|
4-Methylbenzaldehyde
4-Methylbenzaldehyde is the aromatic aldehyde with the formula CH3C6H4CHO. It is a colorless liquid. Commercially available, it may be prepared from the Friedel-Crafts formylation of toluene with carbon monoxide and hydrogen chloride under Gattermann-Koch conditions. 4-Methylbenzaldehyde has a cherry-like scent similar to benzaldehyde Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with a formyl substituent. It is the simplest aromatic aldehyde and one of the most industrially useful. It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic almond-like odor. .... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Methylbenzaldehyde, 4- Benzaldehydes 4-Tolyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with a formyl substituent. It is the simplest aromatic aldehyde and one of the most industrially useful. It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic almond-like odor. The primary component of bitter almond oil, benzaldehyde can be extracted from a number of other natural sources. Synthetic benzaldehyde is the flavoring agent in imitation almond extract, which is used to flavor cakes and other baked goods. History Benzaldehyde was first extracted in 1803 by the French pharmacist Martrès. His experiments focused on elucidating the nature of amygdalin, the poisonous material found in bitter almonds, the fruit of ''Prunus dulcis''. Further work on the oil by Pierre Robiquet and Antoine Boutron-Charlard, two French chemists, produced benzaldehyde. In 1832, Friedrich Wöhler and Justus von Liebig first synthesized benzaldehyde. Production As of 1999, 7000 tonnes of synthetic and 100 tonnes of natural b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are common and play important roles in the technology and biological spheres. Structure and bonding Aldehydes feature a carbon center that is connected by a double bond to oxygen and a single bond to hydrogen and single bond to a third substituent, which is carbon or, in the case of formaldehyde, hydrogen. The central carbon is often described as being sp2- hybridized. The aldehyde group is somewhat polar. The C=O bond length is about 120-122 picometers. Physical properties and characterization Aldehydes have properties that are diverse and that depend on the remainder of the molecule. Smaller aldehydes are more soluble in water, formaldehyde and acetaldehyde completely so. The volatile aldehydes have pungent odors. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toluene
Toluene (), also known as toluol (), is a substituted aromatic hydrocarbon. It is a colorless, water-insoluble liquid with the smell associated with paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, consisting of a methyl group (CH3) attached to a phenyl group. As such, its systematic IUPAC name is methylbenzene. Toluene is predominantly used as an industrial feedstock and a solvent. As the solvent in some types of paint thinner, permanent markers, contact cement and certain types of glue, toluene is sometimes used as a recreational inhalant and has the potential of causing severe neurological harm. History The compound was first isolated in 1837 through a distillation of pine oil by the Polish chemist Filip Walter, who named it ''rétinnaphte''. In 1841, French chemist Henri Étienne Sainte-Claire Deville isolated a hydrocarbon from balsam of Tolu (an aromatic extract from the tropical Colombian tree ''Myroxylon balsamum''), which Deville recognized as similar to Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family. In coordination complexes the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds, when insufficient oxygen or heat is present to produce carbon dioxide. There are also numerous environmental and biological sources that generate and emit a significant amount of carbon monoxide. It is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Upon emission into the atmosphere, carbon monoxide affects several processes that contribute to climate change. Carbon monoxide has important biological roles across phylogenetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry. Hydrochloric acid, the aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride, is also commonly given the formula HCl. Reactions Hydrogen chloride is a diatomic molecule, consisting of a hydrogen atom H and a chlorine atom Cl connected by a polar covalent bond. The chlorine atom is much more electronegative than the hydrogen atom, which makes this bond polar. Consequently, the molecule has a large dipole moment with a negative partial charge (δ−) at the chlorine atom and a positive partial charge (δ+) at the hydrogen atom. In part because of its high polarity, HCl is very soluble in water (and in other polar solvents). Upon contact, and HCl combine to form hydronium cations and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
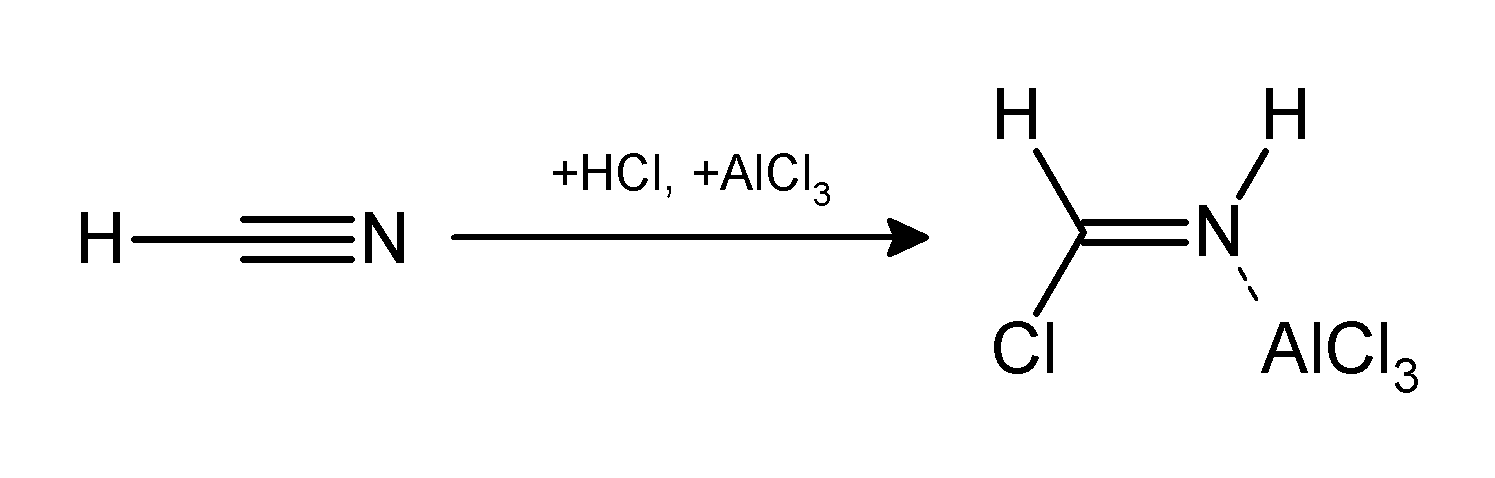
Gattermann-Koch Reaction
The Gattermann reaction, (also known as the Gattermann formylation and the Gattermann salicylaldehyde synthesis) is a chemical reaction in which aromatic compounds are formylated by a mixture of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst such as AlCl3. It is named for the German chemist Ludwig Gattermann and is similar to the Friedel–Crafts reaction. Modifications have shown that it is possible to use sodium cyanide or cyanogen bromide in place of hydrogen cyanide. The reaction can be simplified by replacing the HCN/AlCl3 combination with zinc cyanide. Although it is also highly toxic, Zn(CN)2 is a solid, making it safer to work with than gaseous HCN. The Zn(CN)2 reacts with the HCl to form the key HCN reactant and Zn(Cl)2 that serves as the Lewis-acid catalyst ''in-situ''. An example of the Zn(CN)2 method is the synthesis of mesitaldehyde from mesitylene. Gattermann–Koch reaction The Gattermann–Koch reaction, nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with a formyl substituent. It is the simplest aromatic aldehyde and one of the most industrially useful. It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic almond-like odor. The primary component of bitter almond oil, benzaldehyde can be extracted from a number of other natural sources. Synthetic benzaldehyde is the flavoring agent in imitation almond extract, which is used to flavor cakes and other baked goods. History Benzaldehyde was first extracted in 1803 by the French pharmacist Martrès. His experiments focused on elucidating the nature of amygdalin, the poisonous material found in bitter almonds, the fruit of ''Prunus dulcis''. Further work on the oil by Pierre Robiquet and Antoine Boutron-Charlard, two French chemists, produced benzaldehyde. In 1832, Friedrich Wöhler and Justus von Liebig first synthesized benzaldehyde. Production As of 1999, 7000 tonnes of synthetic and 100 tonnes of natural b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzaldehydes
Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with a formyl substituent. It is the simplest aromatic aldehyde and one of the most industrially useful. It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic almond-like odor. The primary component of bitter almond oil, benzaldehyde can be extracted from a number of other natural sources. Synthetic benzaldehyde is the flavoring agent in imitation almond extract, which is used to flavor cakes and other baked goods. History Benzaldehyde was first extracted in 1803 by the French pharmacist Martrès. His experiments focused on elucidating the nature of amygdalin, the poisonous material found in bitter almonds, the fruit of ''Prunus dulcis''. Further work on the oil by Pierre Robiquet and Antoine Boutron-Charlard, two French chemists, produced benzaldehyde. In 1832, Friedrich Wöhler and Justus von Liebig first synthesized benzaldehyde. Production As of 1999, 7000 tonnes of synthetic and 100 tonnes of natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |