|
7-Hydroxymitragynine
7-Hydroxymitragynine is a terpenoid indole alkaloid from the plant ''Mitragyna speciosa'', commonly known as Kratom. It is often referred to as ‘7-OH’. It was first described in 1994 and is a natural product derived from the mitragynine present in the Kratom leaf. It is considered an oxidized derivative and active metabolite of mitragynine. 7-OH binds to opioid receptors like mitragynine, but research suggests that 7-OH binds with greater potency and contributes heavily to the analgesic activity of mitragynine as a metabolite. Metabolism After a kratom study, it was revealed that 7-OH converts into Mitragynine pseudoindoxyl. Pharmacology 7-Hydroxymitragynine, like mitragynine, appears to be a mixed opioid receptor agonist/ antagonist, acting as a partial agonist at µ-opioid receptors and as a competitive antagonist at the δ- and κ-opioid receptors. Evidence suggests that 7-OH is more potent than both mitragynine and morphine. 7-OH does not activate the β-ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioids
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use disorder, reversing opioid overdose, and suppressing cough. Extremely potent opioids such as carfentanil are approved only for veterinary use. Opioids are also frequently used non-medically for their euphoric effects or to prevent withdrawal. Opioids can cause death and have been used for executions in the United States. Side effects of opioids may include itchiness, sedation, nausea, respiratory depression, constipation, and euphoria. Long-term use can cause tolerance, meaning that increased doses are required to achieve the same effect, and physical dependence, meaning that abruptly discontinuing the drug leads to unpleasant withdrawal symptoms. The euphoria attracts recreational use, and frequent, escalating recreational use of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kratom
''Mitragyna speciosa'' (commonly known as kratom, an herbal leaf from a tree of the Rubiaceae family, ) is a tropical evergreen tree in the coffee family native to Southeast Asia. It is indigenous to Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, and Papua New Guinea, where it has been used in herbal medicine since at least the nineteenth century. It has also historically been used for chewing, smoking, and tea. Kratom has opioid properties and some stimulant-like effects. , the efficacy and safety of kratom are unclear, and the drug was not approved as a therapeutic agent in the United States due to the poor quality of the research. In 2019, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) stated that there is no evidence that kratom is safe or effective for treating any condition. Some people take it for managing chronic pain, for treating opioid withdrawal symptoms, or for recreational purposes. The onset of effects typically begins within five to ten minutes and lasts for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitragyna Speciosa
''Mitragyna speciosa'' (commonly known as kratom, an herbal leaf from a tree of the Rubiaceae family, ) is a tropical evergreen tree in the coffee family native to Southeast Asia. It is indigenous to Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, and Papua New Guinea, where it has been used in herbal medicine since at least the nineteenth century. It has also historically been used for chewing, smoking, and tea. Kratom has opioid properties and some stimulant-like effects. , the efficacy and safety of kratom are unclear, and the drug was not approved as a therapeutic agent in the United States due to the poor quality of the research. In 2019, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) stated that there is no evidence that kratom is safe or effective for treating any condition. Some people take it for managing chronic pain, for treating opioid withdrawal symptoms, or for recreational purposes. The onset of effects typically begins within five to ten minutes and lasts for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitraphylline
Mitraphylline, an oxindole derivative, is an active alkaloid in the leaves of the tree ''Mitragyna speciosa'', commonly known as kratom. As a non-narcotic constituent, it also occurs to a significant amount in the bark of ''Uncaria tomentosa'' (Cat's Claw) along with a number of isomeric alkaloids. Current research is focusing on antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects and its ''in vivo'' efficacy to induce apoptosis in human breast cancer, sarcoma A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal (connective tissue) origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, fat, vascular, or hematopoietic tissues, and sarcom ... as well as lymphoblastic leukaemia cell lines. References {{reflist Indole alkaloids Spiro compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Abstracts Service
CAS (formerly Chemical Abstracts Service) is a division of the American Chemical Society. It is a source of chemical information. CAS is located in Columbus, Ohio, United States. Print periodicals ''Chemical Abstracts'' is a periodical index that provides numerous tools such as SciFinder as well as tagged keywords, summaries, indexes of disclosures, and structures of compounds in recently published scientific documents. Approximately 8,000 journals, technical reports, dissertations, conference proceedings, and new books, available in at least 50 different languages, are monitored yearly, as are patent specifications from 27 countries and two international organizations. ''Chemical Abstracts'' ceased print publication on January 1, 2010. Databases The two principal databases that support the different products are CAplus and Registry. CAS References CAS References consists of bibliographic information and abstracts for all articles in chemical journals worldwide, and chemistry-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biased Ligands
Bias is an inclination toward something, or a predisposition, partiality, prejudice, preference, or predilection. Bias may also refer to: Scientific method and statistics * The bias introduced into an experiment through a confounder * Algorithmic bias, machine learning algorithms that exhibit politically unacceptable behavior * Cultural bias, interpreting and judging phenomena in terms particular to one's own culture * Funding bias, bias relative to the commercial interests of a study's financial sponsor * Infrastructure bias, the influence of existing social or scientific infrastructure on scientific observations * Publication bias, bias toward publication of certain experimental results * Bias (statistics), the systematic distortion of a statistic ** Biased sample, a sample falsely taken to be typical of a population ** Estimator bias, a bias from an estimator whose expectation differs from the true value of the parameter * Personal equation, a concept in 19th- and early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
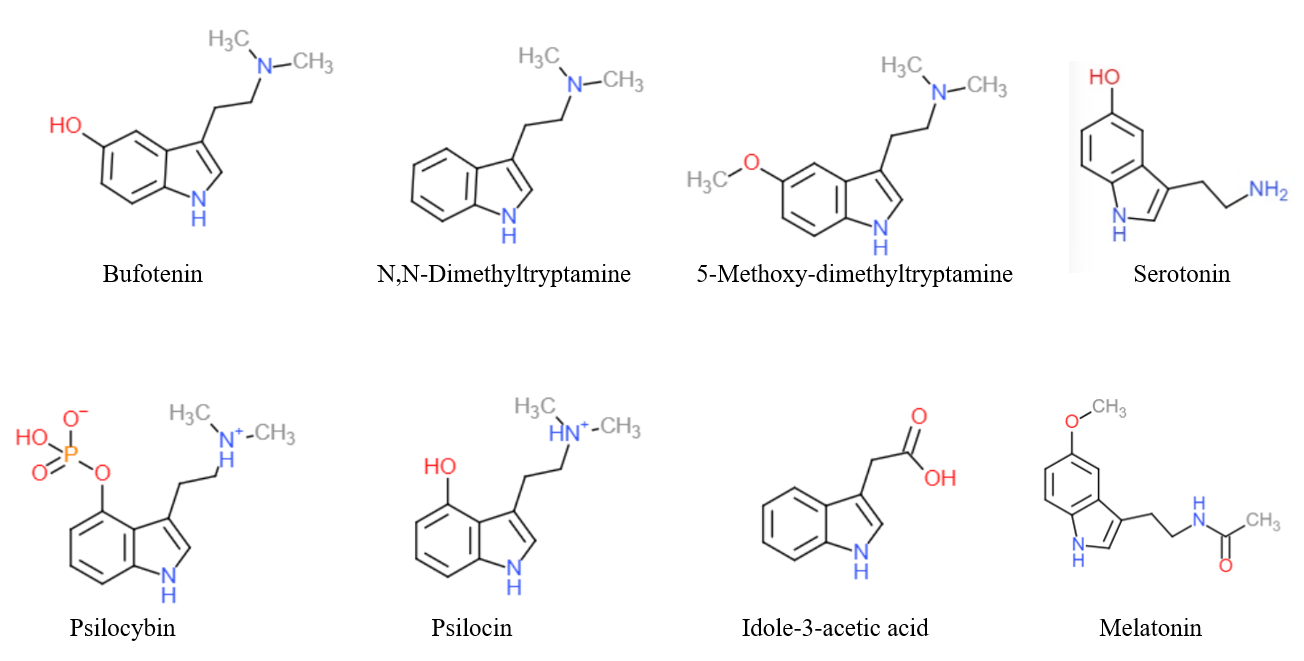
Tryptamine Alkaloids
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole ─ a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prodine
Prodine (trade names Prisilidine and Nisentil) is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of pethidine (meperidine). It was developed in Germany in the late 1940s. There are two isomers of the trans form of prodine, alphaprodine and betaprodine. Both exhibit optical isomerism and alphaprodine and betaprodine are racemates. Alphaprodine is closely related to desomorphine in steric configuration. The cis form also has active isomers but none are used in medicine. Betaprodine is around five times more potent than alphaprodine but is metabolized more rapidly, and only alphaprodine was developed for medicinal use. It has similar activity to pethidine, but with a more rapid onset and shorter duration of effects. Betaprodine produces more euphoria and side effects than alphaprodine at all dose levels, and it was found that 5 to 10 mg of betaprodine is equivalent to 25 to 40 mg of alphaprodine. Testing in rats showed alphaprodine to be 97% the strength of morphine via the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |