|
53rd Parallel South
The 53rd parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 53 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the Pacific Ocean and South America. At this latitude the sun is visible for 16 hours, 56 minutes during the December solstice and 7 hours, 34 minutes during the June solstice. Approximately 53º18' South, south of this parallel, during the December summer solstice, the sun is visible for 17 hours exactly. Around the world Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastwards, the parallel 53° south passes through: : See also *52nd parallel south *54th parallel south The 54th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 54 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the Pacific Ocean and South America. At this latitude the sun is visible for 17 hours, ... References {{Reflist s53 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle Of Latitude
A circle of latitude or line of latitude on Earth is an abstract east–west small circle connecting all locations around Earth (ignoring elevation) at a given latitude coordinate line. Circles of latitude are often called parallels because they are parallel to each other; that is, planes that contain any of these circles never intersect each other. A location's position along a circle of latitude is given by its longitude. Circles of latitude are unlike circles of longitude, which are all great circles with the centre of Earth in the middle, as the circles of latitude get smaller as the distance from the Equator increases. Their length can be calculated by a common sine or cosine function. The 60th parallel north or south is half as long as the Equator (disregarding Earth's minor flattening by 0.335%). On the Mercator projection or on the Gall-Peters projection, a circle of latitude is perpendicular to all meridians. On the ellipsoid or on spherical projection, all circle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
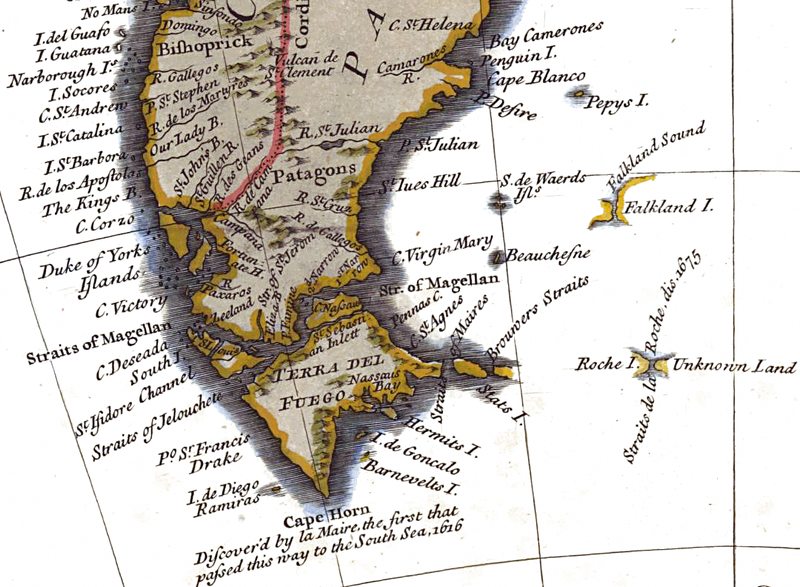
Desolación Island
Desolación Island () (Spanish for ''Desolation'') is an island at the western end of the Strait of Magellan in the Magallanes y la Antártica Chilena Region, Chile. Its northwestern point is called ''Cabo Pilar'' (Cape Pillar), and marks the entrance to the Strait of Magellan. Off Cape Pillar are three rocks in the sea, called '' Islotes Evangelistas'' (the Apostles). Desolación Island in fiction The Douglas Preston and Lincoln Child novel '' The Ice Limit'' described an expedition to Isla Desolacion near Cape Horn in Chile. The map in the (paperback) edition incorrectly identifies easterly Isla Wollastone as Isla Desolacion. The authors, in a note, say this is intentional. James Michener's novel ''Hawaii'' depicts an attempt by a sailing ship to pass the Straits of Magellan, describing the western exit past Desolation Island as the most difficult part of the passage. In Herman Melville's novel '' Moby-Dick'', narrator Ishmael recalls a marble tablet at a whalemen's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
52nd Parallel South
The 52nd parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 52 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the Pacific Ocean and South America. The parallel defines part of the border between Argentina and Chile. At this latitude the sun is visible for 16 hours, 44 minutes during the December solstice and 7 hours, 44 minutes during the June solstice. Around the world Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastwards, the parallel 52° south passes through: : See also *51st parallel south *53rd parallel south The 53rd parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 53 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the Pacific Ocean and South America. At this latitude the sun is visible for 16 hours, 5 ... References {{Reflist s52 Argentina–Chile border ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beauchene Island
Beauchene Island is the southernmost of the Falkland Islands, lying about south of Porpoise Point in Lafonia. It was discovered in 1701 by Jacques Gouin de Beauchêne, after whom it was named. Geography Beauchene is the most isolated island of the Falkland archipelago. It is uninhabited, free of introduced predators and, because it is so remote, has been protected from disturbance. It is in area. The north of the island is covered in dense tussac grass with boulder beaches on the western coast and sloping up gently to about in height. In the south of the island the land rises to around . There are higher cliffs on the eastern coast and the "southern quarter of the island is almost bare of vegetation." The island has a natural anchorage on the east side of the island that can only be used in fair weather. There is no resident population and visitors require the permission of the Falkland Islands Executive Committee. A typical example was a request by Falklands Conservation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tierra Del Fuego Province, Argentina
Tierra del Fuego ( Spanish for "''Land of Fire''"; ), officially the Province of Tierra del Fuego, Antarctica and South Atlantic Islands ( Spanish: ''Provincia de Tierra del Fuego, Antártida e Islas del Atlántico Sur''), is the southernmost, smallest, and least populous Argentine province. The territory of the current province had been inhabited by indigenous people for more than 12,000 years, since they migrated south of the mainland. It was first encountered by a European in 1520 when spotted by Ferdinand Magellan. Even after Argentina achieved independence, this territory remained under indigenous control until the nation's campaign known as the Conquest of the Desert in the 1870s, after which Argentina organised this section in 1885 as a territory. European immigration followed due to a gold rush and rapid expansion of sheep farming on large ranches in the area. Tierra del Fuego is the most recent Argentine territory to gain provincial status, which occurred in 1990. Ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isla Grande De Tierra Del Fuego
Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego ( English: ''Big Island of the Land of Fire'') also formerly ''Isla de Xátiva'' Cercle Català d'Història, ''www.cch.cat'', accessed 5 February 2021 is an island near the southern tip of from which it is separated by the Strait of Magellan. The western portion (61.4%) of the island () is in ( [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brunswick Peninsula
Brunswick Peninsula () is a large peninsula in Magallanes y la Antártica Region, Patagonia, Chile, at . Geography The Brunswick Peninsula is triangular in shape, joined to the mainland in the north by a wide isthmus. It widens to almost in the south. The Strait of Magellan defines the eastern and southern limits while the Otway Sound (Seno Otway) delimits its western shores. It measures in length from the base to Cape Froward, the southernmost point of the American mainland. This yields an area of more than . Origin of name Brunswick is a city, and former duchy in Germany. It was the seat of the Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel. In 1815 Frederick William, Duke of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, nephew of Britain's George III, joined the Duke of Wellington in the Quatre Bras Battle against Napoleon Bonaparte and was killed in battle.Regina B. Johnson: Strait of Magellan, a voyage throughout History XVI-XXI centuries/ref> In his honor, English explorers gave the name Bruns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seno Otway
Seno Otway is a large inland sound lying between Brunswick Peninsula and Riesco Island in southern Chile. Alternatively called Otway Sound, this natural waterway occupies a valley blocked by a large terminal moraine left by the retreat of a glacier during the last glacial period. In spite of being located east of the Andes, it is connected to the open Pacific Ocean through the Strait of Magellan via a narrow passage, which cuts into the Andean Massif. Seno Otway also is hydrologically connected with Seno Skyring by the Fitzroy Channel The Fitzroy Channel is a river in the Magallanes y la Antártica Chilena Region in southern Chile Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and .... Ecology There are a variety of marine species within the Otway Sound, as well as along the coastal terrestrial and intertidal zones. Notably there is a moderately large colony of the Magel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riesco Island
Riesco Island () lies at west of the Brunswick Peninsula, Chile. It is one of the largest islands in Chile, with an area of . Its highest point is Mount Atalaya at . The island is bordered by two large piedmont embayments: Otway Sound and Skyring Sound. The narrow Fitzroy Channel connects both bodies of water and separates the island from mainland Patagonia. The island is separated from the southern part of the Muñoz Gamero Peninsula by another narrow channel, the Geronimo Channel. Riesco Island hosts Chile's largest known coal reserves, with mining activities dating back to 1880. There were the mines ''Magdalena'', ''Elena'' and ''Josefina''. In 1940 ''Magdalena'' and ''Josefina'' produced 100,000 tons.Article in Chilean newspaper La Prensa AustralEl canal Fitz Roy by Silvestre Fugellie11 on 11 July 2012, retrieved on 12 February 2013 It is thought to contain more than 300 million tonnes of low-quality coal in three deposits located in the colonized portion of the island: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muñoz Gamero Peninsula
Muñoz Gamero Peninsula () is a peninsula in Chile. It is bordered on the west by the Smyth Channel and is connected to the Patagonia mainland by a narrow isthmus, between Skyring Sound to the south and the Obstrucción estuary to the north. The peninsula consists of several smaller peninsulas jutting from its central land mass. Riesco Island was considered part of this peninsula until 1904. The lake that occupies a significant part of its central portion was discovered in 1945. The peninsula is home to Monte Burney and Gran Campo Nevado. There have so far been two attempts to settle the peninsula, the first at ''fin de siècle () is a French term meaning "end of century,” a phrase which typically encompasses both the meaning of the similar English idiom "turn of the century" and also makes reference to the closing of one era and onset of another. Without context, ...'' and a second during the presidency of Eduardo Frei Montalva (1964–1970). Environmental conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strait Of Magellan
The Strait of Magellan (), also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural passage between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. It was discovered and first traversed by the Spanish expedition of Ferdinand Magellan in 1520, after whom it is named. Prior to this, the strait had been navigated by canoe-faring indigenous peoples including the Kawésqar. Magellan's original name for the strait was ''Estrecho de Todos los Santos'' ("Strait of All Saints"). The King of Spain, Emperor Charles V, who sponsored the Magellan-Elcano expedition, changed the name to the Strait of Magellan in honor of Magellan. The route is difficult to navigate due to frequent narrows and unpredictable winds and currents. Maritime piloting is now compulsory. The strait is shorter and more sheltered than the Drake Passage, the often stormy open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magallanes Region
The Magallanes Region (), officially the Magallanes y la Antártica Chilena Region ( es, Región de Magallanes y de la Antártica Chilena), is one of Chile's 16 first order administrative divisions. It is the southernmost, largest, and second least populated region of Chile. It comprises four provinces: Última Esperanza, Magallanes, Tierra del Fuego, and Antártica Chilena. Magallanes's geographical features include Torres del Paine, Cape Horn, Tierra del Fuego island, and the Strait of Magellan. It also includes the Antarctic territory claimed by Chile. Despite its large area, much of the land in the region is rugged or closed off for sheep farming, and is unsuitable for settlement. 80% of the population lives in the capital Punta Arenas, a major market city and one of the main hubs for Antarctic exploration. The main economic activities are sheep farming, oil extraction, and tourism. It is also the region with the lowest poverty level in Chile (5.8%); households in Maga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |