlife Fund, 2008. It was known among Russians in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea ("Norse Sea"); the current name of the sea is after the historical Netherlands, Dutch navigator Willem Barentsz. The Barents Sea is a rather shallow Continental shelf, shelf sea, with an average depth of , and it is an important site for both fishing and hydrocarbon exploration.O. G. Austvik, 2006. It is bordered by the Kola Peninsula to the south, the shelf edge towards the Norwegian Sea to the west, and the archipelagos of Svalbard to the northwest, Franz Josef Land to the northeast and Novaya Zemlya to the east. The islands of Novaya Zemlya, an extension of the northern end of the Ural Mountains, separate the Barents Sea from the Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |