|
5e Régiment De Dragons
The 5th Dragoon Regiment (''5e Régiment de Dragons'' or ''5e RD'') is a cavalry unit of the French Army, created under the Ancien Régime in 1656 and reactivated in 2015. This regiment has a double heritage. History *1656–59: La Fronde *1667–68: Spanish War of Devolution *Flanders Campaign: Senef 1674, Battle of Cassel (1677) * War of the League of Augsburg: Siege of Namur, Steenkerque 1692, Neerwinden 1693 * War of the Spanish Succession: Spire 1703, Ramillies 1706, Lorch 1707, Malplaquet 1709 * War of the Austrian Succession: Rocoux 1746, Lauffeld 1747 * Seven Years' War: Hastenbeck 1757 *French Army of the North: Valmy 1792, Neerwinden 1793 and Wattignies 1793 * Ardennes and Sambre-et-Meuse Armies 1794–95 * Army of Italy: Mondovì, Castiglione, Bassano 1796, Cremona 1799, Marengo 1800 As part of Napoleon's ''Grande Armée'' it fought at Wertingen, Auterlitz in 1805, Nasielsk in 1806, Eylau, and the Battle of Friedland in 1807. *Spain: Almonacid, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (french: Armée de Terre, ), is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces. It is responsible to the Government of France, along with the other components of the Armed Forces. The current Chief of Staff of the French Army (CEMAT) is General , a direct subordinate of the Chief of the Defence Staff (CEMA). General Schill is also responsible to the Ministry of the Armed Forces for organization, preparation, use of forces, as well as planning and programming, equipment and Army future acquisitions. For active service, Army units are placed under the authority of the Chief of the Defence Staff (CEMA), who is responsible to the President of France for planning for, and use of forces. All French soldiers are considered professionals, following the suspension of French military conscription, voted in parliament in 1997 and made effective in 2001. , the French Army employed 118,600 personnel (including the Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fronde
The Fronde () was a series of civil wars in France between 1648 and 1653, occurring in the midst of the Franco-Spanish War, which had begun in 1635. King Louis XIV confronted the combined opposition of the princes, the nobility, the law courts (''parlements''), as well as most of the French people, and managed to subdue them all. The dispute started when the government of France issued seven fiscal edicts, six of which were to increase taxation. The ''parlements'' resisted and questioned the constitutionality of the King's actions and sought to check his powers. The Fronde was divided into two campaigns, the Parlementary Fronde and the Fronde of the Princes. The timing of the outbreak of the Parlementary Fronde, directly after the Peace of Westphalia (1648) that ended the Thirty Years' War, was significant. The nuclei of the armed bands that terrorized parts of France under aristocratic leaders during that period had been hardened in a generation of war in Germany, where troo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Lauffeld
The Battle of Lauffeld, variously known as Lafelt, Laffeld, Lawfeld, Lawfeldt, Maastricht, or Val, took place on 2 July 1747, between Tongeren in modern Belgium, and the Dutch city of Maastricht. Part of the War of the Austrian Succession, a French army of 80,000 under Marshal Saxe defeated a Pragmatic Army of 120,000, led by the Duke of Cumberland. Arguably the most talented general of his generation, Saxe conquered much of the Austrian Netherlands between 1744 to 1746 although he failed to achieve decisive victory. In the spring of 1747, Cumberland planned an offensive to retake Antwerp but was forced to fall back when the French threatened to cut him off from his supply base at Maastricht. When the two armies met at Lauffeld, a series of mistakes by Cumberland compromised his position and only counterattacks by the Allied cavalry prevented a serious defeat. The battle ended Allied hopes of regaining lost ground and Saxe captured Bergen op Zoom in September, then Maastricht ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Rocoux
The Battle of Rocoux took place on 11 October 1746 during the War of the Austrian Succession, at Rocourt (or Rocoux), near Liège in the Prince-Bishopric of Liège, now modern Belgium. It was fought between a French army under Marshal Saxe and a combined British, Dutch, German and Austrian force led by Charles of Lorraine, John Ligonier and Prince Waldeck. The battle ended the 1746 campaign and the two armies went into winter quarters. Despite a series of victories in Flanders, by this point France was struggling to finance the war and had opened bilateral peace negotiations with Britain at the Congress of Breda in August 1746. While Rocoux confirmed French control of the Austrian Netherlands, Saxe had failed to achieve the decisive victory needed to end the war. Background When the War of the Austrian Succession began in 1740, Britain was still fighting the War of Jenkins' Ear with Spain; from 1739 to 1742, the main area of operations was in the Caribbean. British and Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession () was a European conflict that took place between 1740 and 1748. Fought primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic and Mediterranean, related conflicts included King George's War in North America, the War of Jenkins' Ear, the First Carnatic War and the First Silesian War, First and Second Silesian Wars. Its pretext was the right of Maria Theresa to succeed her father Emperor Charles VI as ruler of the Habsburg monarchy. Kingdom of France, France, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia and Electorate of Bavaria, Bavaria saw it as an opportunity to challenge Habsburg power, while Maria Theresa was backed by Kingdom of Great Britain, Britain, the Dutch Republic and Electorate of Hanover, Hanover, collectively known as the Pragmatic Sanction of 1713, Pragmatic Allies. As the conflict widened, it drew in other participants, among them History of Spain (1700–1810), Spain, Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia, Electorate of Saxony, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Malplaquet
The Battle of Malplaquet took place on 11 September 1709 during the War of the Spanish Succession and was fought between a French army commanded by the Duke of Villars and a Grand Alliance force under the Duke of Marlborough. In one of the bloodiest battles of the 18th century, the Allies won a narrow victory but suffered heavy casualties, while the French were able to withdraw in good order. At the start of 1709, the French state seemed on the verge of collapse, its treasury empty and food scarce while Allied advances in 1708 left the kingdom open to an invasion. These factors made the Allies overconfident and their excessive demands led to the collapse of peace talks in April. Villars had been instructed to avoid battle but after the capture of Tournai in early September, the Allies moved against Mons and Louis XIV of France ordered him to prevent its loss. Although the two armies made contact on 10 September, Marlborough delayed his attack until the next day, giving Villar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Ramillies
The Battle of Ramillies (), fought on 23 May 1706, was a battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. For the Grand Alliance – Austria, England, and the Dutch Republic – the battle had followed an indecisive campaign against the Bourbon armies of King Louis XIV of France in 1705. Although the Allies had captured Barcelona that year, they had been forced to abandon their campaign on the Moselle, had stalled in the Spanish Netherlands and suffered defeat in northern Italy. Yet despite his opponents' setbacks Louis XIV wanted peace, but on reasonable terms. Because of this, as well as to maintain their momentum, the French and their allies took the offensive in 1706. The campaign began well for Louis XIV's generals: in Italy Marshal Vendôme defeated the Austrians at the Battle of Calcinato in April, while in Alsace Marshal Villars forced the Margrave of Baden back across the Rhine. Encouraged by these early gains Louis XIV urged Marshal Villeroi to go over to the offensiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Philip of Anjou and Charles of Austria, and their respective supporters, among them Spain, Austria, France, the Dutch Republic, Savoy and Great Britain. Related conflicts include the 1700–1721 Great Northern War, Rákóczi's War of Independence in Hungary, the Camisards revolt in southern France, Queen Anne's War in North America and minor trade wars in India and South America. Although weakened by over a century of continuous conflict, Spain remained a global power whose territories included the Spanish Netherlands, large parts of Italy, the Philippines, and much of the Americas, which meant its acquisition by either France or Austria potentially threatened the European balance of power. Attempts by Louis XIV of France and William III o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Landen
The Battle of Landen, also known as Neerwinden, took place on 29 July 1693, during the Nine Years' War near Landen in modern Belgium. A French army under Marshal Luxembourg defeated an Allied force led by William III. By 1693, all combatants were struggling with the financial and material costs of the conflict. Hoping to end the war with a favourable negotiated peace, Louis XIV of France decided first to improve his position by taking the offensive. Luxembourg, French commander in the Spanish Netherlands saw a chance to engage William near Landen. The allies were in a strong but extremely dangerous position, with a river to their rear. Most of the fighting took place on the Allied right, around the only bridge over the river, which was strongly fortified and defended by the bulk of their artillery. The French assaulted the position three times before finally breaking through the defences; the Allies were forced to retreat and abandon their guns. Although a clear French vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Steenkerque
The Battle of Steenkerque, also known as ''Steenkerke'', ''Steenkirk'' or ''Steinkirk'' was fought on 3 August 1692, during the Nine Years' War, near Steenkerque, then part of the Spanish Netherlands but now in modern Belgium A French force under Marshal François-Henri de Montmorency, duc de Luxembourg, defeated an Allied army led by William of Orange. The Allies were forced to retreat after several hours of heavy fighting, although the French were too exhausted to follow up their victory. Background Luxembourg had already achieved his main objective for 1692 by capturing Namur in June and wanted to avoid battle. He therefore adopted a strong defensive position facing north-west, with his right anchored on the Zenne at Steenkerque and his left near Enghien, assuming the Allies would not dare to attack it. This approach conformed with then accepted tactical wisdom, with battles considered too risky and unpredictable, unless there was a clear chance of defeating the enem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
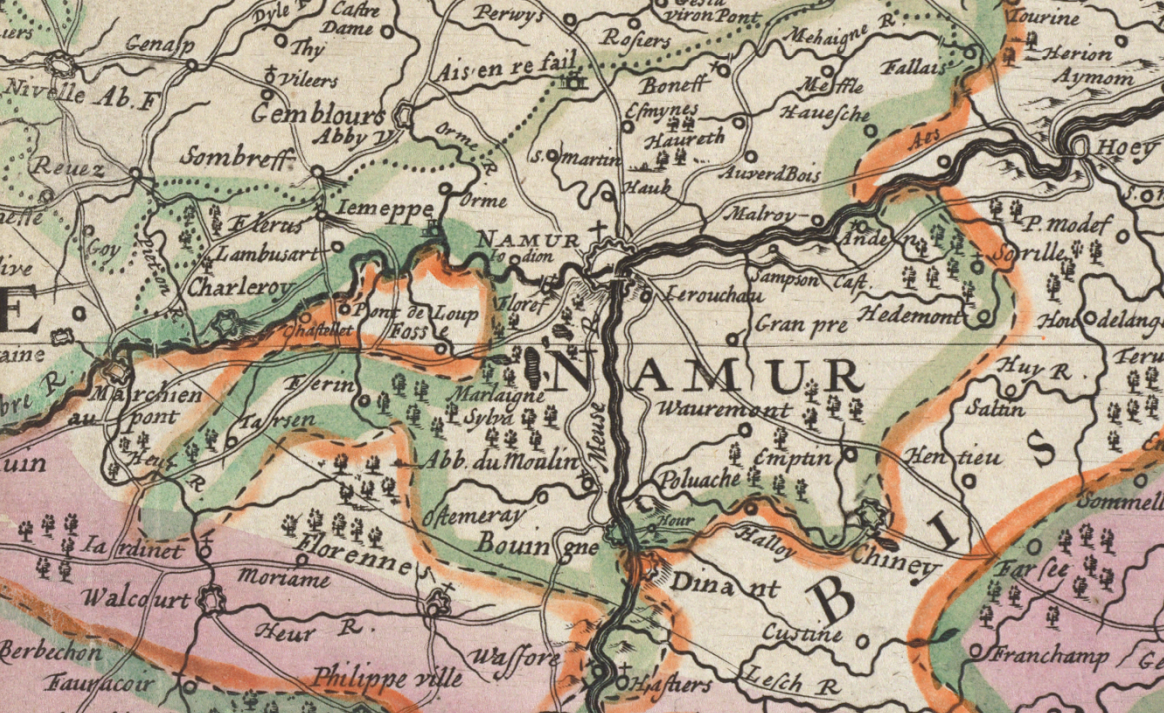
Siege Of Namur (1692)
The siege of Namur, 25 May–30 June 1692, was a major engagement of the Nine Years' War, and was part of the French grand plan (devised over the winter of 1691–92) to defeat the forces of the Grand Alliance and bring a swift conclusion to the war. Namur, sitting on the confluence of the Meuse and Sambre rivers, was a considerable fortress, and was a significant political and military asset. French forces, guided by Vauban, forced the town's surrender on 5 June, but the citadel, staunchly defended by Menno van Coehoorn, managed to hold on until 30 June before capitulating, bringing an end to the 36-day siege. Concerned that King William III planned to recapture the stronghold, King Louis XIV subsequently ordered his commander-in-chief, the duc de Luxembourg, to join battle with the Allies in the field, resulting in the bloody Battle of Steenkerque on 3 August. Background As in 1691, five large armies were created for the five major fronts of the war: Flanders, the Moselle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarchy), the Dutch Republic, England, Spain, Savoy, Sweden and Portugal. Although not the first European war to spill over to Europe's overseas colonies, the events of the war spread to such far away places as the Americas, India, and West Africa. It is for this reason that it is sometimes considered the first world war. The conflict encompassed the Glorious Revolution in England, where William of Orange deposed the unpopular James VII and II and subsequently struggled against him for control of Scotland and Ireland, and a campaign in colonial North America between French and English settlers and their respective Native American allies. Louis XIV of France had emerged from the Franco-Dutch War in 1678 as the most powerful monarch in Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





.jpg)