|
5 August 2018 Lombok Earthquake
On 5 August 2018, a destructive and shallow earthquake measuring Mw 6.9 ( according to BMKG) struck the island of Lombok, Indonesia. It was the main shock following its foreshock, a nearby 6.4 earthquake on 29 July. It was followed by a nearby 6.9 earthquake on 19 August 2018. The epicentre was located inland, near Loloan Village in North Lombok Regency. The fault rupture spread to the north and reached the sea, creating tsunamis. Severe shaking was reported throughout the entire island, while strong shaking was reported on the neighboring islands of Bali and Sumbawa. Widespread damage was reported in Lombok and Bali. Officials stated that at least 80% of structures in North Lombok were damaged or destroyed. In the aftermath of the sequence of earthquakes in August, a total of 563 people were confirmed killed while more than 1,000 were confirmed injured. More than 417,000 people were displaced. This earthquake is the largest and the strongest earthquake to have hit Lombok i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time In Indonesia
The Indonesian Archipelago geographically stretches across four time zones from UTC+06:00 in Aceh to UTC+09:00 in Papua. However, the Indonesian government recognises only three time zones in its territory, namely: *Western Indonesia Time (WIB) — seven hours ahead ( UTC+07:00) of the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC); *Central Indonesia Time (WITA) — eight hours ahead ( UTC+08:00) of UTC; *Eastern Indonesia Time (WIT) — nine hours ahead ( UTC+09:00) of UTC. The boundary between the Western and Central time zones was established as a line running north between Java and Bali through the provincial boundaries of West and Central Kalimantan. The border between the Central and Eastern time zones runs north from the eastern tip of Indonesian Timor to the eastern tip of Sulawesi. Daylight saving time (DST) is no longer observed anywhere in Indonesia. Current usage In Indonesia Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1992 Flores Earthquake And Tsunami
The 1992 Flores earthquake and tsunami occurred on December 12 on the island of Flores in Indonesia. With a magnitude of 7.8 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (''Severe''), it was the largest and also the deadliest earthquake in 1992 and in the Lesser Sunda Islands region. Description The quake hit at 13:29:26 WITA and was followed by several serious aftershocks.Reports 1–9 At least 2,500 people were killed or missing near Flores, including 1,490 at |
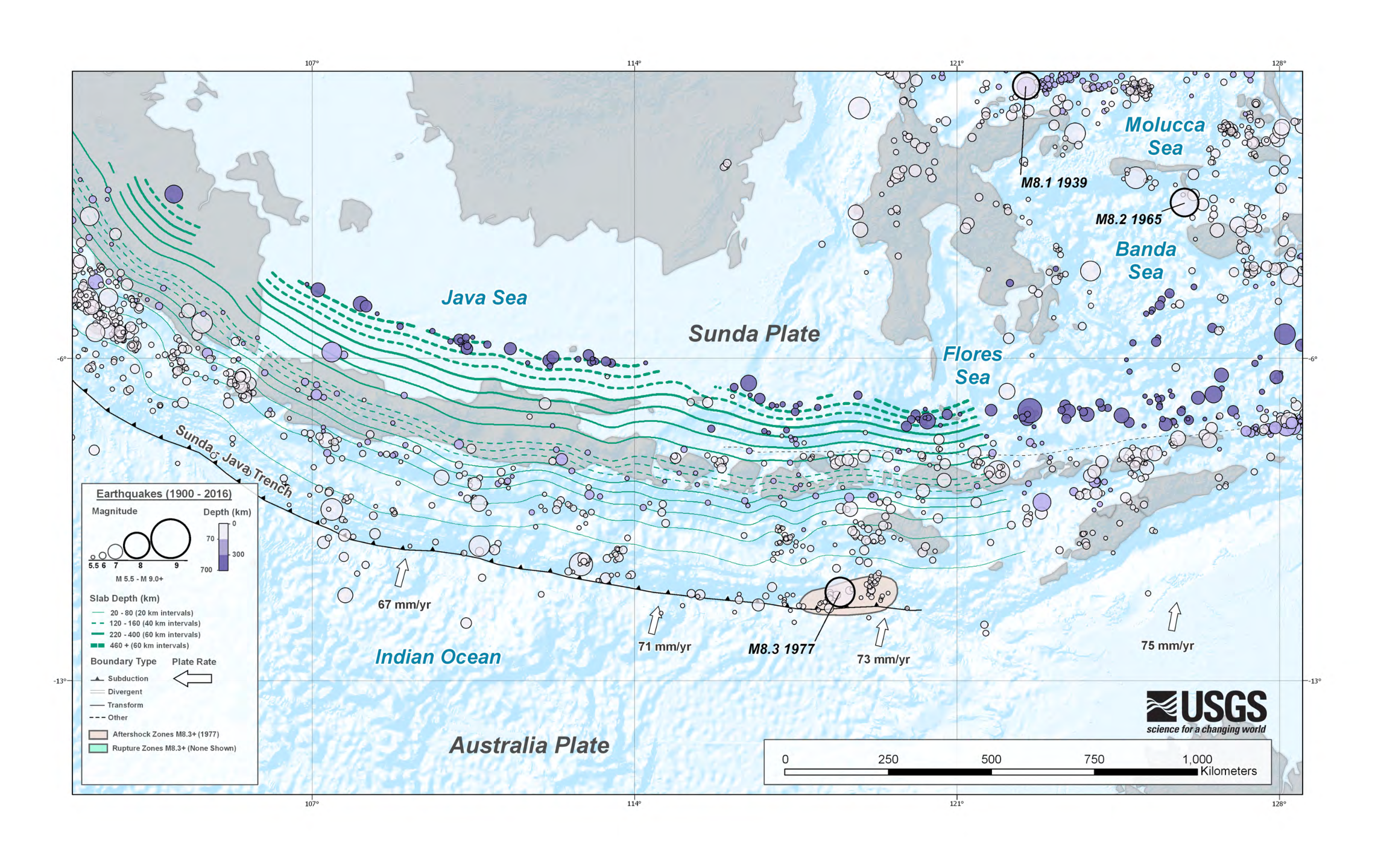
1977 Sumba Earthquake
The 1977 Sumba earthquake (also called the Sumbawa earthquake) occurred approximately south of Bima, Sumbawa, and beneath the Indian Ocean, at . With a moment magnitude of 8.3, the earthquake is notable for having an unusually great magnitude for a shock with a normal faulting focal mechanism. The shock occurred near the southern section of the Sunda Trench where several other tsunami-generating earthquakes have occurred. The earthquake was at the time the largest outer-rise earthquake ever recorded in Indonesia, and aftershocks along the trench extended about eastward and westward from the epicenter. Although damage from the earthquake was limited to Indonesia, ground movement was reportedly felt as far afield as Albany in Australia, and the power supply was briefly cut in Port Hedland. A tsunami was generated with observed run-up heights of up to and inundation distances of up to at several locations on Sumba and Sumbawa. The combined number of victims from both the ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banda Arc
The Banda Arc (main arc, Inner, and Outer) is a set of island arcs in eastern Indonesia. It is the result of the collision of a continent and an intra-oceanic island arc. The presently active arc is located on what appears to be oceanic crust whereas the associated subduction trench is underlain by continental crust. The convergence of the Indo-Australian plates and Eurasia resulted in the formation of the Sunda and Banda island arcs. The transitional zone between the arcs is located south of Flores Island and is characterized by the change in the tectonic regime along the boundary. Terminology Some academic literature refers to the arcs by location – so that main arc can be referred to as the 'southern', the 'western' Situated at the centre of three converging and colliding major tectonic plates, Indo-Australia, Eurasia, Pacific, the Banda arc includes young oceanic crust enclosed by a volcanic inner arc, outer arc islands and a trough parallel to the Australian contine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunda Arc
The Sunda Arc is a volcanic arc that produced the volcanoes that form the topographic spine of the islands of Sumatra, Nusa Tenggara, and Java, the Sunda Strait and the Lesser Sunda Islands. The Sunda Arc begins at Sumatra and ends at Flores, and is adjacent to the Banda Arc. The Sunda Arc is formed via the subduction of the Indo-Australian Plate beneath the Sunda and Burma plates at a velocity of 63–70 mm/year. Formation and geologic setting Mid-oceanic ridge basalts (MORB) form most of the oceanic basin south of Sunda, according to geodynamic studies. These plates began to converge in the Early Miocene. The Indo-Australian Plate is subducting beneath the Eurasian Plate with the dip angle of 49-56 degrees. The slab subducting under Java is continuous down to the lower mantle. However, the slab appears to beak apart under Sumatra Island''.'' Earthquake depth records indicate that there is no deep seismic activity in Sumatra, likely due to the age of the subducting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
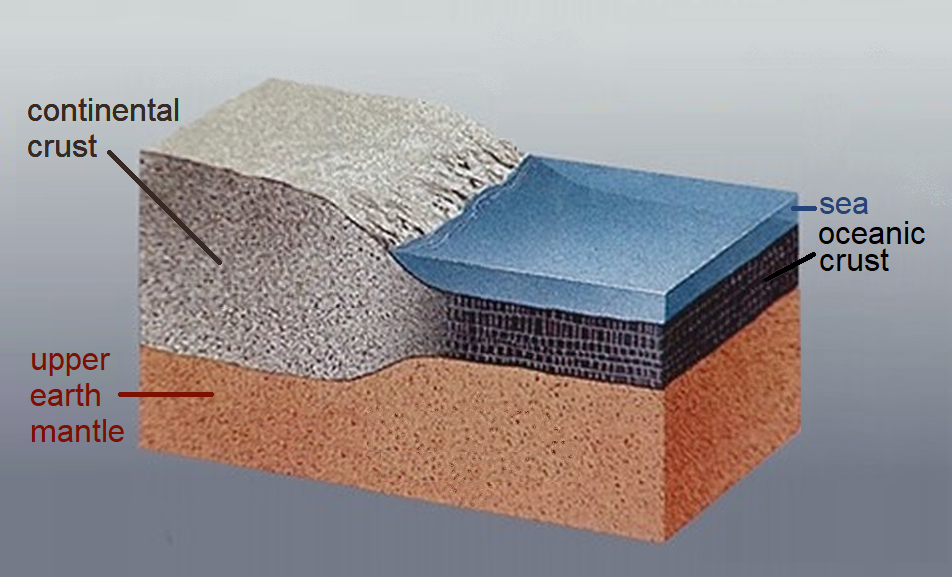
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called ''sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called ''sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. The continental crust consists of various layers, with a bulk composition that is intermediate (SiO2 wt% = 60.6). The average density of continental crust is about , less dense than the ultramafic material that makes up the mantle, which has a density of around . Continental crust is also less dense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destructive Boundary
A convergent boundary (also known as a destructive boundary) is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a plane where many earthquakes occur, called the Wadati–Benioff zone. These collisions happen on scales of millions to tens of millions of years and can lead to volcanism, earthquakes, orogenesis, destruction of lithosphere, and deformation. Convergent boundaries occur between oceanic-oceanic lithosphere, oceanic-continental lithosphere, and continental-continental lithosphere. The geologic features related to convergent boundaries vary depending on crust types. Plate tectonics is driven by convection cells in the mantle. Convection cells are the result of heat generated by the radioactive decay of elements in the mantle escaping to the surface and the return of cool materials from the surface to the mantle. These convection cells bring hot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
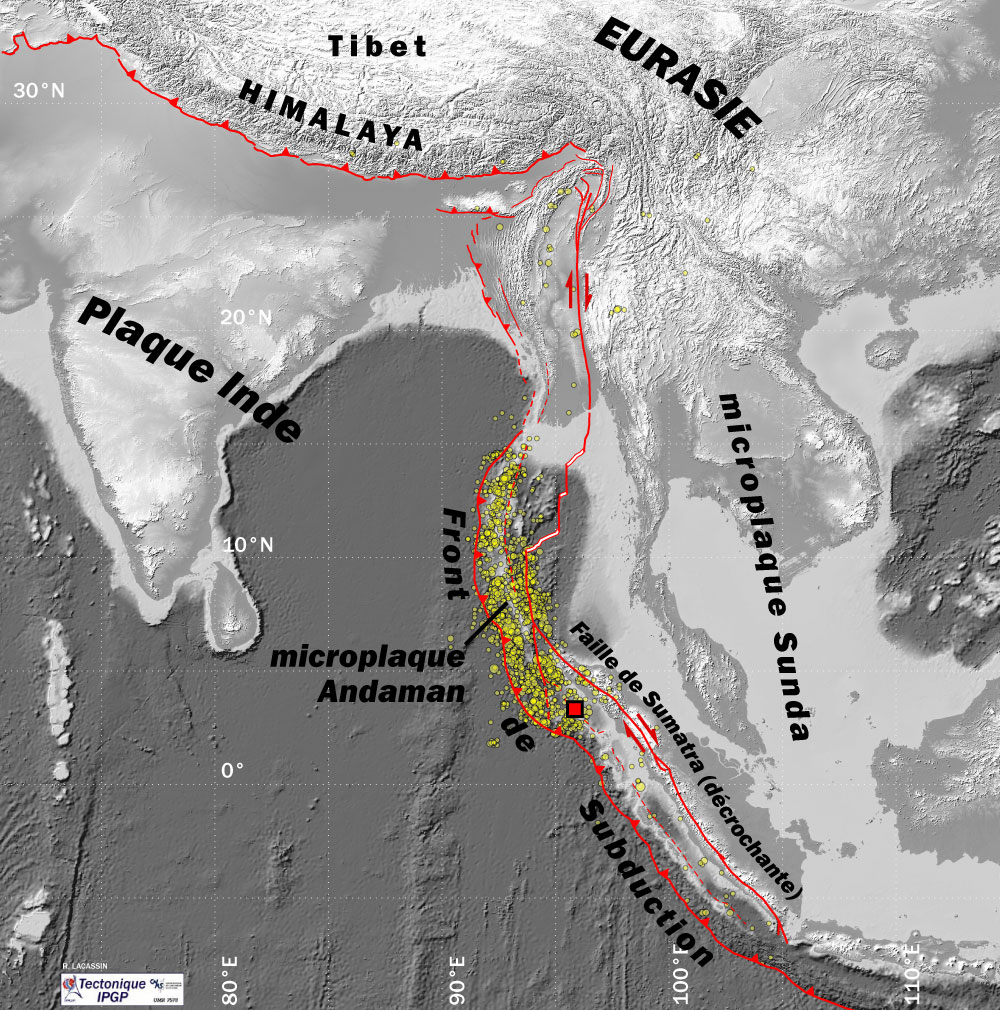
2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake And Tsunami
An earthquake and a tsunami, known as the Boxing Day Tsunami and, by the scientific community, the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, occurred at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+7) on 26 December 2004, with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. It was an undersea megathrust earthquake that registered a magnitude of 9.1–9.3 , reaching a Mercalli intensity up to IX in certain areas. The earthquake was caused by a rupture along the fault between the Burma Plate and the Indian Plate. A series of massive tsunami waves grew up to high once heading inland, after being created by the underwater seismic activity offshore. Communities along the surrounding coasts of the Indian Ocean were devastated, and the tsunamis killed an estimated 227,898 people in 14 countries, making it one of the deadliest natural disasters in recorded history. The direct results caused major disruptions to living conditions and commerce in coastal provinces of surrounded countries, including Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunda Trench
The Sunda Trench, earlier known as and sometimes still indicated as the Java Trench, is an oceanic trench located in the Indian Ocean near Sumatra, formed where the Australian- Capricorn plates subduct under a part of the Eurasian Plate. It is long with a maximum depth of 7,290 metres (23,920 feet). Its maximum depth is the deepest point in the Indian Ocean. The trench stretches from the Lesser Sunda Islands past Java, around the southern coast of Sumatra on to the Andaman Islands, and forms the boundary between Indo-Australian Plate and Eurasian plate (more specifically, Sunda Plate). The trench is considered to be part of the Pacific Ring of Fire as well as one of a ring of oceanic trenches around the northern edges of the Australian Plate. In 2005, scientists found evidence that the 2004 earthquake activity in the area of the Java Trench could lead to further catastrophic shifting within a relatively short period of time, perhaps less than a decade. This threat has resulted i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunda Plate
The Sunda Plate is a minor tectonic plate straddling the Equator in the Eastern Hemisphere on which the majority of Southeast Asia is located. The Sunda Plate was formerly considered a part of the Eurasian Plate, but the GPS measurements have confirmed its independent movement at 10 mm/yr eastward relative to Eurasia. Extent The Sunda Plate includes the South China Sea, the Andaman Sea, southern parts of Vietnam and Thailand along with Malaysia and the islands of Borneo, Sumatra, Java, and part of Sulawesi in Indonesia, plus the south-western Philippines islands of Palawan and the Sulu Archipelago. The Sunda is bounded in the east by the Philippine Mobile Belt, Molucca Sea Collision Zone, Molucca Sea Plate, Banda Sea Plate and Timor Plate; to the south and west by the Australian Plate; and to the north by the Burma Plate, Eurasian Plate; and Yangtze Plate. The Indo-Australian Plate dips beneath the Sunda Plate along the Sunda Trench, which generates frequent earthq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Plate
The Australian Plate is a major tectonic plate in the eastern and, largely, southern hemispheres. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, Australia remained connected to India and Antarctica until approximately when India broke away and began moving north. Australia and Antarctica began rifting and completely separated roughly . The Australian plate later fused with the adjacent Indian Plate beneath the Indian Ocean to form a single Indo-Australian Plate. However, recent studies suggest that the two plates have once again split apart and have been separate plates for at least 3 million years and likely longer. The Australian Plate includes the continent of Australia, including Tasmania, as well as portions of New Guinea, New Zealand and the Indian Ocean basin. Scope The continental crust of this plate covers the whole of Australia, the Gulf of Carpentaria, southern New Guinea, the Arafura Sea, the Coral Sea. The continental crust also includes northwestern N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate. The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and Izanagi Plates. The Pacific Plate subsequently grew to where it underlies most of the Pacific Ocean basin. This reduced the Farallon Plate to a few remnants along the west coast of North America and the Phoenix Plate to a small remnant near the Drake Passage, and destroyed the Izanagi Plate by subduction under Asia. The Pacific Plate contains an interior hot spot forming the Hawaiian Islands. Boundaries The north-eastern side is a divergent boundary with the Explorer Plate, the Juan de Fuca Plate and the Gorda Plate forming respectively the Explorer Ridge, the Juan de Fuca Ridge and the Gorda Ridge. In the middle of the eastern side is a transform boundary with the North American Plate along the San Andreas Fault, and a boundary with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |