|
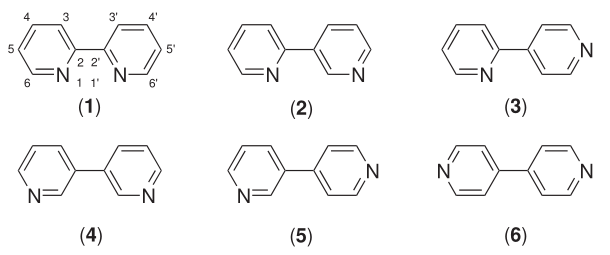
4,4'-bipyridine
4,4′-Bipyridine (abbreviated to 4,4′-bipy or 4,4′-bpy) is an organic compound with the formula . It is one of several isomers of bipyridine. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in organic solvents. is mainly used as a precursor to ''N'',''N''′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium C5H4NCH3)2sup>2+, known as paraquat. History 4,4′-Bipyridine was first obtained in 1868 by the Scottish chemist Thomas Anderson via heating pyridine with sodium metal. However, Anderson's empirical formula for 4,4′-bipyridine was incorrect. The correct empirical formula, and the correct molecular structure, for 4,4′-bipyridine was provided in 1882 by the Austrian chemist Hugo Weidel and his student M. Russo. Uses 4,4'-Bipyridine is an intermediate in the production of paraquat, a widely-used herbicide. In this process, pyridine is oxidized to 4,4'-bipyridine in a coupling reaction, followed by dimethylation to form paraquat. : Reactions The reducing agent is N,N'-bis(trimethylsilyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipyridine
Bipyridines also known as bipyridyls, dipyridyls, and dipyridines, are a family of chemical compounds with the formula (C5H4N)2, consisting of two pyridyl (C5H4N) rings. Pyridine is an aromatic nitrogen-containing heterocycle. Bipyridines are of significance in pesticides. Six isomers of bipyridine exist, but two are prominent: 2,2′-bipyridine is a popular ligand. 4,4'-Bipyridine is a precursor to the commercial herbicide paraquat. The bipyridines are all colourless solids, which are soluble in organic solvents and slightly soluble in water. 2,2′-Bipyridine 2,2′-Bipyridine (2,2′-bipy) is a chelating ligand that forms complexes with most transition metal ions that are of broad academic interest. Many of these complexes have distinctive optical properties, and some are of interest for analysis. Its complexes are used in studies of electron and energy transfer, supramolecular and materials chemistry, and catalysis. 2,2′-Bipyridine is used in the manufacture of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt-free Reduction
In chemistry, salt-free reduction describes methodology for reduction of metal halides by electron-rich trimethylsilyl reagents. Traditional reductions of metal halides are accomplished with alkali metals, a process that cogenerates alkali metal salts. Using the salt-free reduction, the reduction of metal halides is accompanied by formation of neutral organic compounds that can be easily removed from the inorganic or organometallic product. In addition to the reduction of metal halides, the reagents associated with this methodology are applicable to deoxygenation of organic substrates. A typical reducing agent is N,N'-bis(trimethylsilyl)-4,4'-bipyridinylidene. Related pyrazine- and cyclohexadiene-based reagents have been developed. They are red or orange THF-soluble solids. The bipyridine reagent is produced by reduction of 4,4'-bipyridine in the presence of trimethylsilyl chloride (Me = CH3): : A typical reduction reaction is the conversion of tungsten hexachloride Tungste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraquat Synthesis
Paraquat (trivial name; ), or ''N'',''N''′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride (systematic name), also known as methyl viologen, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H7N)2l2. It is classified as a viologen, a family of redox-active heterocycles of similar structure. This salt is one of the most widely used herbicides. It is quick-acting and non-selective, killing green plant tissue on contact. It is also toxic (lethal) to human beings and animals due to its redox activity, which produces superoxide anions. It has been linked to the development of Parkinson's disease and is banned in several countries. Paraquat may be in the form of salt with chloride or other anions; quantities of the substance are sometimes expressed by cation mass alone (paraquat cation, paraquat ion). The name is derived from the ''para'' positions of the ''quaternary'' nitrogens. Production Pyridine is coupled by treatment with sodium in ammonia followed by oxidation to give 4,4′ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraquat
Paraquat (trivial name; ), or ''N'',''N''′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride ( systematic name), also known as methyl viologen, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H7N)2l2. It is classified as a viologen, a family of redox-active heterocycles of similar structure. This salt is one of the most widely used herbicides. It is quick-acting and non-selective, killing green plant tissue on contact. It is also toxic (lethal) to human beings and animals due to its redox activity, which produces superoxide anions. It has been linked to the development of Parkinson's disease and is banned in several countries. Paraquat may be in the form of salt with chloride or other anions; quantities of the substance are sometimes expressed by cation mass alone (paraquat cation, paraquat ion). The name is derived from the ''para'' positions of the ''quaternary'' nitrogens. Production Pyridine is coupled by treatment with sodium in ammonia followed by oxidation to give 4,4� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debye
The debye (symbol: D) (; ) is a CGS unit (a non- SI metric unit) of electric dipole momentTwo equal and opposite charges separated by some distance constitute an electric dipole. This dipole possesses an electric dipole moment whose value is given as charge times length of separation, it is a vector whose direction is in the direction of the unit vector of the position vector of the positive charge w.r.t negative charge: :p = ''q''r. named in honour of the physicist Peter J. W. Debye. It is defined as statcoulomb- centimeters.The statcoulomb is also known as the franklin or electrostatic unit of charge. :1 statC = 1 Fr = 1 esu = 1 cm3/2⋅g1/2⋅s−1. Historically the debye was defined as the dipole moment resulting from two charges of opposite sign but an equal magnitude of 10−10 statcoulomb10−10 statcoulomb corresponds to approximately 0.2083 units of elementary charge. (generally called e.s.u. (electrostatic unit) in older scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Weidel
Hugo Weidel (13 November 1849 – 7 June 1899) was an Austrian chemist known for inventing Weidel's reaction and describing the structure of organic compound niacin. For his achievements, Weidel received the Lieben Prize in 1880. Life and work Hugo Weidel was born in Vienna in 1849. He studied at the Vienna University of Technology with Heinrich Hlasiwetz. He later moved to the University of Heidelberg, Germany, and obtained a PhD degree there in 1870. After returning to Vienna, Weidel became assistant of Hlasiwetz in 1871. During that time, he started his research on oxidation products of cinchonine and nicotine alkaloids. He became lecturer at the University in 1874, and, after Ludwig Barth von Barthenau became the chair of the department, Weidel could intensify his research on alkaloids. Although the oxidation of nicotine was already known, Weidel was the first to isolate large enough amounts to determine the properties of the material. That work earned him the Lieben Prize i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethylsilyl Chloride
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound (silyl halide), with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry. Preparation TMSCl is prepared on a large scale by the ''direct process'', the reaction of methyl chloride with a silicon-copper alloy. The principal target of this process is dimethyldichlorosilane, but substantial amounts of the trimethyl and monomethyl products are also obtained. The relevant reactions are (Me = CH3): : x MeCl + Si → Me3SiCl, Me2SiCl2, MeSiCl3, other products Typically about 2–4% of the product stream is the monochloride, which forms an azeotrope with MeSiCl3. Reactions and uses TMSCl is reactive toward nucleophiles, resulting in the replacement of the chloride. In a characteristic reaction of TMSCl, the nucleophile is water, resulting in hydrolysis to give the hexameth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPCS INCHEM
The International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS) was formed in 1980 and is a collaboration between three United Nations bodies, the World Health Organization, the International Labour Organization and the United Nations Environment Programme, to establish a scientific basis for safe use of chemicals and to strengthen national capabilities and capacities for chemical safety. A related joint project with the same aim, IPCS INCHEM, is a collaboration between IPCS and the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety (CCOHS). The IPCS identifies the following as "chemicals of major public health concern": *Air pollution *Arsenic * Asbestos *Benzene *Cadmium *Dioxin and dioxin-like substances *Inadequate or excess fluoride *Lead * Mercury *Highly hazardous pesticides See also * Acceptable daily intake * International Chemical Safety Card * Concise International Chemical Assessment Document * Food safety Food safety (or food hygiene) is used as a scientific method/disci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These terms are commonly used in chemistry, biochemistry, soil science, and the biological sciences. In biological systems, methylation is catalyzed by enzymes; such methylation can be involved in modification of heavy metals, regulation of gene expression, regulation of protein function, and RNA processing. In vitro methylation of tissue samples is also one method for reducing certain histological staining artifacts. The reverse of methylation is demethylation. In biology In biological systems, methylation is accomplished by enzymes. Methylation can modify heavy metals, regulate gene expression, RNA processing and protein function. It has been recognized as a key process underlying epigenetics. Methanogenesis Methanogenesis, the proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coupling Reaction
A coupling reaction in organic chemistry is a general term for a variety of reactions where two fragments are joined together with the aid of a metal catalyst. In one important reaction type, a main group organometallic compound of the type R-M (R = organic fragment, M = main group center) reacts with an organic halide of the type R'-X with formation of a new carbon-carbon bond in the product R-R'. The most common type of coupling reaction is the cross coupling reaction. Richard F. Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki were awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing palladium-catalyzed cross coupling reactions. Broadly speaking, two types of coupling reactions are recognized: *Heterocouplings combine two different partners, such as in the Heck reaction of an alkene (RC=CH) and an alkyl halide (R'-X) to give a substituted alkene, or the Corey–House synthesis of an alkane by the reaction of a lithium diorganylcuprate (R2CuLi) with an organyl (pseudo)halide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic (chemistry), basic heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide. Properties Physical properties The molecular electric dipole moment is 2.2 debyes. Pyridine is diamagnetism, diamagnetic and has a Magnetic susceptibility, diamagnetic susceptibility of −48.7 × 10−6 cm3·mol−1. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empirical Formula
In chemistry, the empirical formula of a chemical compound is the simplest whole number ratio of atoms present in a compound. A simple example of this concept is that the empirical formula of sulfur monoxide, or SO, would simply be SO, as is the empirical formula of disulfur dioxide, S2O2. Thus, sulfur monoxide and disulfur dioxide, both compounds of sulfur and oxygen, have the same empirical formula. However, their molecular formulas, which express the number of atoms in each molecule of a chemical compound, are not the same. An empirical formula makes no mention of the arrangement or number of atoms. It is standard for many ionic compounds, like calcium chloride (CaCl2), and for macromolecules, such as silicon dioxide (SiO2). The molecular formula, on the other hand, shows the number of each type of atom in a molecule. The structural formula shows the arrangement of the molecule. It is also possible for different types of compounds to have equal empirical formulas. Sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |