|
4-8-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a 4-8-8-2 is a locomotive with four leading wheels, two sets of eight driving wheels, and a two-wheel trailing truck. Other equivalent classifications are: UIC classification: 2DD1 (also known as German classification and Italian classification) French classification: 240+041 Turkish classification: 46+45 Swiss classification: 4/6+4/5 The equivalent UIC classification is refined to (2'D)D1' for Mallet locomotives. A locomotive of that length must be an articulated locomotive; meaning all have a joint between the first and second groups of driving wheels. All examples of this type are cab forwards. Normally, the leading truck sits under the smokebox and the trailing truck under the firebox. On a cab-forward, the leading truck supports the firebox and the trailing truck and smokebox are at the rear next to the tender. A 4-8-8-2 is effectively a 2-8-8-4 that always runs in reverse. Southern Pacific The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
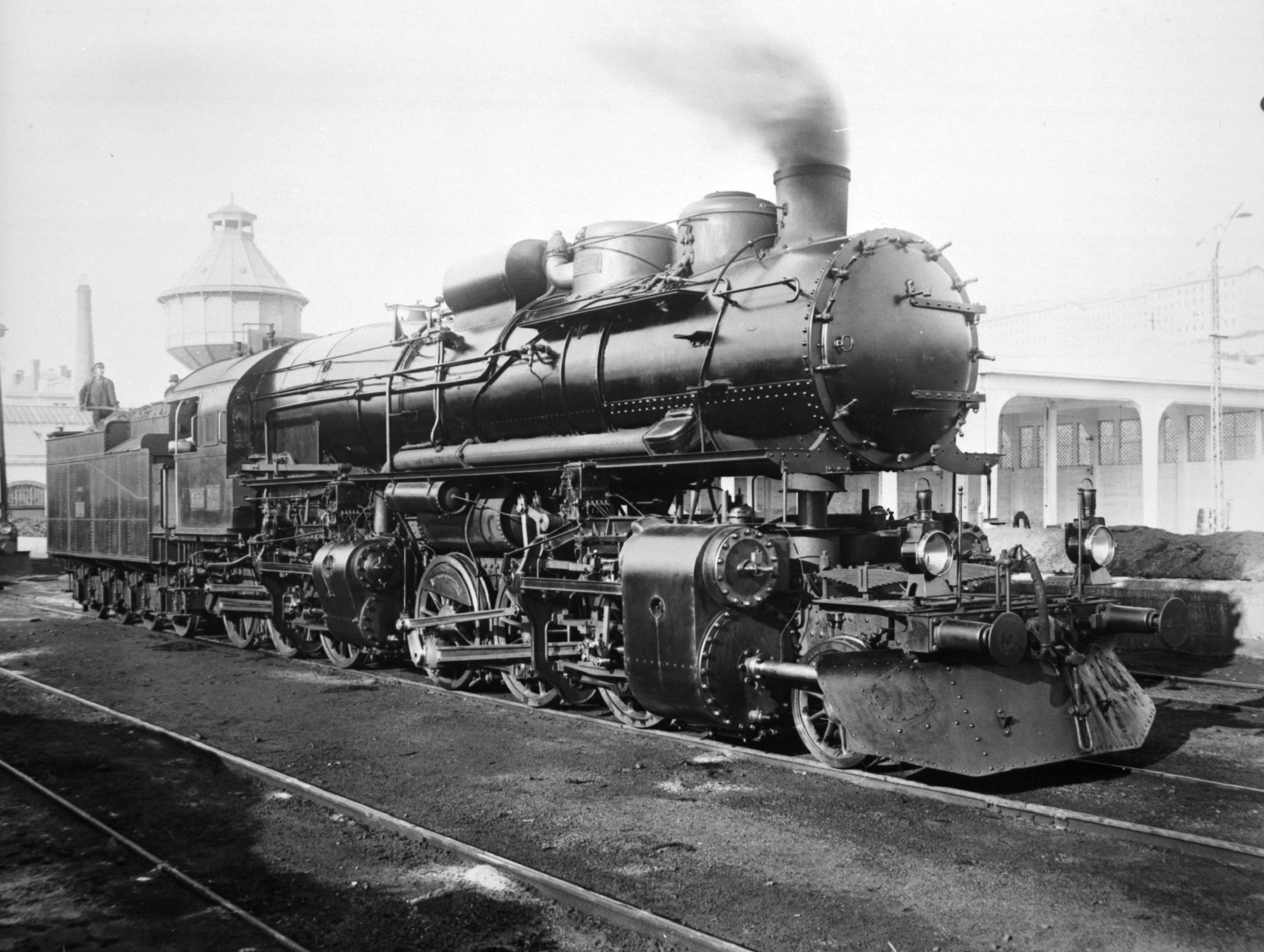
Southern Pacific 4294
Southern Pacific 4294 is a class " AC-12" 4-8-8-2 Cab forward type steam locomotive that was owned and operated by the Southern Pacific Railroad (SP). It was built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in March 1944 and was used hauling SP's trains over the Sierra Nevada, often working on Donner Pass in California. Today it is preserved at the California State Railroad Museum (CSRM) in Sacramento, California. History No. 4294 was the last of 20 Southern Pacific class AC-12 4-8-8-2 cab forward locomotives in a larger series of 256 Southern Pacific articulated cab forwards starting with class AC-1. Articulated locomotives are essentially two locomotives sharing fire box, boiler and crew. The front locomotive has its cranks quartered 90 degrees apart. The front and rear drive axles are free to roll out of phase with respect to each other. If unloaded, the locomotive has a vertical oscillation, near 50 mph, that can lift the tires above the rails. Its most distinguishing feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Pacific Railroad
The Southern Pacific (or Espee from the railroad initials- SP) was an American Class I railroad network that existed from 1865 to 1996 and operated largely in the Western United States. The system was operated by various companies under the names Southern Pacific Railroad, Southern Pacific Company and Southern Pacific Transportation Company. The original Southern Pacific began in 1865 as a land holding company. The last incarnation of the Southern Pacific, the Southern Pacific Transportation Company, was founded in 1969 and assumed control of the Southern Pacific system. The Southern Pacific Transportation Company was acquired in 1996 by the Union Pacific Corporation and merged with their Union Pacific Railroad. The Southern Pacific legacy founded hospitals in San Francisco, Tucson, and Houston. In the 1970s, it also founded a telecommunications network with a state-of-the-art microwave and fiber optic backbone. This telecommunications network became part of Sprint, a compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cab Forward
The term cab forward refers to various rail and road vehicle designs that place the driver's compartment substantially farther towards the front than is common practice. Rail locomotives In steam locomotive design, a cab forward design will typically have the driver's compartment or cab placed forward of the boiler at the very front of the engine. On a coal-fired locomotive, the fireman's station remains on the footplate behind the firebox so as to be next to the tender. On an oil-fired locomotive, the fireman's station could be (and normally is) in the forward cab. This type of design was widely, though not commonly, used throughout Europe in the first half of the 20th century, often in conjunction with an enclosed body design and/or streamlining. Visibility is greatly improved from the cab, and fumes from the chimney do not fill a forward cab in tunnels. However, the crew's prospects in the event of a collision are worse, and if the driver and fireman are in separate pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whyte Notation
Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twentieth century following a December 1900 editorial in ''American Engineer and Railroad Journal''. The notation was adopted and remains in use in North America and the United Kingdom to describe the wheel arrangements of steam locomotives (in the latter case also for diesel and electric locomotives), but for modern locomotives, multiple units and trams it has been supplanted by the UIC system in Europe and by the AAR system (essentially a simplification of the UIC system) in North America. Structure of the system Basic form The notation in its basic form counts the number of leading wheels, then the number of driving wheels, and finally the number of trailing wheels, numbers being separated by dashes. For example, a locomotive with two leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California State Railroad Museum
The California State Railroad Museum is a museum in the state park system of California, United States, interpreting the role of the "iron horse" in connecting California to the rest of the nation. It is located in Old Sacramento State Historic Park at 111 I Street, Sacramento. The museum features 21 restored locomotives and railroad cars, some dating back to 1862. The "Sierra Scene" shows a large scale mockup of a construction scene high in the Sierra Nevada representing Donner Pass circa 1867, featuring the locomotive ''Gov. Stanford''. Other exhibits show how the influence of railroads changed American society, influencing travel, commerce and daily life, as well as the lives of railroaders and the diversity of people who work on railroads. Changing exhibits featuring photography, ephemera, and artifacts from the museum's collection, add depth and incidental information to the overall story of railroad history. The museum has an extensive educational program for elementary stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railroad locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, in the early 20th century. The company was for decades the world's largest producer of steam locomotives, but struggled to compete as demand switched to diesel locomotives. Baldwin produced the last of its 70,000-plus locomotives in 1951, before merging with the Lima-Hamilton Corporation on September 11, 1951, to form the Baldwin-Lima-Hamilton Corporation. The company has no relation to the E.M. Baldwin and Sons of New South Wales, Australia, a builder of small diesel locomotives for sugar cane railroads. History: 19th century Beginning The Baldwin Locomotive Works had a humble beginning. Matthias W. Baldwin, the founder, was a jeweler and whitesmith, who, in 1825, formed a partnership with machinist David H. Mason, and engaged in the manufacture of bookbinders' tools and cylinders for cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Pacific 4294, A Cab-forward Steam Locomotive
Southern may refer to: Businesses * China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China * Southern Airways, defunct US airline * Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US * Southern Airways Express, Memphis-based passenger air transportation company, serving eight cities in the US * Southern Company, US electricity corporation * Southern Music (now Peermusic), US record label * Southern Railway (other), various railways * Southern Records, independent British record label * Southern Studios, recording studio in London, England * Southern Television, defunct UK television company * Southern (Govia Thameslink Railway), brand used for some train services in Southern England Media * ''Southern Daily'' or ''Nanfang Daily'', the official Communist Party newspaper based in Guangdong, China * ''Southern Weekly'', a newspaper in Guangzhou, China * Heart Sussex, a radio station in Sussex, England, previously known as "Southern FM" * 88 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacramento, California
) , image_map = Sacramento County California Incorporated and Unincorporated areas Sacramento Highlighted.svg , mapsize = 250x200px , map_caption = Location within Sacramento County in California , pushpin_map = California#USA , pushpin_label = Sacramento , pushpin_map_caption = Location within California##Location in the United States , pushpin_relief = yes , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_type1 = U.S. state, State , subdivision_name1 = California , subdivision_type2 = List of counties in California, County , subdivision_name2 = Sacramento County, California, Sacramento ---- , subdivision_type3 = List of regions of California, Region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallet (locomotive)
The Mallet locomotive is a type of articulated steam railway locomotive, invented by the Swiss engineer Anatole Mallet (1837–1919). The front of the locomotive articulated on a bogie. The compound steam system fed steam at boiler pressure to high-pressure cylinders driving the rear set of driving wheels (rigidly connected to the boiler). The exhaust steam from these cylinders was fed into a low-pressure receiver and was then sent to low-pressure cylinders that powered the driving wheels on the swiveling bogie towards the front of locomotive. Compounding Steam under pressure is converted into mechanical energy more efficiently if it is used in a compound engine; in such an engine steam from a boiler is used in high-pressure (HP) cylinders and then under reduced pressure in a second set of cylinders. The lower-pressure steam occupies a larger volume and the low-pressure (LP) cylinders are larger than the high-pressure cylinders. A third stage (triple expansion) may be empl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow Shed
Avalanche control or avalanche defense activities reduce the hazard avalanches pose to human life, activity, and property."Mitigation and Land Use - Avalanches" , Colorado Geological Survey Avalanche control begins with a risk assessment conducted by surveying for potential avalanche terrain by identifying geographic features such as vegetation patterns, drainages, and seasonal snow distribution that are indicative of avalanches. From the identified avalanche risks, the hazard is assessed by identifying threatened human geographic features such as roads, ski-hills, and buildings. Avalanche control programs address the avalanche hazard by formulating prevention and mitigation plans, which are then executed during the winter season. The prevention and mitigation plans combine extensive snow pack observation wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-8-8-4
A 2-8-8-4 steam locomotive, under the Whyte notation, has two leading wheels, two sets of eight driving wheels, and a four-wheel trailing truck. The type was generally named the ''Yellowstone'', a name given it by the first owner, the Northern Pacific Railway, whose lines ran near Yellowstone National Park. Seventy-two Yellowstone-type locomotives were built for four U.S. railroads. Other equivalent classifications are: *UIC classification: 1DD2 (also known as German classification and Italian classification) *French classification: 140+042 *Turkish classification: 45+46 *Swiss classification: 4/5+4/6 *Russian classification: 1-4-0+0-4-2 The equivalent UIC classification is, refined for Mallet locomotives, (1′D)D2′. A locomotive of this length must be an articulated locomotive. All Yellowstones had fairly small drivers of . (For greater speeds, the Union Pacific Railroad chose a four-wheel leading truck and drivers of for its Big Boy 4-8-8-4 class.) Several classes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articulated Locomotive
An articulated locomotive is a steam locomotive (rarely, an electric locomotive) with one or more engine units that can move independent of the main frame. Articulation allows the operation of locomotives that would otherwise be too large to negotiate a railroad's curves, whether mainlines or special lines with extreme curvature such as logging, industrial, or mountain railways. Articulated locomotives saw service in many nations, but were very popular on narrow-gauge railways in Europe. The largest examples were developed in the United States, where the Union Pacific Big Boy 4-8-8-4s and the Allegheny H-8 2-6-6-6s were some of the largest steam locomotives ever built. Many schemes for articulation were developed over the years. Of these, the Mallet locomotive and its simple-expansion derivative were the most popular, followed by the Garratt type (mostly built in the United Kingdom, popular throughout Europe, Africa and European colonies), and the various geared steam locomot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)


