|
6-O-methylguanine
6-''O''-Methylguanine is a derivative of the nucleobase guanine in which a methyl group is attached to the oxygen atom. It base-pairs to thymine rather than cytosine, causing a G:C to A:T transition in DNA. Formation 6-''O''-Methylguanine is formed in DNA by alkylation of the oxygen atom of guanine, most often by N-nitroso compounds (NOC) and sometimes due to methylation by other compounds such as endogenous S-adenosyl methionine. NOC are alkylating agents formed by the reaction of nitrite or other nitrogen oxides with secondary amines and N-alkylamides, yielding N-alkylnitrosamines and N-alkylnitrosamides. NOC are found in some foods (bacon, sausages, cheese) and tobacco smoke, and are formed in the gastrointestinal tract, especially after consumption of red meat. In addition, endogenous nitric oxide levels were found to be enhanced under chronic inflammatory conditions, and this could favor NOC formation in the large intestine. Repair and carcinogenicity Repair of 6- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-6-methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase
''O''6-alkylguanine DNA alkyltransferase (also known as AGT, MGMT or AGAT) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''O''6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (''MGMT'') gene. O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase is crucial for genome stability. It repairs the naturally occurring mutagenic DNA lesion O6-methylguanine back to guanine and prevents mismatch and errors during DNA replication and transcription. Accordingly, loss of ''MGMT'' increases the carcinogenic risk in mice after exposure to alkylating agents. The two bacterial isozymes are Ada and Ogt. Function and mechanism Although alkylating mutagens preferentially modify the guanine base at the N7 position, ''O''6-alkyl-guanine is a major carcinogenic lesion in DNA. This DNA adduct is removed by the repair protein ''O''6-alkylguanine DNA alkyltransferase through an SN2 mechanism. This protein is not a true enzyme since it removes the alkyl group from the lesion in a stoichiometric reaction and the active enzyme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma-Aldrich
Sigma-Aldrich (formally MilliporeSigma) is an American chemical, life science, and biotechnology company that is owned by the German chemical conglomerate Merck Group. Sigma-Aldrich was created in 1975 by the merger of Sigma Chemical Company and Aldrich Chemical Company. It grew through various acquisitions until it had over 9,600 employees and was listed on the Fortune 1000. The company is headquartered in St. Louis and has operations in approximately 40 countries. In 2015, the German chemical conglomerate Merck Group acquired Sigma-Aldrich for $17 billion. The company is currently a part of Merck's life science business and in combination with Merck's earlier acquired Millipore Corporation, Millipore, operates as MilliporeSigma. History Sigma Chemical Company of St. Louis and Aldrich Chemical Company of Milwaukee were both American specialty chemical companies when they merged in August 1975. The company grew throughout the 1980s and 1990s, with significant expansion in fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, ... (•N=O or •NO). Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a class of molecules whose study spawned early modern molecular orbital theory, theories of chemical bonding. An important Reaction intermediate, intermediate in chemical industry, industrial chemistry, nitric oxide forms in combustion systems and can be generated by lightning in thunderstorms. In mammals, including humans, nitric oxide is a signaling molecule in many physiological and pathological pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temozolomide
Temozolomide (TMZ), sold under the brand name Temodar among others, is a medication used to treat brain tumors such as glioblastoma and anaplastic astrocytoma. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged. It is taken by mouth or via intravenous infusion. The most common side effects with temozolomide are nausea, vomiting, constipation, loss of appetite, alopecia (hair loss), headache, fatigue, convulsions (seizures), rash, neutropenia or lymphopenia (low white-blood-cell counts), and thrombocytopenia (low blood platelet counts). People receiving the solution for infusion may also have injection-site reactions, such as pain, irritation, itching, warmth, swelling and redness, as well as bruising. Temozolomide is an alkylating agent used to treat serious brain cancers; most commonly as second-line treatments for astrocytoma and as the first-line treatment for glioblastoma. Olaparib in combinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMS Mutagenesis
Ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) is a mutagenic, teratogenic, and carcinogenic organic compound with formula C3H8SO3. It produces random mutations in genetic material by nucleotide substitution; particularly through G:C to A:T transitions induced by guanine alkylation. EMS typically produces only point mutations. Due to its potency and well understood mutational spectrum, EMS is the most commonly used chemical mutagen in experimental genetics. Mutations induced by EMS exposure can then be studied in genetic screens or other assays. Use in biological research EMS can induce mutations at a rate of 5x10−4 to 5x10−2 per gene without substantial killing. A 5x10−4 per gene mutation rate observed in a typical EMS mutagenesis experiment of the model organism ''C. elegans'', corresponds to a raw mutation rate of ~7x10−6 mutations per G/C base pair, or about 250 mutations within an originally mutagenized gamete (containing a ~100 Mbp, 36% GC haploid genome). Such a mutagenized game ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
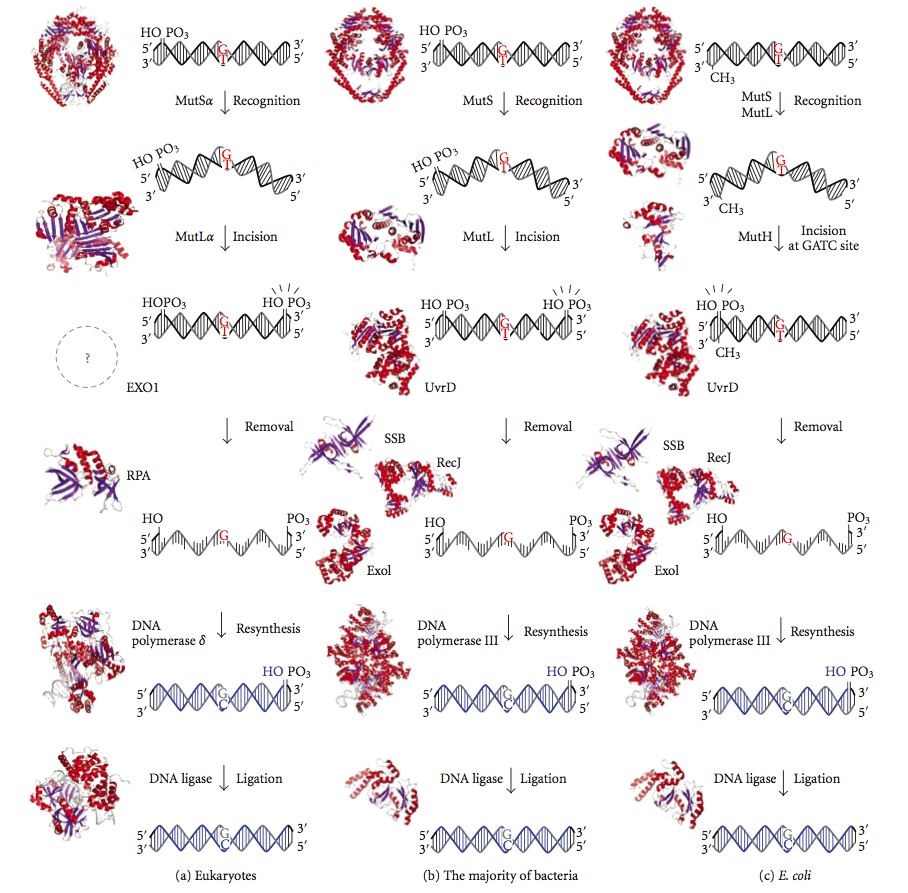
DNA Mismatch Repair
DNA mismatch repair (MMR) is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion, and mis-incorporation of nucleobase, bases that can arise during DNA replication and Genetic recombination, recombination, as well as DNA repair, repairing some forms of DNA damage. Mismatch repair is strand-specific. During DNA synthesis the newly synthesised (daughter) strand will commonly include errors. In order to begin repair, the mismatch repair machinery distinguishes the newly synthesised strand from the template (parental). In gram-negative bacteria, transient methylase, hemimethylation distinguishes the strands (the parental is methylated and daughter is not). However, in other prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the exact mechanism is not clear. It is suspected that, in eukaryotes, newly synthesized lagging-strand DNA transiently contains Nick (DNA), nicks (before being sealed by DNA ligase) and provides a signal that directs mismatch proofreading systems to the appropriate str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Chromatid Exchange
Sister chromatid exchange (SCE) is the exchange of genetic material between two identical sister chromatids. It was first discovered by using the Giemsa staining method on one chromatid belonging to the sister chromatid complex before anaphase in mitosis. The staining revealed that few segments were passed to the sister chromatid which were not dyed. The Giemsa staining was able to stain due to the presence of bromodeoxyuridine analogous base which was introduced to the desired chromatid. The reason for the (SCE) is not known but it is required and used as a mutagenic testing of many products. Four to five sister chromatid exchanges per chromosome pair, per mitosis is in the normal distribution, while 14-100 exchanges is not normal and presents a danger to the organism. SCE is elevated in pathologies including Bloom syndrome, having recombination rates ~10-100 times above normal, depending on cell type. Frequent SCEs may also be related to formation of tumors. Sister chromatid ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Epigenetics
Cancer epigenetics is the study of epigenetics, epigenetic modifications to the DNA of cancer cells that do not involve a change in the nucleotide sequence, but instead involve a change in the way the genetic code is expressed. Epigenetic mechanisms are necessary to maintain normal sequences of tissue specific gene expression and are crucial for normal development. They may be just as important, if not even more important, than mutation, genetic mutations in a cell's transformation to cancer. The disturbance of epigenetic processes in cancers, can lead to a loss of gene expression, expression of genes that occurs about 10 times more frequently by transcription silencing (caused by epigenetic promoter hypermethylation of CpG site#Methylation, silencing, cancer, and aging, CpG islands) than by mutations. As Vogelstein et al. points out, in a colorectal cancer there are usually about 3 to 6 driver mutations and 33 to 66 Genetic hitchhiking, hitchhiker or passenger mutations. However, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amines
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. Aromatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleobase
Nucleobases, also known as ''nitrogenous bases'' or often simply ''bases'', are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nucleic acids. The ability of nucleobases to form base pairs and to stack one upon another leads directly to long-chain helical structures such as ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Five nucleobases—adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T), and uracil (U)—are called ''primary'' or ''canonical''. They function as the fundamental units of the genetic code, with the bases A, G, C, and T being found in DNA while A, G, C, and U are found in RNA. Thymine and uracil are distinguished by merely the presence or absence of a methyl group on the fifth carbon (C5) of these heterocyclic six-membered rings. In addition, some viruses have aminoadenine (Z) instead of adenine. It differs in having an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkylation
Alkylation is the transfer of an alkyl group from one molecule to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents. Nucleophilic alkylating agents Nucleophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl anion ( carbanion). The formal "alkyl anion" attacks an electrophile, forming a new covalent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |