|
5-Piece Handicap
The 5-Piece (五枚落ち ''gomai-ochi'') or One Knight handicap in shogi has both of White's major pieces, the rook and the bishop, removed as well as their lances and right knight. Thus, White is left with pawns, golds, silvers, and the left knight. Black has the usual setup of twenty pieces. The 5-Piece handicap is not currently part of the Japan Shogi Association's official list of handicaps. It is also not commonly used. Although uncommon, many professionals feel that the 5-Piece is useful as there is a very large difference between 4-Piece and 6-Piece handicaps according to Kaufman. Openings Bishop-66 Opposing Rook variation 1...G-72. White opens with their right gold. White is more free to focus on the right side of their board compared to the 6-Piece handicap since White's left camp has a stronger defense due to the addition of the left knight. In particular, the knight protects the 33 square from the beginning. So, when Black opens their bishop diagonal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handicap (shogi)
In shogi, a handicap game (駒落戦 ''koma ochisen,'' 駒落ち ''koma ochi,'' ハンデキャップ ''handekyappu,'' 手合割 ''teaiwari'') is a game setup used between players of disparate strengths, in which one or more pieces are removed from the stronger player's side. (Note that the missing pieces are not available for drops and play no further part in the game.) In Japanese, the higher ranked player is called 上手 ''uwate'' "handicapped player" while the lower player is 下手 ''shitate'' "lower player." These terms are usually translated in English simply as ''White'' and ''Black,'' respectively just like the way 後手 ''gote'' and 先手 ''sente'' are translated as ''White'' and ''Black'', respectively. The imbalance created by this method of handicapping is not as strong as it is in western chess because material advantage is not as powerful in shogi. An even game (that is, a non-handicap game) is known as 平手 ''hirate'' in Japanese. Culture, tradition, pedagog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as Western chess, '' chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and ''janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in its present form was played as early as the 16th century, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Shogi Association
The , or JSA, is the primary organizing body for professional shogi in Japan. The JSA sets the professional calendar, negotiates sponsorship and media promotion deals, helps organize tournaments and title matches, publishes shogi-related materials, supervises and trains apprentice professionals as well as many other activities. History For much of its early history, shogi followed an iemoto system centered around three families (schools): the , the and the . The Meijin title was hereditary and could only be held by members of these three families. These three schools were supported by the Tokugawa shogunate and thus controlled the professional shogi world up until 1868 when the Meiji Restoration began. By the time , the eighth and last head of the Itō school and the 11th Hereditary Meijin, had died in 1893, the influence of the families had decreased to such an extent that they had no real power at all. In 1921, there were three groups of professional players in the Tokyo ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6-Piece Handicap
The 6-Piece (六枚落ち ''rokumai-ochi'') handicap in shogi has both of White's major pieces, the rook and the bishop, removed as well as their lances and knights. Thus, White is left with pawns, golds, and silvers. Black has the usual setup of twenty pieces. The handicap is a part of the official handicap system. Openings Ninth File Edge Attack 9筋攻め First File Edge Attack See also * Handicap (shogi) * 8-Piece handicap * Shogi opening References Bibliography * * · translated from ''Shōgi Taikan'' by Yoshio Kimura * · Rook & Lance, 2-Piece, 4-Piece, and 6-Piece handicap games from 1981 * * * * * * External links Handicap Series: Six piece handicapby Larry Kaufman * YouTubeHow To Play Shogi (将棋): Lesson 25: Handicapped Games (1/2)by HIDETCHI from 7:15 to 9:04 * YouTube Japan Shogi Association by professional player Akira Nishio is a Japanese professional shogi player ranked 7-dan. He is currently serving as an executive directo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opposing Rook
In shogi, Opposing Rook (向かい飛車 ''mukaibisha,'' also Opposite Rook, Second File Rook) is a class of Ranging Rook openings in which the player's rook swings over to the second file if played by White or the eighth file if played by Black. The ''opposing'' name is used since if the Opposing Rook player's opponent is playing Static Rook, then the Opposing Rook player's rook will be on the same file as the opponent and the rooks will be facing or opposing each other. In order to play Opposing Rook, the player's bishop must be moved from its starting position (88 or 22 squares). This is usually done by either moving the bishop to the seventh file for Black or the third file for White or by exchanging bishops. If the opponent initiates the bishop exchange, the Opposing Rook player will capture the opponent's bishop with their rook. Traditional Opposing Rook White's Opposing Rook The opening starts by the usual four-move sequence that characterizes Static Rook vs Rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
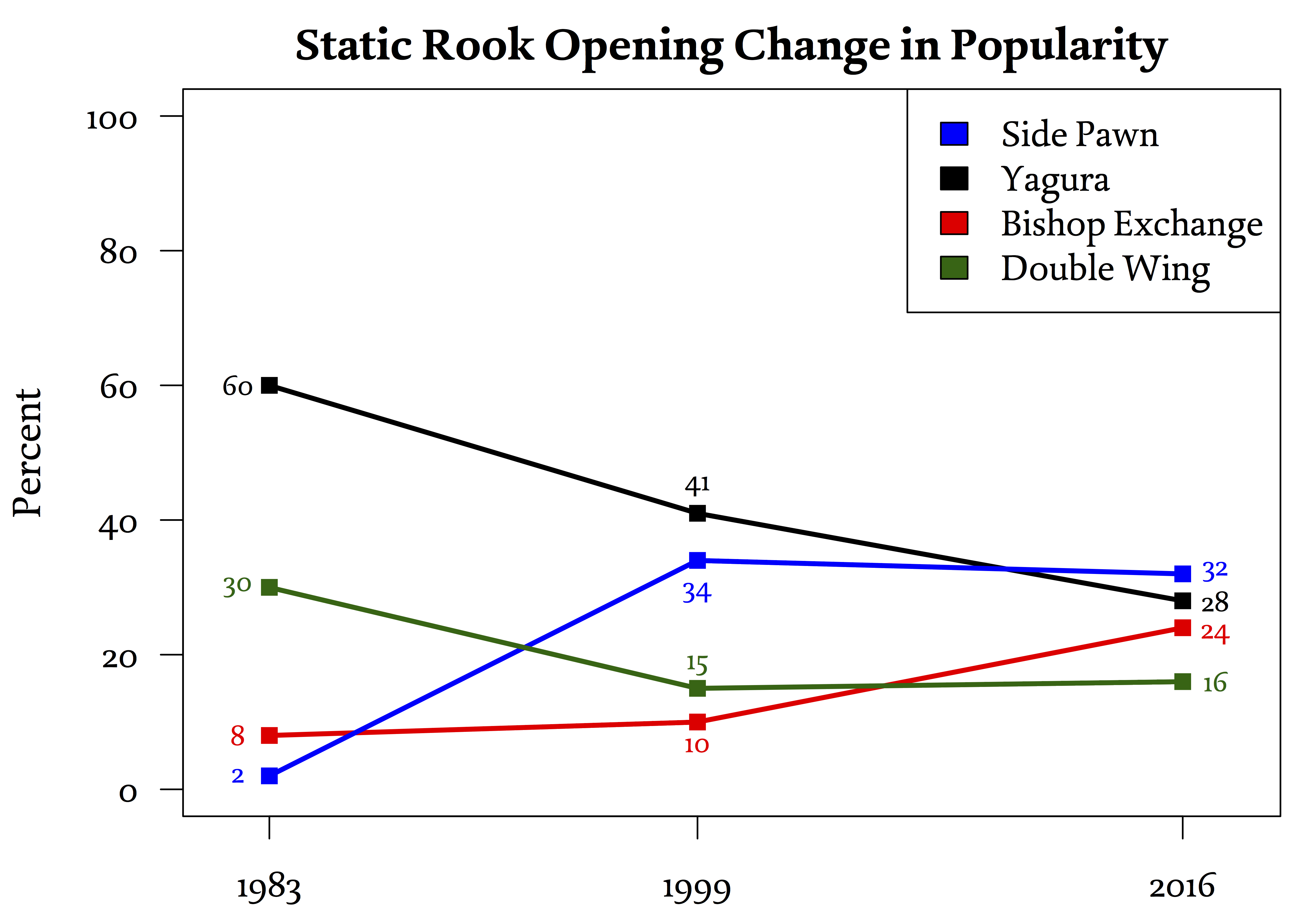
Shogi Opening
A shogi opening ( ) is the sequence of initial moves of a shogi game before the middle game. The more general Japanese term for the beginning of the game is ()''.'' A '' jōseki'' () is the especially recommended sequence of moves for a given opening that was considered balanced play at one point in time for both sides by professional players. (However, some ''s'' have become outdated when they are reevaluated to no longer give balanced play.) ''s'' also typically include commentary about the possible reasons to deviate from the especially regarding blunders. Note that not all openings have ''s''. For example, trap openings like Demon Slayer, while they may have standard moves, are considered to favor one player and are not balanced play. Thus, the Demon Slayer opening is not a jōseki. Introduction The very first opening moves in most games are pawn pushes. In particular, most games start with two types of pawn pushes. A player can move the rook pawn forward (P-26) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larry Kaufman
Lawrence Charles Kaufman (born November 15, 1947) is an American chess and shōgi player. In chess, he was awarded the title Grandmaster by FIDE for winning the 2008 World Seniors Championship (which he later retroactively shared with Mihai Suba). Kaufman had been previously awarded the title International Master in 1980. Background A longtime researcher in computer chess, Kaufman has made several contributions to chess-related works. He helped write the opening book for the pioneering program Mac Hack, co-developed Socrates II and its commercial adaptation, Kasparov's Gambit, edited the journal ''Computer Chess Reports'', and worked on many other research and commercial chess engines. He is also known for his work on computer chess engine Rybka 3, and several books and articles, includinThe Evaluation of Material Imbalances He helped develop the chess program Komodo with Don Dailey, with whom he had worked on the Socrates series of programs. After Dailey's death in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Openings
, also known as Japanese chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and ''janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in its present form was played as early as the 16th century, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |