|
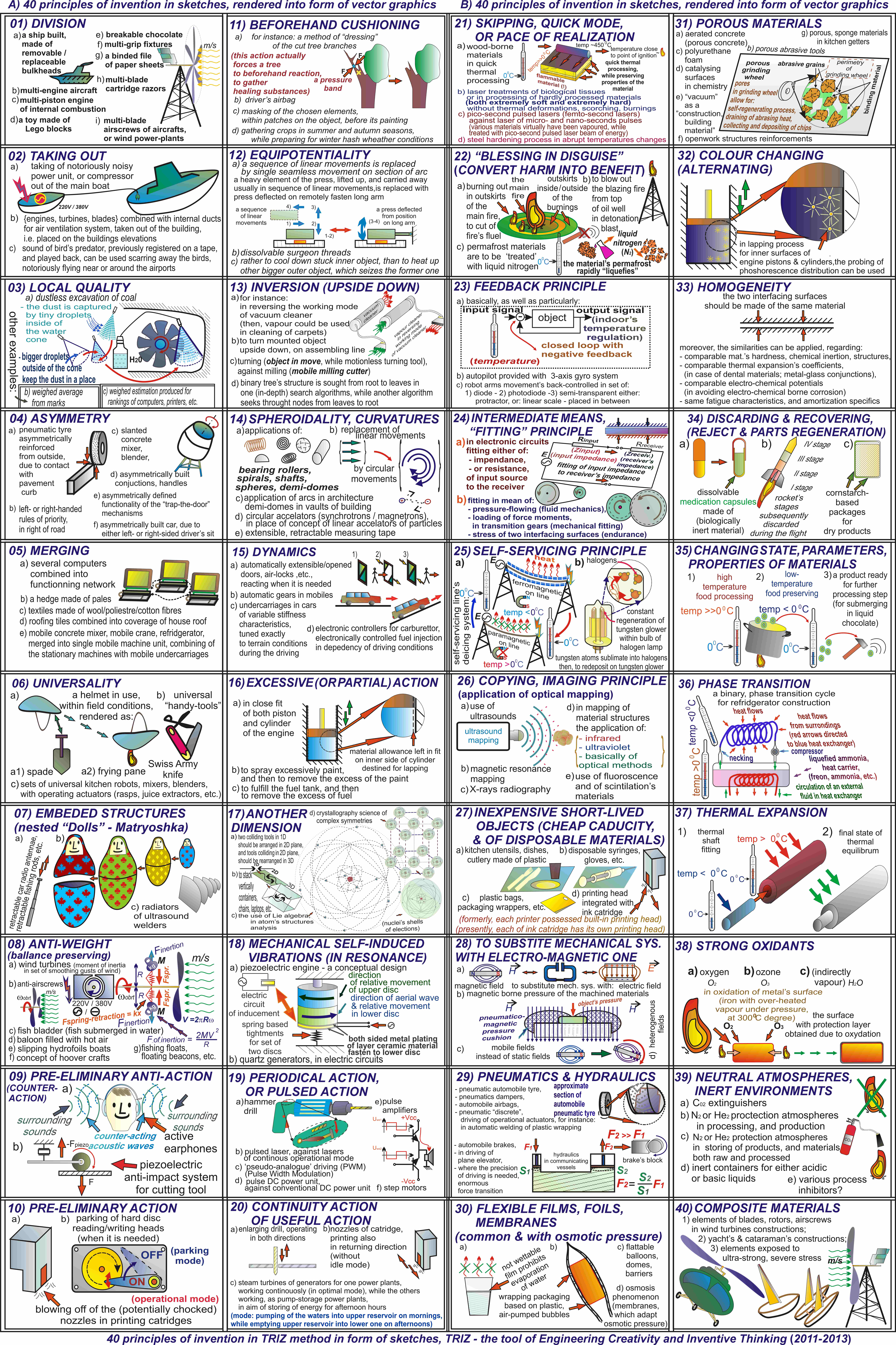
40 Principles Of Invention
The 40 Principles of invention are a suite of ideas that purport to aid in solving hard technical problems. The principles are based on TRIZ, a theory about problem solving. They are used together with Contradiction Matrices. Contradiction matrix A Contradiction Matrix is a structured and systematic representation of basic engineering parameter A parameter (), generally, is any characteristic that can help in defining or classifying a particular system (meaning an event, project, object, situation, etc.). That is, a parameter is an element of a system that is useful, or critical, when ...s of objects, or systems, such as weight, length and manufacturing tolerances. TRIZ TRIZ claims that by studying an individual parameter that is causing a problem (e.g., the weight of an object needs to be reduced), and the other parameters with which it conflicts (e.g., the lower weight would require thinner material, which is more likely to undergo catastrophic failure), solutions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRIZ
TRIZ (; russian: теория решения изобретательских задач, ', lit. "theory of inventive problem solving") is “the next evolutionary step in creating an organized and systematic approach to problem solving. The development and improvement of products and technologies according to TRIZ are guided by the objective Laws of Engineering System Evolution. TRIZ Problem Solving Tools and Methods are based on them.” In another description, TRIZ is "a problem-solving, analysis and forecasting tool derived from the study of patterns of invention in the global patent literature". It was developed by the Soviet inventor and science-fiction author Genrich Altshuller (1926-1998) and his colleagues, beginning in 1946. In English the name is typically rendered as the theory of inventive problem solving, and occasionally goes by the English acronym TIPS. Following Altshuller's insight, the theory developed on a foundation of extensive research covering hundreds of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
40 Principles Of TRIZ Method 960dpi
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. In mathematics Four is the smallest composite number, its proper divisors being and . Four is the sum and product of two with itself: 2 + 2 = 4 = 2 x 2, the only number b such that a + a = b = a x a, which also makes four the smallest squared prime number p^. In Knuth's up-arrow notation, , and so forth, for any number of up arrows. By consequence, four is the only square one more than a prime number, specifically three. The sum of the first four prime numbers two + three + five + seven is the only sum of four consecutive prime numbers that yields an odd prime number, seventeen, which is the fourth super-prime. Four lies between the first proper pair of twin primes, three and five, which are the first two Fermat primes, like seventeen, which is the third. On the other hand, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contradiction Matrix Of TRIZ Method 360dpi
In traditional logic, a contradiction occurs when a proposition conflicts either with itself or established fact. It is often used as a tool to detect disingenuous beliefs and bias. Illustrating a general tendency in applied logic, Aristotle's law of noncontradiction states that "It is impossible that the same thing can at the same time both belong and not belong to the same object and in the same respect." In modern formal logic and type theory, the term is mainly used instead for a ''single'' proposition, often denoted by the falsum symbol \bot; a proposition is a contradiction if false can be derived from it, using the rules of the logic. It is a proposition that is unconditionally false (i.e., a self-contradictory proposition). This can be generalized to a collection of propositions, which is then said to "contain" a contradiction. History By creation of a paradox, Plato's '' Euthydemus'' dialogue demonstrates the need for the notion of ''contradiction''. In the ensui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parameter
A parameter (), generally, is any characteristic that can help in defining or classifying a particular system (meaning an event, project, object, situation, etc.). That is, a parameter is an element of a system that is useful, or critical, when identifying the system, or when evaluating its performance, status, condition, etc. ''Parameter'' has more specific meanings within various disciplines, including mathematics, computer programming, engineering, statistics, logic, linguistics, and electronic musical composition. In addition to its technical uses, there are also extended uses, especially in non-scientific contexts, where it is used to mean defining characteristics or boundaries, as in the phrases 'test parameters' or 'game play parameters'. Modelization When a system is modeled by equations, the values that describe the system are called ''parameters''. For example, in mechanics, the masses, the dimensions and shapes (for solid bodies), the densities and the viscosities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering Tolerance
Engineering tolerance is the permissible limit or limits of variation in: # a physical dimension; # a measured value or physical property of a material, manufactured object, system, or service; # other measured values (such as temperature, humidity, etc.); # in engineering and safety, a physical distance or space (tolerance), as in a truck (lorry), train or boat under a bridge as well as a train in a tunnel (see structure gauge and loading gauge); # in mechanical engineering, the space between a bolt and a nut or a hole, etc. Dimensions, properties, or conditions may have some variation without significantly affecting functioning of systems, machines, structures, etc. A variation beyond the tolerance (for example, a temperature that is too hot or too cold) is said to be noncompliant, rejected, or exceeding the tolerance. Considerations when setting tolerances A primary concern is to determine how wide the tolerances may be without affecting other factors or the outcome of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genrich Altshuller
Genrikh Saulovich Altshuller (Ге́нрих Сау́лович Альтшу́ллер, ) (born Tashkent, Uzbek SSR, USSR, 15 October 1926; died Petrozavodsk, Russia, 24 September 1998), was a Soviet engineer, inventor, and writer. He is most notable for the creation of the Theory of Inventive Problem Solving, better known by its Russia acronym TRIZ. He founded the Azerbaijan Public Institute for Inventive Creation, and was the first President of the TRIZ Association. He also wrote science fiction under the pen-name Genrikh Altov. Early life Working as a clerk in a patent office, Altshuller embarked on finding some generic rules that would explain creation of new, inventive, patentable ideas. He eventually created the ''Teoriya Resheniya Izobreatatelskikh Zadach'' (Theory of Inventive Problem Solving or TRIZ)). Arrest and imprisonment During Joseph Stalin's political purges of members of the Communist Party in 1950, he was imprisoned for political reasons and continued his s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |