|
62nd Air Defense Artillery Regiment
The 62nd Air Defense Artillery Regiment is an Air Defense Artillery regiment in the United States Army. The lineages of some of the units that have been part of the 62nd Air Defense Artillery and its predecessors give the regiment campaign credit for the War of 1812. History Lineage Constituted 27 April 1798 as the 62nd Artillery (CAC). Activated at Fort Winfield Scott 7 January 1918. Assigned to 33rd Brigade CAC, and shipped to Camp Mills New York arrived in France 21 July 1918; returned from France 19 February 1919, Demobilized at Camp Eustis March 1919. * Reconstituted 1 August 1921 as the 2nd Antiaircraft Battalion (CAC) and organized 4 September 1921 at Fort Totten (New York), with HHD&CT, Search Light, Gun, and Machine Gun Batteries. *Redesignated 1 June 1922 as 62nd Antiaircraft Battalion, (CAC), and firing batteries consolidated with inactive serially numbered companies as follows * Searchlight Battery as Battery A. consolidated with 82nd Company (CAC) * Gun Battery a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Defense Artillery Branch (United States)
The Air Defense Artillery Branch is the branch of the United States Army that specializes in anti-aircraft weapons (such as surface to air missiles). In the U.S. Army, these groups are composed of mainly air defense systems such as the Patriot Missile System, Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD), and the Avenger Air Defense system which fires the FIM-92 Stinger missile. The Air Defense Artillery branch descended from Anti-Aircraft Artillery (part of the U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps until 1950, then part of the Artillery Branch) into a separate branch on 20 June 1968. On 1 December 1968, the ADA branch was authorized to wear modified Artillery insignia, crossed field guns with missile. The Branch Motto, "First To Fire", was adopted in 1986 by the attendees of the ADA Commanders' Conference at Fort Bliss. The motto refers to a speech given by General Jonathan Wainwright to veterans of the 200th Coast Artillery (Antiaircraft) stating they were the 'First to Fire' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camp Kilmer
Located in Central New Jersey, Camp Kilmer is a former United States Army camp that was activated in June 1942 as a staging area and part of an installation of the New York Port of Embarkation. The camp was organized as part of the Army Service Forces Transportation Corps. Troops were quartered at Camp Kilmer in preparation for transport to the European Theater of Operations in World War II. Eventually, it became the largest processing center for troops heading overseas and returning from World War II, processing over 2.5 million soldiers. It officially closed in 2009. Origins and history The camp was named for Joyce Kilmer, a poet killed in World War I while serving with 69th Infantry Regiment. His home was in nearby New Brunswick, New Jersey.Camp Kilmer Pamphlet, p. 1. The site was selected in 1941 by the War Department as the best site to serve the New York Port of Embarkation. Construction began in early 1942. Located in Piscataway Township, New Jersey and Edison Township ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coast Artillery Regiments Of The United States Army
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in natural ecosystems, often home to a wide range of biodiversity. On land, they harbor important ecosystems such as freshwater or estuarine wetlands, which are important for bird populations and other terrestrial animals. In wave-protected areas they harbor saltmarshes, mangroves or seagrasses, all of which can provide nursery habitat for finfish, shellfish, and other aquatic species. Rocky shores are usually found along exposed coasts and provide habitat for a wide range of sessile animals (e.g. mussels, starfish, barnacles) and various kinds of seaweeds. Along tropical coasts with clear, nutrient-poor water, coral reefs can often be found between depths of . According to a United Nations atlas, 44% of all people live within 5 km (3.3mi) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
THAAD
Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD), formerly Theater High Altitude Area Defense, is an American anti-ballistic missile defense system designed to shoot down short-, medium-, and intermediate-range ballistic missiles in their terminal phase (descent or reentry) by intercepting with a hit-to-kill approach. THAAD was developed after the experience of Iraq's Scud missile attacks during the Gulf War in 1991. The THAAD interceptor carries no warhead, instead relying on its kinetic energy of impact to destroy the incoming missile. Originally a United States Army program, THAAD has come under the umbrella of the Missile Defense Agency. The Navy has a similar program, the sea-based Aegis Ballistic Missile Defense System, which also has a land component ("Aegis Ashore"). THAAD was originally scheduled for deployment in 2012, but initial deployment took place in May 2008. THAAD has been deployed in the United Arab Emirates, Israel, Romania, and South Korea. On 17 January 202 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat Arms Regimental System
The Combat Arms Regimental System (CARS), was the method of assigning unit designations to units of some of the combat arms branches of the United States Army, including Infantry, Special Forces, Field Artillery, and Armor, from 1957 to 1981. Air Defense Artillery was added in 1968. CARS was superseded by the U.S. Army Regimental System (USARS) in 1981, although the term "Regiment" was never appended to the official name or designation of CARS regiments, and was not added to USARS regiments until 2005. History Before the adoption of CARS, there was no satisfactory means of maintaining the active life of the combat arms organizations. Whenever the nation entered periods of military retrenchment, units were invariably broken up, reorganized, consolidated, or disbanded. During periods of mobilization, large numbers of new units were created. Changes in weapons and techniques of warfare produced new types of units to replace the old ones. As a result, soldiers frequently served in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Armored Division (United States)
The 2nd Armored Division ("Hell on Wheels") was an armored division of the United States Army. The division played important roles during World War II in the invasions of Germany, North Africa, and Sicily and in the liberation of France, Belgium, and the Netherlands. During the Cold War, the division was primarily based at Fort Hood, Texas, and had a reinforced brigade forward stationed in Garlstedt, West Germany. After participation in the Persian Gulf War, the division was inactivated in 1995. World War II The 2nd Armored Division was formed at Fort Benning, Georgia on July 15, 1940, by reorganizing and redesignating the Provisional Tank Brigade (the 66th Infantry Regiment (Light Tanks), 67th Infantry Regiment (Medium Tanks), and 68th Infantry Regiment (Light Tanks)). It was originally commanded by Major General Charles L. Scott, with Colonel George S. Patton Jr. in charge of training. Scott was promoted to command the I Armored Corps in November of that year, which put P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Bliss
Fort Bliss is a United States Army post in New Mexico and Texas, with its headquarters in El Paso, Texas. Named in honor of William Wallace Smith Bliss, LTC William Bliss (1815–1853), a mathematics professor who was the son-in-law of President Zachary Taylor, Ft. Bliss has an area of about ; it is the largest installation in FORSCOM (United States Army Forces Command) and second-largest in the Army overall (the largest being the adjacent White Sands Missile Range). The portion of the post located in El Paso County, Texas, is a census-designated place with a population of 8,591 as of the time of the United States Census, 2010, 2010 census. Fort Bliss provides the largest contiguous tract () of restricted airspace in the Continental United States, used for missile and artillery training and testing, and at 992,000 acres boasts the largest maneuver area (ahead of the Fort Irwin National Training Center, National Training Center, which has 642,000 acres). The garrison's land area i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palermo, Sicily
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital of both the autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan province. The city is noted for its history, culture, architecture and gastronomy, playing an important role throughout much of its existence; it is over 2,700 years old. Palermo is in the northwest of the island of Sicily, by the Gulf of Palermo in the Tyrrhenian Sea. The city was founded in 734 BC by the Phoenicians as ("flower"). Palermo then became a possession of Carthage. Two Greek colonies were established, known collectively as ; the Carthaginians used this name on their coins after the 5th centuryBC. As , the town became part of the Roman Republic and Empire for over a thousand years. From 831 to 1072 the city was under Arab rule in the Emirate of Sicily when the city became the capital of Sicily for the first time. During this time the city was known as . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Licata, Sicily
Licata (, ; grc, Φιντίας, whence la, Phintias or ''Plintis''), formerly also Alicata (), is a city and ''comune'' located on the south coast of Sicily, at the mouth of the Salso River (the ancient ''Himera''), about midway between Agrigento and Gela. It is a major seaport developed at the turn of the twentieth century, shipping sulphur, the refining of which has made Licata the largest European exporting centre, and asphalt, and at times shipping cheese. West of the port city there is a series of pocket beaches separated by wave-cut headlands as high as . (Amore 2002). History Ancient The settlement was frequented by the Phoenicians who traded there between the 12th and 8th centuries BC. At the end of the 7th century BC the Geloi (inhabitants of ancient Gela) built a fortified station to guard the mouth of the Salso (''Himera'') river. In the first half of 6th century BC Phalaris, tyrant of Agrigento, built a fortified outpost. The first settlement was probably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
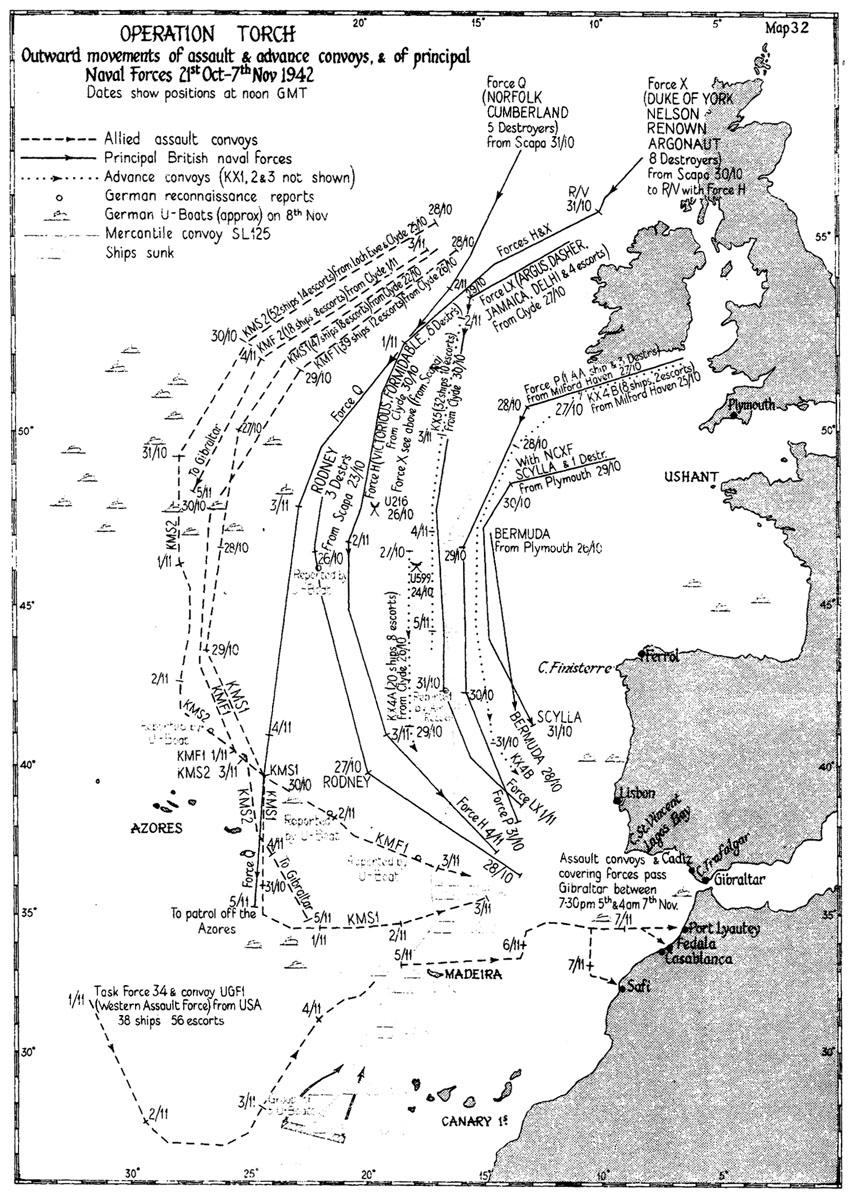
Operation Torch
Operation Torch (8 November 1942 – Run for Tunis, 16 November 1942) was an Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of securing victory in North Africa while allowing American armed forces the opportunity to engage in the fight against Nazi Germany on a limited scale. It was the first mass involvement of US troops in the Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II, European–North African Theatre, and saw the first major airborne assault carried out by the United States. While the French colonies were formally aligned with Germany via Vichy France, the loyalties of the population were mixed. Reports indicated that they might support the Allies. American General Dwight D. Eisenhower, supreme commander of the Allied forces in Mediterranean Theater of Operations, planned a three-pronged attack on Casablanca (Western), Oran (Center) and Algiers (Easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oran, Algeria
Oran ( ar, وَهران, Wahrān) is a major coastal city located in the north-west of Algeria. It is considered the second most important city of Algeria after the capital Algiers, due to its population and commercial, industrial, and cultural importance. It is west-south-west from Algiers. The total population of the city was 803,329 in 2008, while the metropolitan area has a population of approximately 1,500,000 making it the second-largest city in Algeria. Etymology The word ''Wahran'' comes from the Berber expression ''wa - iharan'' (place of lions). A locally popular legend tells that in the period around AD 900, there were sightings of Barbary lions in the area. The last two lions were killed on a mountain near Oran, and it became known as ''la montagne des lions'' ("The Mountain of Lions"). Two giant lion statues stand in front of Oran's city hall, symbolizing the city. History Overview During the Roman Empire, a small settlement called ''Unica Colonia'' existed in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bluie
Bluie was the United States military code name for Greenland during World War II. It is remembered by the numbered sequence of base locations identified by the 1941 United States Coast Guard South Greenland Survey Expedition, and subsequently used in radio communications by airmen unfamiliar with pronunciation of the Inuit and Old Norse names of those locations. These were typically spoken BLUIE (direction) (number), with direction being east or west along the Greenland coast from Cape Farewell.Morison, p.62 * Bluie East One: Torgilsbu radio and weather station at near Aqissiat on Prince Christian Sound * Bluie East Two: Ikateq airfield with radio and weather station at * Bluie East Three: Gurreholm radio and weather station at at geonames.org; retrieved 25 July 2021 on |