|
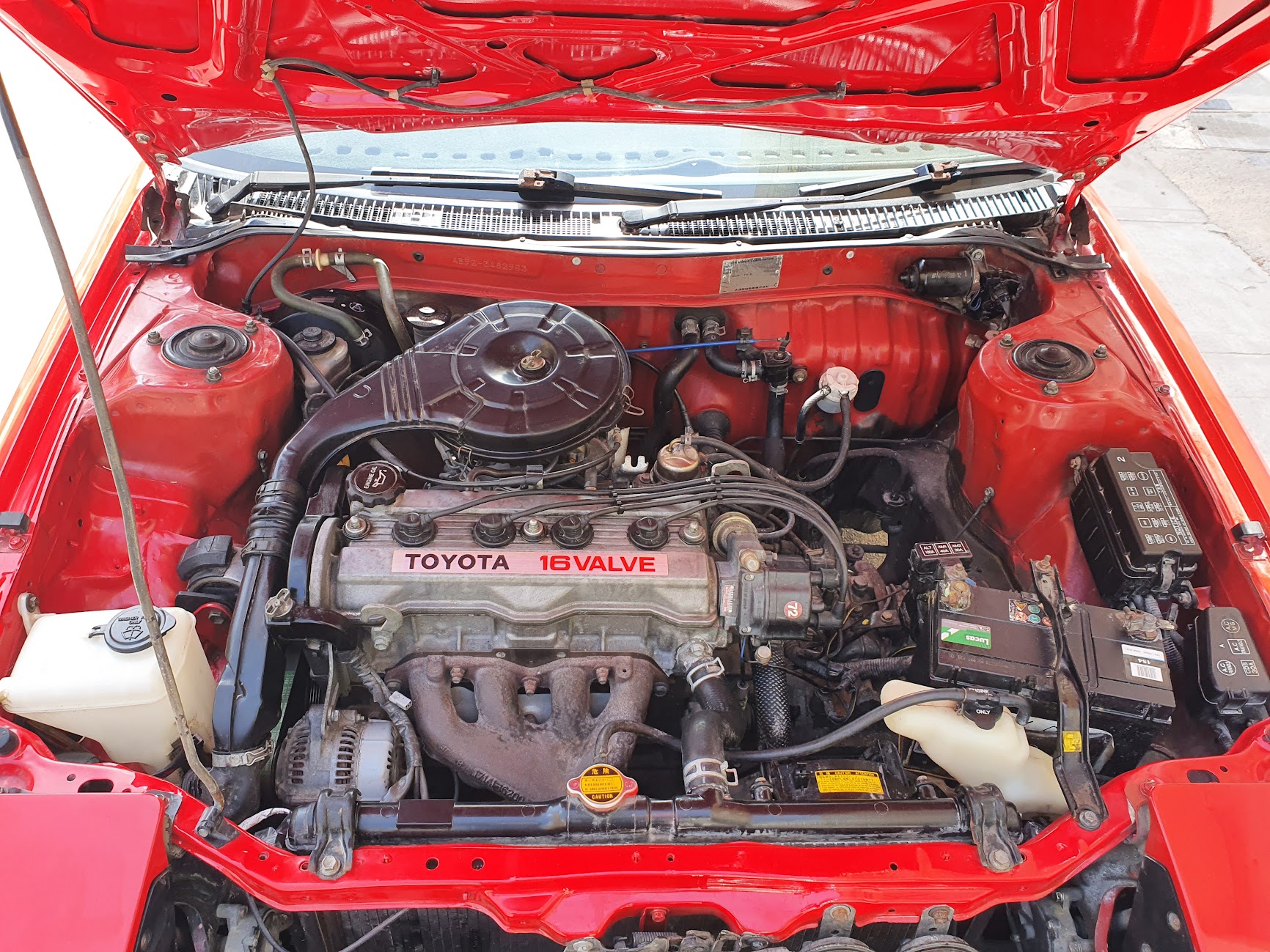
4AGE
The Toyota A Series engines are a family of Inline-four engine, inline-four internal combustion engines with Engine displacement, displacement from 1.3 L to 1.8 L produced by Toyota Motor Corporation. The series has cast iron engine blocks and aluminum cylinder heads. To make the engine as short as possible, the cylinders are Siamesed cylinders, siamesed. The development of the series began in the late 1970s, when Toyota wanted to develop a completely new engine for the Toyota Tercel, the successor of Toyota's Toyota K engine, K engine. The goal was to achieve good fuel efficiency and performance as well as low emissions with a modern design. The A-series includes one of the first Japanese mass-production DOHC, Multi-valve#Four valves, four-valve-per-cylinder engines, the 4A-GE, and a later version of the same engine was one of the first production five-valve-per-cylinder engines. Toyota joint venture partner Tianjin FAW Xiali produces the 1.3 L #8A, 8A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyota A Engine
The Toyota A Series engines are a family of inline-four internal combustion engines with displacement from 1.3 L to 1.8 L produced by Toyota Motor Corporation. The series has cast iron engine blocks and aluminum cylinder heads. To make the engine as short as possible, the cylinders are siamesed. The development of the series began in the late 1970s, when Toyota wanted to develop a completely new engine for the Toyota Tercel, the successor of Toyota's K engine. The goal was to achieve good fuel efficiency and performance as well as low emissions with a modern design. The A-series includes one of the first Japanese mass-production DOHC, four-valve-per-cylinder engines, the 4A-GE, and a later version of the same engine was one of the first production five-valve-per-cylinder engines. Toyota joint venture partner Tianjin FAW Xiali produces the 1.3 L 8A and resumed production of the 5A in 2007. 1A The 1.5 L 1A was produced between 1978 and 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-valve
In automotive engineering a multi-valve or multivalve engine is one where each cylinder has more than two valves. A multi-valve engine has better breathing and may be able to operate at higher revolutions per minute (RPM) than a two-valve engine, delivering more power. Multi-valve rationale Multi-valve engine design A multi-valve engine design has three, four, or five valves per cylinder to achieve improved performance. Any four-stroke internal combustion engine needs at least two valves per cylinder: one for ''intake'' of air (and often fuel), and another for ''exhaust'' of combustion gases. Adding more valves increases valve area and improves the flow of intake and exhaust gases, thereby enhancing combustion, volumetric efficiency, and power output. Multi-valve geometry allows the spark plug to be ideally located within the combustion chamber for optimal flame propagation. Multi-valve engines tend to have smaller valves that have lower reciprocating mass, which can red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyota
is a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan. It was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda and incorporated on . Toyota is one of the largest automobile manufacturers in the world, producing about 10 million vehicles per year. The company was originally founded as a spinoff of Toyota Industries, a machine maker started by Sakichi Toyoda, Kiichiro's father. Both companies are now part of the Toyota Group, one of the largest conglomerates in the world. While still a department of Toyota Industries, the company developed its first product, the Type A engine in 1934 and its first passenger car in 1936, the Toyota AA. After World War II, Toyota benefited from Japan's alliance with the United States to learn from American automakers and other companies, which would give rise to The Toyota Way (a management philosophy) and the Toyota Production System (a lean manufacturing practice) that would transform the small company into a leader in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyota Tercel
The is a subcompact car manufactured by Toyota from 1978 until 1999 across five generations, in five body configurations sized between the Corolla and the Starlet. Manufactured at the Takaoka plant in Toyota City, Japan, and sharing its platform with the Cynos (aka Paseo) and the Starlet, the Tercel was marketed variously as the — sold at Toyota Japanese dealerships called ''Toyota Corolla Stores'' — and was replaced by the Platz in 1999. It was also known as the and sold at Toyopet Store locations. Starting with the second generation, the Tercel dealership network was changed to ''Vista Store'', as its badge engineered sibling, the Corolla II, was exclusive to ''Corolla Store'' locations. The Tercel was the first front-wheel drive vehicle produced by Toyota, although it was the only front-wheel drive Toyota to have a longitudinally mounted engine. For example, the E80 series Corolla's frame (except AE85 and AE86) is similar to the L20 series Tercel's frame. Also, To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Air Intake
Carburetor, carburettor, carburator, carburettor heat (usually abbreviated to 'carb heat') is a system used in automobile and piston-powered light aircraft engines to prevent or clear carburetor icing. It consists of a moveable flap which draws hot air into the engine intake. The air is drawn from the heat stove, a metal plate around the (very hot) exhaust manifold. Operation Carburetor icing is caused by the temperature drop in the carburetor, as an effect of fuel vaporization, and the temperature drop associated with the pressure drop in the venturi. If the temperature drops below freezing, water vapor will freeze onto the throttle valve, and other internal surfaces of the carburetor. The venturi effect can drop the ambient air temperature by 70 absolute degrees Fahrenheit (F), or 38.89 absolute degrees Celsius (C). In other words, air at an outside temperature of 100 degree F (37.7 degrees C), can drop to 30 degrees F (-1.1 degrees C) in the carburetor. Carburetor ici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choke Valve
In internal combustion engines with carburetors, a choke valve or choke modifies the air pressure in the intake manifold, thereby altering the air–fuel ratio entering the engine. Choke valves are generally used in naturally aspirated engines to supply a richer fuel mixture when starting the engine. Most choke valves in engines are butterfly valves mounted upstream of the carburetor jet to produce a higher partial vacuum, which increases the fuel draw. In heavy industrial or fluid engineering contexts, including oil and gas production, a choke valve or choke is a particular design of valve with a solid cylinder placed inside another slotted or perforated cylinder. Carburetor A choke valve is sometimes installed in the carburetor of internal combustion engines. Its purpose is to restrict the flow of air, thereby enriching the fuel-air mixture while starting the engine. Depending on engine design and application, the valve can be activated manually by the operator of the engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyota E Engine
The Toyota E engine family is a straight-four piston engine series, and uses timing belts rather than chains. The E engines were the first multi-valve engines from Toyota designed with economy, practicality and everyday use in mind (rather than performance). Like many other Toyota engines from the era, the E engine series features a cast iron block, along with an aluminium cylinder head. E engines are lighter than earlier Toyota engines, due to the hollow crankshaft, thinned casting of the cylinder block, and several other reductions in auxiliaries as well as in the engine itself. Carbureted versions include a newly designed, variable-venturi carburetor. All of these changes improved economy and emissions. The members of the E engine family, range from 1.0 L to 1.5 L. The E family supplanted the '' K'' engines in most applications. A large number of parts in the E engine series are interchangeable between each other. 1E The 1E is a carbureted 12-valve SOHC engine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually used with internal combustion engines fueled by gasoline or diesel, including lean-burn engines, and sometimes on kerosene heaters and stoves. The first widespread introduction of catalytic converters was in the United States automobile market. To comply with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's stricter regulation of exhaust emissions, most gasoline-powered vehicles starting with the 1975 model year are equipped with catalytic converters. These "two-way" converters combine oxygen with carbon monoxide (CO) and unburned hydrocarbons (HC) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). Although two-way converters on gasoline engines were rendered obsolete in 1981 by "three-way" converters that also reduce oxides of nitrogen (); they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse-flow Cylinder Head
In engine technology, a reverse-flow or non-crossflow cylinder head is one that locates the intake and exhaust ports on the same side of the engine. The gases can be thought to enter the cylinder head and then change direction to exit the head. This is in contrast to the crossflow cylinder head design. Advantages The main advantage of the reverse-flow cylinder head is that both the entering inlet charge and the exiting exhaust gas cause a tendency to swirl in the same direction in the combustion chamber. In a crossflow head the inlet and exhaust gases promote swirl in opposite directions so that during overlap the swirl changes directions. The constant swirl during overlap which results in a reverse-flow cylinder head promotes better mixing, hence better scavenging of the end gas. The fact that the inlet charge must change direction before exiting the exhaust makes it less likely that fresh mixture will exit the exhaust before mixing during overlap. Overall this improves volu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
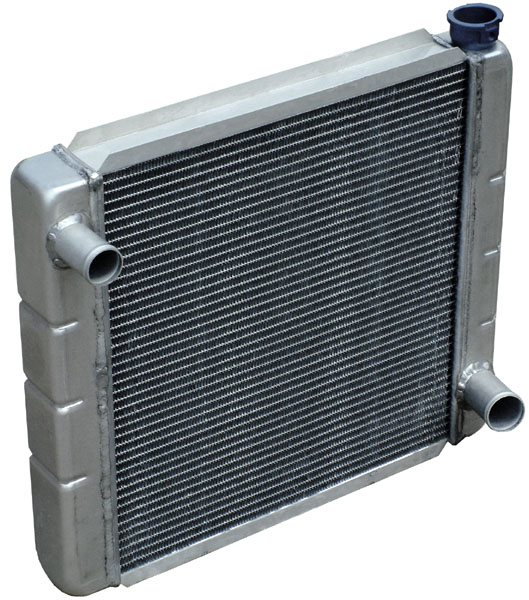
Radiator (engine Cooling)
Radiators are heat exchangers used for cooling internal combustion engines, mainly in automobiles but also in piston-engined aircraft, railway locomotives, motorcycles, stationary generating plant or any similar use of such an engine. Internal combustion engines are often cooled by circulating a liquid called ''engine coolant'' through the engine block, and cylinder head where it is heated, then through a radiator where it loses heat to the atmosphere, and then returned to the engine. Engine coolant is usually water-based, but may also be oil. It is common to employ a water pump to force the engine coolant to circulate, and also for an axial fan to force air through the radiator. Automobiles and motorcycles In automobiles and motorcycles with a liquid-cooled internal combustion engine, a radiator is connected to channels running through the engine and cylinder head, through which a liquid (coolant) is pumped. This liquid may be water (in climates where water is unlik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
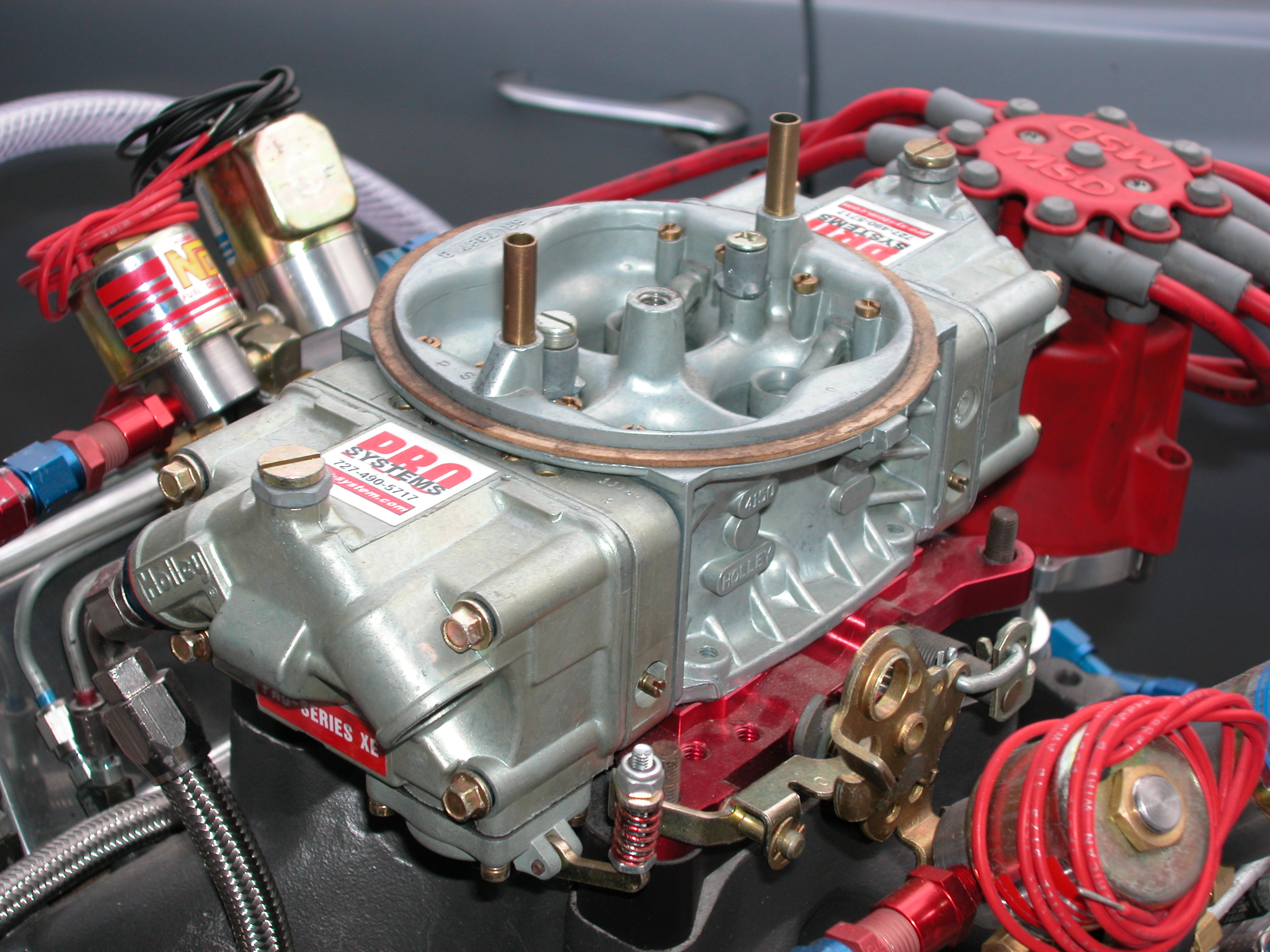
Carburetor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main metering circuit, however various other components are also used to provide extra fuel or air in specific circumstances. Since the 1990s, carburetors have been largely replaced by fuel injection for cars and trucks, however carburetors are still used by some small engines (e.g. lawnmowers, generators and concrete mixers) and motorcycles. Diesel engines have always used fuel injection instead of carburetors. Etymology The name "carburetor" is derived from the verb ''carburet'', which means "to combine with carbon," or in particular, "to enrich a gas by combining it with carbon or hydrocarbons." Thus a carburetor mixes intake air with hydrocarbon-based fuel, such as petrol or autogas (LPG). The name is spelled "carburetor" in American English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |