|
51st Battalion, Far North Queensland Regiment
The 51st Battalion, Far North Queensland Regiment (51 FNQR) is an Australian Army Regional Force Surveillance Unit headquartered at Porton Barracks in Cairns. The battalion's primary role is to conduct reconnaissance and surveillance tasks in support of border security operations. Its area of operations includes the Torres Strait (especially Australia's border with Papua New Guinea) and the Cape York littoral environment. Additional tasks for 51FNQR include the collection and collation of military geographic information as well as community engagement and disaster relief operations. Soldiers in the unit are cross-trained in a variety of "low-visibility" skills such as weapons, survival, sniping, medic, small boat handling, driving, tracking, air operations. It is the only battalion of the Far North Queensland Regiment, and draws its lineage from an Australian Imperial Force (AIF) light infantry battalion, which was raised for service during World War I. History World War I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Army
The Australian Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of Australia, a part of the Australian Defence Force (ADF) along with the Royal Australian Navy and the Royal Australian Air Force. The Army is commanded by the Chief of Army (Australia), Chief of Army (CA), who is subordinate to the Chief of the Defence Force (Australia), Chief of the Defence Force (CDF) who commands the ADF. The CA is also directly responsible to the Minister of Defence (Australia), Minister for Defence, with the Department of Defence (Australia), Department of Defence administering the ADF and the Army. Formed in 1901, as the Commonwealth Military Forces, through the amalgamation of the colonial forces of Australia following the Federation of Australia. Although Australian soldiers have been involved in a number of minor and major conflicts throughout Australia's history, only during the Second World War has Australian territory come under direct attack. The Australian Army was initially composed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Division (Australia)
The 1st Division is headquartered in Enoggera, a suburb of Brisbane. The division was first formed in 1914 for service during World War I as a part of the Australian Imperial Force (AIF). It was initially part of the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC) and served with that formation during the Gallipoli campaign, before later serving on the Western Front. After the war, the division became a part-time unit based in New South Wales, and during World War II it undertook defensive duties in Australia before being disbanded in 1945. After World War II, the division remained off the Australian Army's order of battle until the 1960s, when it was reformed in New South Wales. In 1965 it adopted a certification role, determining the operational readiness of units deploying to Vietnam. It was re-formed in 1973 as a full division based in Queensland and in the decades that followed it formed the Australian Army's main formation, including both Regular and Reserve personnel. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
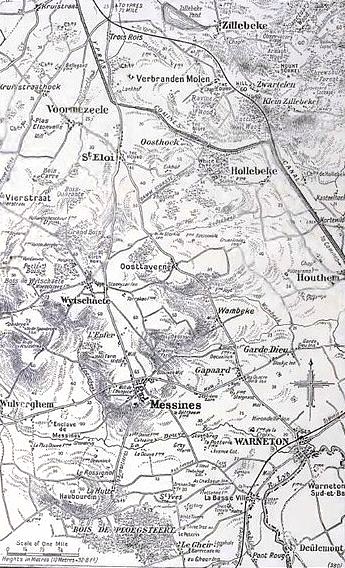
Battle Of Messines (1917)
The Battle of Messines (7–14 June 1917) was an attack by the British Second Army (General Sir Herbert Plumer), on the Western Front, near the village of Messines (now Mesen) in West Flanders, Belgium, during the First World War. The Nivelle Offensive in April and May had failed to achieve its more grandiose aims, had led to the 1917 French Army mutinies, demoralisation of French troops and confounded the Anglo-French strategy for 1917. The attack forced the Germans to move reserves to Flanders from the Arras and Aisne fronts, relieving pressure on the French. The British tactical objective was to capture the German defences on the ridge, which ran from Ploegsteert Wood (Plugstreet to the British) in the south, through Messines and Wytschaete to Mt Sorrel, depriving the German 4th Army (German Empire), 4th Army of the high ground. The ridge gave commanding views of the British defences and back areas of Ypres to the north, from which the British intended to conduct the North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindenburg Line
The Hindenburg Line (German: , Siegfried Position) was a German defensive position built during the winter of 1916–1917 on the Western Front during the First World War. The line ran from Arras to Laffaux, near Soissons on the Aisne. In 1916, the Battle of Verdun and the Battle of the Somme left the German western armies () exhausted and on the Eastern Front, the Brusilov Offensive had inflicted huge losses on the Austro-Hungarian armies and forced the Germans to take over more of the front. The declaration of war by Romania had placed additional strain on the German army and war economy. The Hindenburg Line, built behind the Noyon Salient, was to replace the old front line as a precaution against a resumption of the Battle of the Somme in 1917. By wasting the intervening ground, the Germans could delay a spring offensive in 1917. A shortened front could be held with fewer troops and with tactical dispersal, reverse-slope positions, defence in depth and camouflage, Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villers-Bretonneux Cross At Soldier's Chapel, St George's Cathedral, Perth, August 2021 01
Villers-Bretonneux () is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. Geography Villers-Bretonneux is situated some 19 km due east of Amiens, on the D1029 road and the A29 motorway. Villers-Bretonneux borders a particularly flat landscape towards the east, which can be considered as the western boundary of the Santerre plateau and the eastern boundary of the Amiénois. The territory of the commune is crossed by the old national road 29 (current RD 1029), perfectly rectilinear road following the route of the ancient Roman road linking Amiens to Saint-Quentin in the Aisne. The agglomeration is located at the crossroads of the D 23 linking Corbie to Moreuil. Villers-Bretonneux station is located on the railway line from Amiens to Laon via Tergnier. History Prehistoric era Polished flints from the neolithic era indicate that a human presence has been in the commune for a long time. Antiquity Roman coins, remains of dwelling and a sandstone mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Mouquet Farm
The Battle of Mouquet Farm, also known as the Fighting for Mouquet Farm was part of the Battle of the Somme and began during the Battle of Pozières (23 July – 3 September). The fighting began on 23 July with attacks by the British Reserve Army. The farm was captured by the 3rd Canadian Division of the Canadian Corps on 16 September. The farm was lost to a German counter-attack, before being re-captured on 26 September during an attack by the 11th (Northern) Division during the Battle of Thiepval Ridge No. 16 Section of the 6th Battalion East Yorkshire (Pioneers) smoked out the last German defenders. Background 1916 Mouquet Farm was to the right of the modern D 73 Pozières–Thiepval road, south of Grandcourt and to the south-west of Courcelette, about north-west of the high ground near Pozières. Following the fighting that had occurred around the village earlier in the year, a decision was made by the British to gain control of the ridge beyond the village to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marseilles
Marseille ( , , ; also spelled in English as Marseilles; oc, Marselha ) is the prefecture of the French department of Bouches-du-Rhône and capital of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region. Situated in the camargue region of southern France, it is located on the coast of the Gulf of Lion, part of the Mediterranean Sea, near the mouth of the Rhône river. Its inhabitants are called ''Marseillais''. Marseille is the second most populous city in France, with 870,731 inhabitants in 2019 (Jan. census) over a municipal territory of . Together with its suburbs and exurbs, the Marseille metropolitan area, which extends over , had a population of 1,873,270 at the Jan. 2019 census, the third most populated in France after those of Paris and Lyon. The cities of Marseille, Aix-en-Provence, and 90 suburban municipalities have formed since 2016 the Aix-Marseille-Provence Metropolis, an indirectly elected metropolitan authority now in charge of wider metropolitan issues, with a populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th Division (Australia)
The Australian 4th Division was formed in the First World War during the expansion of the Australian Imperial Force (AIF) infantry brigades in February 1916. In addition to the experienced 4th Brigade (previously in the original New Zealand and Australian Division) were added the new 12th and 13th Brigades (spawned from the battalions of the 4th and 3rd Brigades respectively). From Egypt the division was sent to France, where it took part in the fighting on the Western Front during 1916–1918. After the war ended, the AIF was demobilised and the division was dissolved. In 1921, the 4th Division was reactivated as a Citizen Military Forces (militia/reserve) formation. The division performed home defence duties for most of World War II. The division's composition during World War II changed frequently, as brigades were rotated between different divisions and moved to different locations as the need arose. The division spent the majority of the war in Western Australia, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th Brigade (Australia)
The 13th Brigade is an Army Reserve formation of the Australian Army. Originally formed in 1912 as a Militia formation in Victoria, the brigade was re-raised as a First Australian Imperial Force unit during World War I and fought on the Western Front. In the interwar years, the brigade was re-raised as a part-time formation based in Western Australia and later fought in the New Britain Campaign during World War II. It is currently headquartered at Perth in Western Australia and has units located across the state in locations such as Geraldton, Kalgoorlie, Albany, Katanning, Joondalup and Rockingham. The current brigade was formed in 1988 and is tasked with the protection of Western Australia. It forms part of the 2nd Division of the Australian Army. History The 13th Brigade traces its origins to 1912, when it was formed as a Militia brigade as part of the introduction of the compulsory training scheme, assigned to the 3rd Military District. At this time, the brigade's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkhas, and 28,330 volunteer reserve personnel. The modern British Army traces back to 1707, with antecedents in the English Army and Scots Army that were created during the Restoration in 1660. The term ''British Army'' was adopted in 1707 after the Acts of Union between England and Scotland. Members of the British Army swear allegiance to the monarch as their commander-in-chief, but the Bill of Rights of 1689 and Claim of Right Act 1689 require parliamentary consent for the Crown to maintain a peacetime standing army. Therefore, Parliament approves the army by passing an Armed Forces Act at least once every five years. The army is administered by the Ministry of Defence and commanded by the Chief of the General Staff. The Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sadlier VC
{{surname, Sadlier ...
Sadlier is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Anna T. Sadlier (1854-1932), Canadian writer, translator *Clifford Sadlier (1892–1964), Australian Victoria Cross recipient *Kieran Sadlier (born 1994), Irish footballer *Mary Anne Sadlier (1820–1903), Irish writer * Richard Sadlier (born 1979), Irish footballer * Tom Sadlier (1890–1960), Australian rules footballer *William Sadlier (bishop) (1867–1935), New Zealand Anglican bishop See also * Sadlier baronets, a title in the Baronetage of England * William H. Sadlier, an American publishing company *Sadliers *Sadleir (other) Sadleir may refer to: People with the surname * Franc Sadleir (1775–1851), Irish academic * James Sadleir (c.1815 – 1881), Irish financier and politician * John Sadleir (1813–1856), Irish financier and politician * Lynette Sadleir (b. 1963 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South African Republic and the Orange Free State) over the Empire's influence in Southern Africa from 1899 to 1902. Following the discovery of gold deposits in the Boer republics, there was a large influx of "foreigners", mostly British from the Cape Colony. They were not permitted to have a vote, and were regarded as "unwelcome visitors", invaders, and they protested to the British authorities in the Cape. Negotiations failed and, in the opening stages of the war, the Boers launched successful attacks against British outposts before being pushed back by imperial reinforcements. Though the British swiftly occupied the Boer republics, numerous Boers refused to accept defeat and engaged in guerrilla warfare. Eventually, British scorched eart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |