|
3q29 Microdeletion Syndrome
3q29 microdeletion syndrome is a rare genetic disorder resulting from the deletion of a segment of chromosome 3. This syndrome was first described in 2005. Presentation The clinical phenotype of 3q29 microdeletion syndrome is variable. Clinical features can include mild to moderate intellectual disability with mildly dysmorphic facial features (long and narrow face, short philtrum and a high nasal bridge). Of the 6 reported patients, additional features including autism, ataxia, chest-wall deformity and long, tapering fingers were found in at least two patients. A review of 14 children with interstitial deletions of 3q29, found 11 who had the common recurrent 1.6Mb deletion and displayed intellectual disability and microcephaly. The variability of phenotype is underscored by the report on a 6 and 9/12-year-old male patient with a de novo chromosome 3q29 microdeletion identified by BAC array comparative genomic hybridization assay (aCGH), with accompanying normal 46,XY high- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development (a ''de novo'' mutation), or it can be Heredity, inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene (autosomal recessive inheritance) or from a parent with the disorder (autosomal dominant inheritance). When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y linkage, Y chromosome or Mitochondrial disease#Causes, mitochondrial DNA (due to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transferrin Receptor
Transferrin receptor (TfR) is a carrier protein for transferrin. It is needed for the import of iron into the cell and is regulated in response to intracellular iron concentration. It imports iron by internalizing the transferrin-iron complex through receptor-mediated endocytosis.Figure 3: The cycle of transferrin and transferrin receptor 1-mediated cellular iron uptake./ref> The existence of a receptor for transferrin iron uptake had been recognized over half a century back. Earlier two transferrin receptors in humans, transferrin receptor 1 and transferrin receptor 2 had been characterized and until recently cellular iron uptake was believed to occur chiefly via these two well documented transferrin receptors. Both these receptors are transmembrane glycoproteins. TfR1 is a high affinity ubiquitously expressed receptor while expression of TfR2 is restricted to certain cell types and is unaffected by intracellular iron concentrations. TfR2 binds to transferrin with a 25-30 fold low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Monosomies And Deletions
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes is collectively known as atDNA or auDNA. For example, humans have a diploid genome that usually contains 22 pairs of autosomes and one allosome pair (46 chromosomes total). The autosome pairs are labeled with numbers (1–22 in humans) roughly in order of their sizes in base pairs, while allosomes are labelled with their letters. By contrast, the allosome pair consists of two X chromosomes in females or one X and one Y chromosome in males. Unusual combinations of XYY, XXY, XXX, XXXX, XXXXX or XXYY, among other Salome combinations, are known to occur and usually cause developmental abnormalities. Autosomes still contain sexual determination genes even though they are not sex chromosomes. For example, the SRY gene on the Y chromosome e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
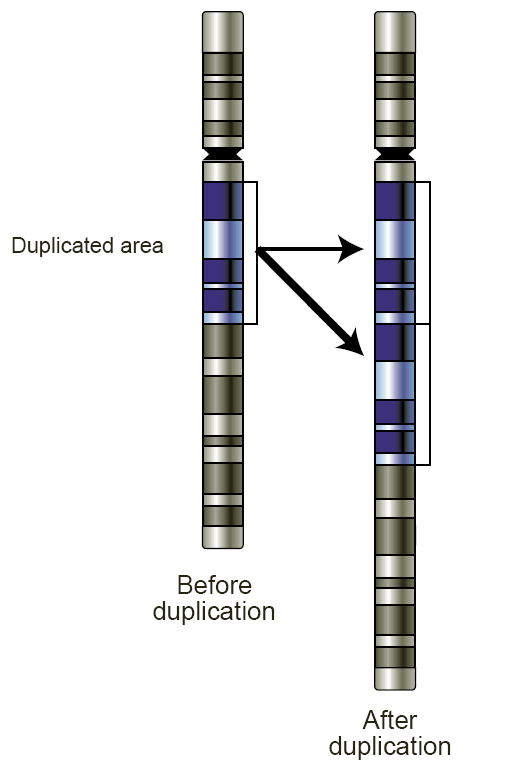
Copy Number Variant
Copy number variation (CNV) is a phenomenon in which sections of the genome are repeated and the number of repeats in the genome varies between individuals. Copy number variation is a type of structural variation: specifically, it is a type of duplication or deletion event that affects a considerable number of base pairs. Approximately two-thirds of the entire human genome may be composed of repeats and 4.8–9.5% of the human genome can be classified as copy number variations. In mammals, copy number variations play an important role in generating necessary variation in the population as well as disease phenotype. Copy number variations can be generally categorized into two main groups: short repeats and long repeats. However, there are no clear boundaries between the two groups and the classification depends on the nature of the loci of interest. Short repeats include mainly dinucleotide repeats (two repeating nucleotides e.g. A-C-A-C-A-C...) and trinucleotide repeats. Long r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdrawal, decreased emotional expression, and apathy. Symptoms typically develop gradually, begin during young adulthood, and in many cases never become resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. To be diagnosed with schizophrenia, symptoms and functional impairment need to be present for six months (DSM-5) or one month (ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially substance use disorders, depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. About 0.3% to 0.7% of people are diagnosed with schizophrenia during their lifetime. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singular: , Modern Hebrew: are a Jewish diaspora population who coalesced in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. Their traditional diaspora language is Yiddish (a West Germanic language with Jewish linguistic elements, including the Hebrew alphabet), which developed during the Middle Ages after they had moved from Germany and France into Northern Europe and Eastern Europe. For centuries, Ashkenazim in Europe used Hebrew only as a sacred language until the revival of Hebrew as a common language in 20th-century Israel. Throughout their numerous centuries living in Europe, Ashkenazim have made many important contributions to its philosophy, scholarship, literature, art, music, and science. The rabbinical term ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BDH1
D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''BDH1'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase gene family. The encoded protein forms a homotetrameric lipid-requiring enzyme of the mitochondrial membrane and has a specific requirement for phosphatidylcholine for optimal enzymatic activity. The encoded protein catalyzes the interconversion of acetoacetate and (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate, the two major ketone bodies produced during fatty acid catabolism. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been described. See also * 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase In enzymology, 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction: : (''R'')-3-hydroxybutanoate + NAD+ \rightleftharpoons acetoacetate + NADH + H+ Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are (''R'')-3-hydr ... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DLG1
Discs large homolog 1 (DLG1), also known as synapse-associated protein 97 or SAP97, is a scaffold protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SAP97'' gene. SAP97 is a mammalian MAGUK-family member protein that is similar to the Drosophila protein Dlg1 (the protein is alternatively referred to as hDlg1, and the human gene is DLG1). SAP97 is expressed throughout the body in epithelial cells. In the brain it is involved in the trafficking of ionotropic receptors from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane, and may be involved in the trafficking AMPAR during synaptic plasticity. Function SAP97 is expressed throughout the body in epithelial cells, including the kidney and brain. There is some evidence that SAP97 regulates cell-to-cell adhesion during cell death, and may interact with HPV. In the brain, SAP97's function is involved in the trafficking of transmembrane receptors from the ER to the plasma membrane. SAP97's function has been investigated by reducing its expr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanotransferrin
Melanotransferrin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MFI2'' gene. MFI2 has also recently been designated CD228 (cluster of differentiation 228). The protein encoded by this gene is a cell-surface glycoprotein found on melanoma cells. The protein shares sequence similarity and iron-binding properties with members of the transferrin superfamily. The importance of the iron binding function has not yet been identified. This gene resides in the same region of chromosome 3 as members of the transferrin superfamily. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants. It is part of neural crest tissue, often present in melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * Clusters of differentiation Human proteins {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Cap-binding Protein Complex
Nuclear cap-binding protein complex is a RNA-binding protein which binds to the 5' cap of pre-mRNA. The cap and nuclear cap-binding protein have many functions in mRNA biogenesis including splicing, 3'-end formation by stabilizing the interaction of the 3'-end processing machinery, nuclear export and protection of the transcripts from nuclease degradation. When RNA is exported to the cytoplasm the nuclear cap-binding protein complex is replaced by cytoplasmic cap binding complex. The nuclear cap-binding complex is a functional heterodimer and composed of Cbc1/Cbc2 in yeast and CBC20/CBC80 in multicellular eukaryotes. Human nuclear cap-binding protein complex shows the large subunit, CBC80 consists of 757 amino acid residues. Its secondary structure contains approximately sixty percent of helical and one percent of beta sheet in the strand. The small subunit, CBC20 has 98 amino acid residues. Its secondary structure contains approximately twenty percent of helical and twenty-four p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAK2
Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PAK2'' gene. PAK2 is one of three members of Group I PAK family of serine/threonine kinases. The PAKs are evolutionary conserved. PAK2 and its cleaved fragment localize in both the cytoplasmic or nuclear compartments. PAK2 signaling modulates apoptosis, endothelial lumen formation, viral pathogenesis, and cancer including, breast, hepatocarcinoma, and gastric and cancer, at-large. Discovery The human PAK2 was identified as a downstream effector of Rac or Cdc42. Gene and spliced variants The PAK2 gene is about 92.7-kb long. The gene contains 15 exons and generates three alternatively spliced transcripts - two of which code proteins of 524 amino acids and 221 amino acids, while the third one is a 371-bp non-coding RNA transcript(Gene from review) There are two transcripts generated from the murine PAK2 gene, a 5.7-kb transcript coding a 524 amino acids long polypeptide and a 1.2-kb long non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |