|
54th Infantry Brigade (United Kingdom)
The 54th Infantry Brigade was an infantry brigade of the British Army that saw active service in both the First and Second World Wars. First World War The brigade was originally raised in September 1914, as the 54th Brigade, in the First World War as part of Kitchener's New Armies and joined the 18th (Eastern) Division, serving with it throughout the war mainly on the Western Front from 1915 to 1918. Order of battle The 54th Brigade was constituted as follows during the war: * 10th (Service) Battalion, Royal Fusiliers (City of London Regiment) ''(left October 1914)'' * 11th (Service) Battalion, Royal Fusiliers (City of London Regiment) * 12th (Service) Battalion, Royal Sussex Regiment ''(left February 1915)'' * 12th (Service) Battalion, Duke of Cambridge's Own (Middlesex Regiment) ''(disbanded February 1918)'' * 8th (Service) Battalion, Northamptonshire Regiment ''(from November 1914)'' * 7th (Service) Battalion, Bedfordshire Regiment ''(joined February 1915)'' * 2nd (Service) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets ''infant''. The individual-soldier te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middlesex Regiment
The Middlesex Regiment (Duke of Cambridge's Own) was a line infantry regiment of the British Army in existence from 1881 until 1966. The regiment was formed, as the Duke of Cambridge's Own (Middlesex Regiment), in 1881 as part of the Childers Reforms when the 57th (West Middlesex) and 77th (East Middlesex) Regiments of Foot were amalgamated with the county's militia and rifle volunteer units. On 31 December 1966 the Middlesex Regiment (Duke of Cambridge's Own) was amalgamated with the other regiments of the Home Counties Brigade, the Queen's Royal Surrey Regiment, the Queen's Own Buffs, The Royal Kent Regiment and the Royal Sussex Regiment to form the Queen's Regiment. The latter regiment was, however, short-lived and itself subject to a merger on 9 September 1992 with the Royal Hampshire Regiment to form the Princess of Wales's Royal Regiment (Queen's and Royal Hampshires). The Middlesex Regiment was one of the principal home counties based regiments with a long tradition. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffolk Regiment
The Suffolk Regiment was an infantry regiment of the line in the British Army with a history dating back to 1685. It saw service for three centuries, participating in many wars and conflicts, including the First and Second World Wars, before being amalgamated with the Royal Norfolk Regiment to form the 1st East Anglian Regiment (Royal Norfolk and Suffolk) in 1959 which, in 1964, was further amalgamated with the 2nd East Anglian Regiment (Duchess of Gloucester's Own Royal Lincolnshire and Northamptonshire), the 3rd East Anglian Regiment (16th/44th Foot) and the Royal Leicestershire Regiment to create the present Royal Anglian Regiment. History Early history In 1685, the Duke of Norfolk's Regiment of Foot was recruited in Norfolk and Suffolk by the Duke of Norfolk. Raised to suppress the Monmouth Rebellion, it became part of the Royal Army and its Colonel Lord Lichfield remained loyal to James II after the 1688 Glorious Revolution. He was replaced by Henry Wharton and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Norfolk Regiment
The Royal Norfolk Regiment was a line infantry regiment of the British Army until 1959. Its predecessor regiment was raised in 1685 as Henry Cornwall's Regiment of Foot. In 1751, it was numbered like most other British Army regiments and named the 9th Regiment of Foot. It was formed as the Norfolk Regiment in 1881 under the Childers Reforms of the British Army as the county regiment of Norfolk by merging the 9th (East Norfolk) Regiment of Foot with the local Militia and Rifle Volunteers battalions. The Norfolk Regiment fought in the First World War on the Western Front and in the Middle East. After the war, the regiment became the Royal Norfolk Regiment on 3 June 1935. The regiment fought with distinction in the Second World War, in action in the Battle of France and Belgium, the Far East, and then in the invasion of, and subsequent operations in, North-west Europe. In 1959, the Royal Norfolk Regiment was amalgamated with the Suffolk Regiment, to become the 1st East Anglian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner Of War
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610. Belligerents hold prisoners of war in custody for a range of legitimate and illegitimate reasons, such as isolating them from the enemy combatants still in the field (releasing and repatriating them in an orderly manner after hostilities), demonstrating military victory, punishing them, prosecuting them for war crimes, exploiting them for their labour, recruiting or even conscripting them as their own combatants, collecting military and political intelligence from them, or indoctrinating them in new political or religious beliefs. Ancient times For most of human history, depending on the culture of the victors, enemy fighters on the losing side in a battle who had surrendered and been taken as prisoners of war could expect to be either slaughtered or enslaved. Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor of Japan as supreme commander of the army and the Imperial Japanese Navy. Later an Inspectorate General of Aviation became the third agency with oversight of the army. During wartime or national emergencies, the nominal command functions of the emperor would be centralized in an Imperial General Headquarters (IGHQ), an ad hoc body consisting of the chief and vice chief of the Army General Staff, the Minister of the Army, the chief and vice chief of the Naval General Staff, the Inspector General of Aviation, and the Inspector General of Military Training. History Origins (1868–1871) In the mid-19th century, Japan had no unified national army and the country was made up of feudal domains (''han'') with the Tokugawa shogunate (''bakuf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
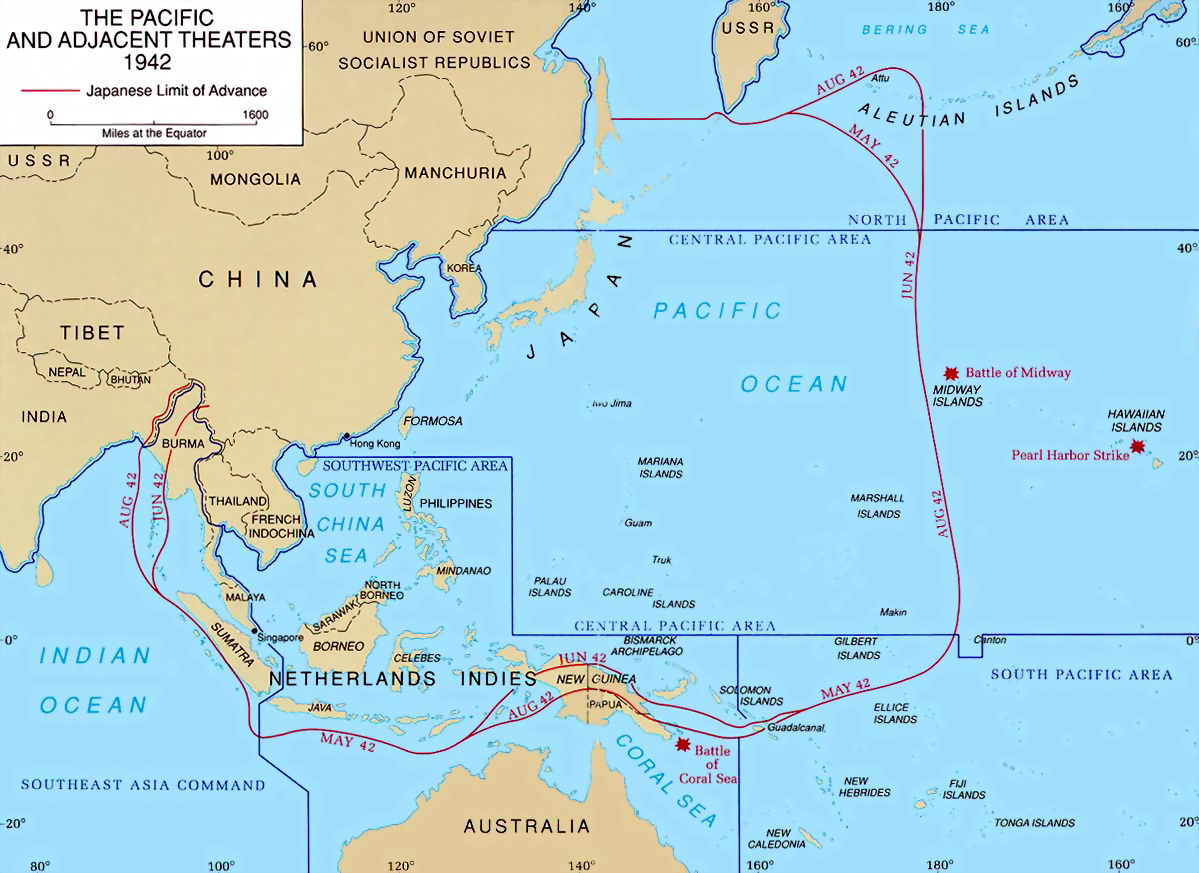
Battle Of Singapore
The Fall of Singapore, also known as the Battle of Singapore,; ta, சிங்கப்பூரின் வீழ்ச்சி; ja, シンガポールの戦い took place in the South–East Asian theatre of the Pacific War. The Empire of Japan captured the British stronghold of Singapore, with fighting lasting from 8 to 15 February 1942. Singapore was the foremost British military base and economic port in South–East Asia and had been of great importance to British interwar defence strategy. The capture of Singapore resulted in the largest British surrender in its history. Prior to the battle, Japanese General Tomoyuki Yamashita had advanced with about 30,000 men down the Malayan Peninsula in the Malayan campaign. The British erroneously considered the jungle terrain impassable, leading to a swift Japanese advance as Allied defences were quickly outflanked. The British Lieutenant-General, Arthur Percival, commanded 85,000 Allied troops at Singapore, although many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Backhouse (British Army Officer)
Brigadier Edward Henry Walford Backhouse (7 February 1895 – 20 November 1973) was a British Army officer who served in both world wars and was unlucky enough to have been taken prisoner in both conflicts. Early life Backhouse was born in Suffolk, the son of Rev. Edward Bell Backhouse and Mary Anne Emmeline Walford. He was educated at St. Lawrence College, Ramsgate, before attending the Royal Military College, Sandhurst. Military career Upon passing out from Sandhurst, Backhouse was commissioned as a second lieutenant into the Suffolk Regiment, a line infantry regiment of the British Army, on 25 February 1914. Three of his fellow graduates were Eric Dorman-Smith, Ronald Scobie and Gerard Bucknall. He was posted to the regiment's 2nd Battalion, then stationed in Curragh, Ireland, as part of the 14th Brigade of Major-General Charles Fergusson's 5th Division. Sent to France with his battalion in the opening stages of the First World War in mid-August 1914, he was wounded and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigadier (United Kingdom)
Brigadier (Brig) is a senior rank in the British Army and the Royal Marines. Brigadier is the superior rank to colonel, and subordinate to major-general. It corresponds to the rank of brigadier general in many other nations. The rank has a NATO rank code of OF-6, placing it equivalent to the Royal Navy commodore and the Royal Air Force air commodore ranks and the brigadier general (1-star general) rank of the United States military and numerous other NATO nations. Insignia The rank insignia for a brigadier is a St Edward's Crown over three "pips" ( "Bath" stars). The rank insignia for a brigadier-general was crossed sword and baton. Usage Brigadier was originally an appointment conferred on colonels (as commodore was an appointment conferred on naval captains) rather than a substantive rank. However, from 1 November 1947 it became a substantive rank in the British Army. The Royal Marines, however, retained it as an acting rank until 1997, when both commodore and brigadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Sea Lion
Operation Sea Lion, also written as Operation Sealion (german: Unternehmen Seelöwe), was Nazi Germany's code name for the plan for an invasion of the United Kingdom during the Battle of Britain in the Second World War. Following the Battle of France, Adolf Hitler, the German Führer and Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces, hoped the British government would accept his offer to end the war, and he reluctantly considered invasion only as a last resort if all other options failed. As a precondition, Hitler specified the achievement of both air and naval superiority over the English Channel and the proposed landing sites, but the German forces did not achieve either at any point during the war, and both the German High Command and Hitler himself had serious doubts about the prospects for success. Nevertheless, both the German Army and Navy undertook a major programme of preparations for an invasion: training troops, developing specialised weapons and equipment, and modify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many List of islands of the United Kingdom, smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Reserve (United Kingdom)
The Army Reserve is the active-duty volunteer reserve force of the British Army. It is separate from the Regular Reserve whose members are ex-Regular personnel who retain a statutory liability for service. The Army Reserve was known as the Territorial Force from 1908 to 1921, the Territorial Army (TA) from 1921 to 1967, the Territorial and Army Volunteer Reserve (TAVR) from 1967 to 1979, and again the Territorial Army (TA) from 1979 to 2014. The Army Reserve was created as the Territorial Force in 1908 by the Secretary of State for War, Richard Haldane, when the Territorial and Reserve Forces Act 1907 combined the previously civilian-administered Volunteer Force, with the mounted Yeomanry (at the same time the Militia was renamed the Special Reserve). Haldane planned a volunteer "Territorial Force", to provide a second line for the six divisions of the Expeditionary Force which he was establishing as the centerpiece of the Regular Army. The Territorial Force was to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |