|
5q- Syndrome
Chromosome 5q deletion syndrome is an acquired, hematological disorder characterized by loss of part of the long arm (q arm, band 5q33.1) of human chromosome 5 in bone marrow myelocyte cells. This chromosome abnormality is most commonly associated with the myelodysplastic syndrome. It should not be confused with "partial trisomy 5q", though both conditions have been observed in the same family. This should not be confused with the germ line cri du chat (5p deletion) syndrome which is a deletion of the short arm of the 5th chromosome. Presentation The 5q-syndrome is characterized by macrocytic anemia, often a moderate thrombocytosis, erythroblastopenia, megakaryocyte hyperplasia with nuclear hypolobation, and an isolated interstitial deletion of chromosome 5. The 5q- syndrome is found predominantly in females of advanced age. Causes Several genes in the deleted region appear to play a role in the pathogenesis of 5q-syndrome. Haploinsufficiency of RPS14 plays a central role, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monosomy
Monosomy is a form of aneuploidy with the presence of only one chromosome from a pair. Partial monosomy occurs when a portion of one chromosome in a pair is missing. Human monosomy Human conditions due to monosomy: * Turner syndrome – People with Turner syndrome typically have one X chromosome instead of the usual two X chromosomes. Turner syndrome is the only full monosomy that is seen in humans — all other cases of full monosomy are lethal and the individual will not survive development. * Cri du chat syndrome – (French for "cry of the cat" after the persons' malformed larynx) a partial monosomy caused by a deletion of the end of the short arm of chromosome 5 * 1p36 deletion syndrome – a partial monosomy caused by a deletion at the end of the short arm of chromosome 1 * 17q12 microdeletion syndrome - a partial monosomy caused by a deletion of part of the long arm of chromosome 17 See also * Anaphase lag * Miscarriage Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
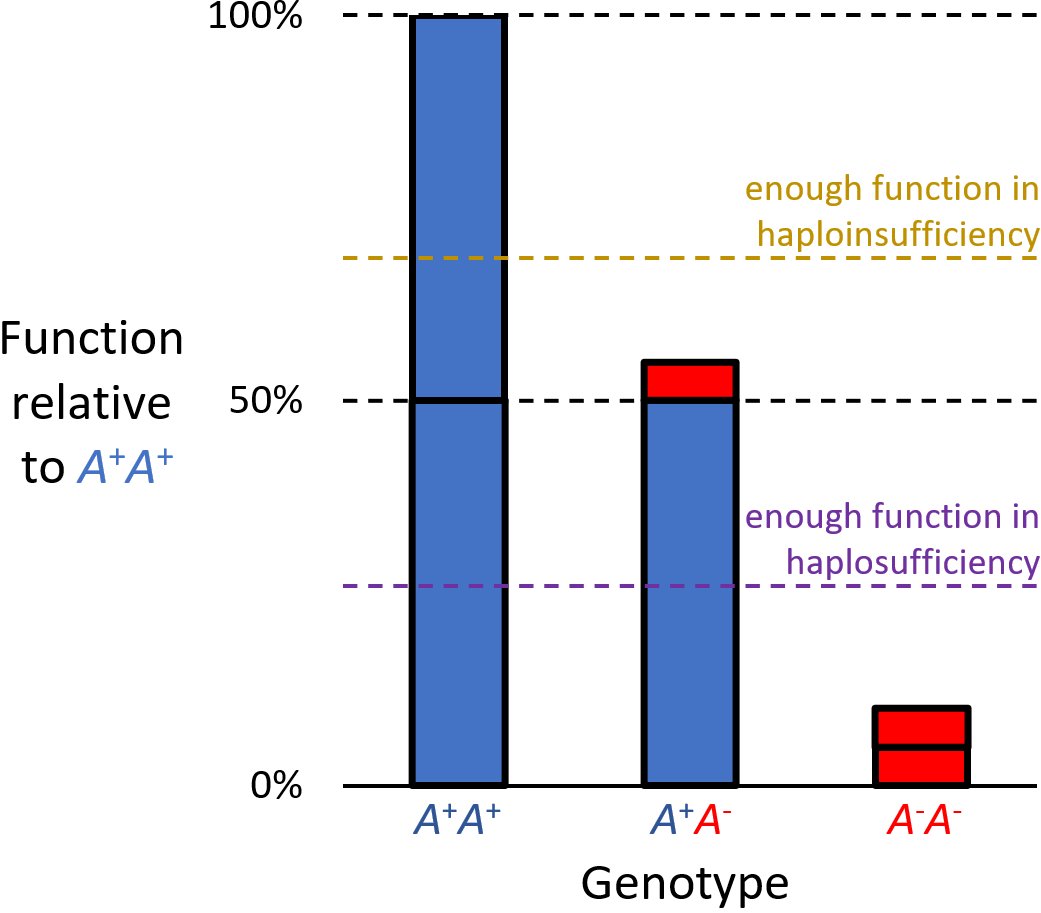
Haploinsufficiency
Haploinsufficiency in genetics describes a model of dominant gene action in diploid organisms, in which a single copy of the wild-type allele at a locus in heterozygous combination with a variant allele is insufficient to produce the wild-type phenotype. Haploinsufficiency may arise from a ''de novo'' or inherited loss-of-function mutation in the variant allele, such that it yields little or no gene product (often a protein). Although the other, standard allele still produces the standard amount of product, the total product is insufficient to produce the standard phenotype. This heterozygous genotype may result in a non- or sub-standard, deleterious, and (or) disease phenotype. Haploinsufficiency is the standard explanation for dominant deleterious alleles. In the alternative case of haplosufficiency, the loss-of-function allele behaves as above, but the single standard allele in the heterozygous genotype produces sufficient gene product to produce the same, standard phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megakaryocytes
A megakaryocyte (''mega-'' + '' karyo-'' + '' -cyte'', "large-nucleus cell") is a large bone marrow cell with a lobated nucleus responsible for the production of blood thrombocytes (platelets), which are necessary for normal blood clotting. In humans, megakaryocytes usually account for 1 out of 10,000 bone marrow cells, but can increase in number nearly 10-fold during the course of certain diseases. Owing to variations in combining forms and spelling, synonyms include megalokaryocyte and megacaryocyte. Structure In general, megakaryocytes are 10 to 15 times larger than a typical red blood cell, averaging 50–100 μm in diameter. During its maturation, the megakaryocyte grows in size and replicates its DNA without cytokinesis in a process called endomitosis. As a result, the nucleus of the megakaryocyte can become very large and lobulated, which, under a light microscope, can give the false impression that there are several nuclei. In some cases, the nucleus may contain up to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Myelogenous Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. Symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, easy bruising and bleeding, and increased risk of infection. Occasionally, spread may occur to the brain, skin, or gums. As an acute leukemia, AML progresses rapidly, and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated. Risk factors include smoking, previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, myelodysplastic syndrome, and exposure to the chemical benzene. The underlying mechanism involves replacement of normal bone marrow with leukemia cells, which results in a drop in red blood cells, platelets, and normal white blood cells. Diagnosis is generally based on bone marrow aspiration and specific blood tests. AML has several subtypes for which treatments and outcomes may vary. The first-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |