|
3830
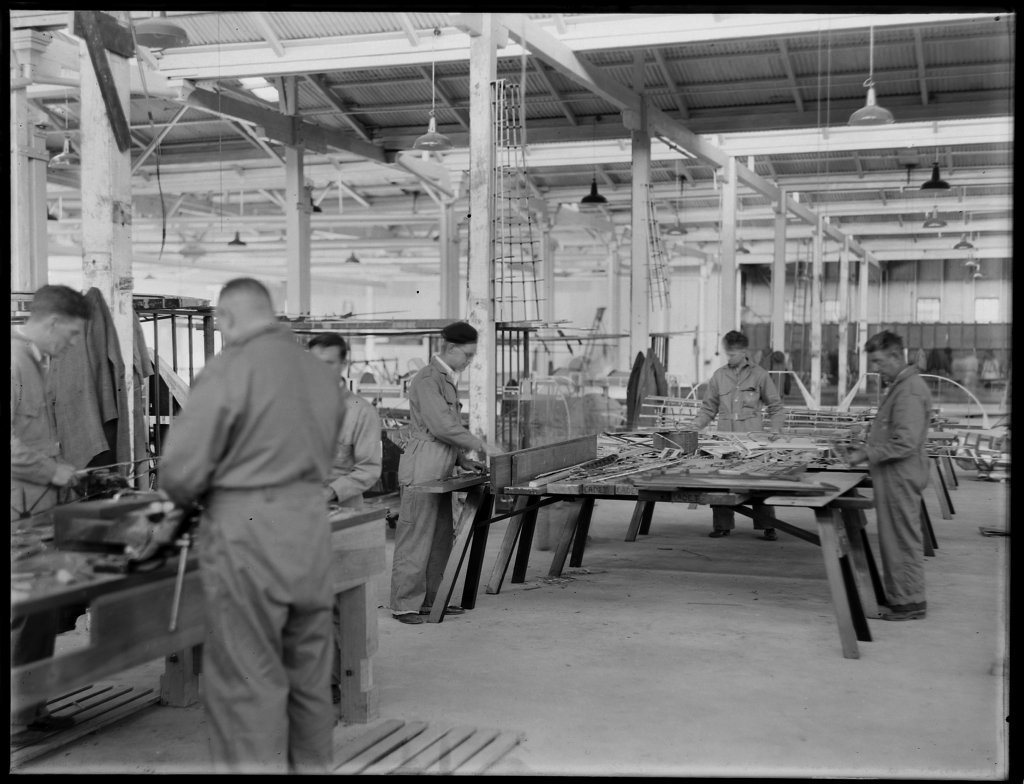
3830 (pronounced Thirty-eight thirty) is a 4-6-2 steam locomotive operated by the New South Wales Government Railways between 1949 and 1967. It has been preserved by the Powerhouse Museum and is based at the NSW Rail Museum, Thirlmere. It was operational from 1997 until 2009 and was scheduled to return to service in 2016 before the need for more extensive boiler repairs was discovered. Construction 3830 was built in 1949 by the New South Wales Government Railways', Eveleigh Railway Workshops as the last of thirty New South Wales C38 class locomotive, 38 class locomotives built to haul express trains. 3830 was the last steam locomotive built in New South Wales. The first five were built by Clyde Engineering to a Streamliner, streamlined design, whilst the later 25 locomotives in the class were built by Eveleigh and Cardiff Locomotive Workshops and were unstreamlined. Construction was delayed mostly due to material shortages during World War II. 3830 was the last engine complete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
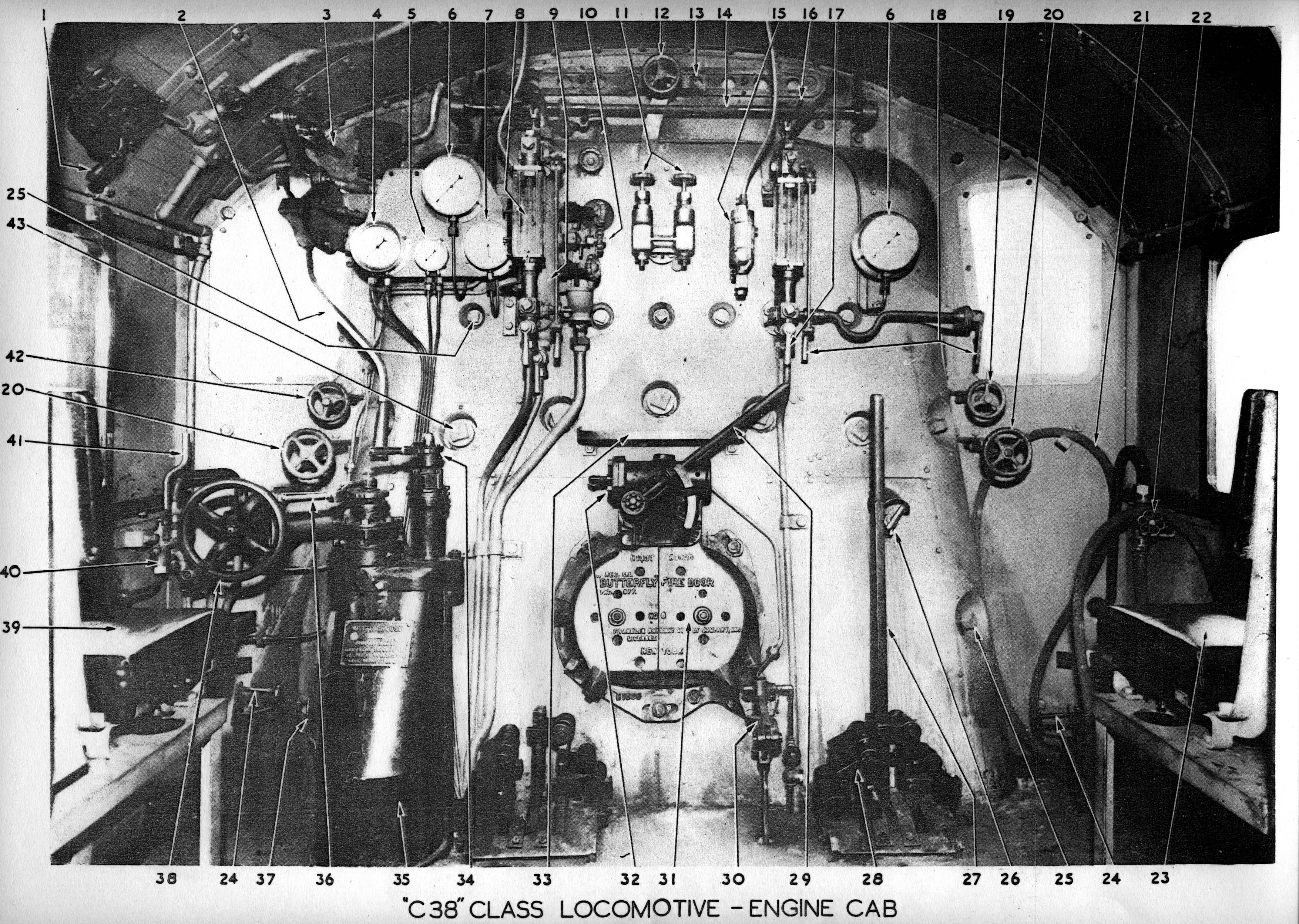
New South Wales C38 Class Locomotive
The C38 class (occasionally known as the 38 class and nicknamed "Pacifics" by some railwaymen) was a class of steam locomotive built for the New South Wales Government Railways in Australia. Constructed between January 1943 and November 1949, the 30 locomotives in the class were designed to haul express passenger services throughout New South Wales. They were the only New South Wales locomotives to use the popular Pacific 4-6-2 wheel arrangement and were the last steam locomotives in the state to be built for passenger train operation, all subsequent deliveries being specifically for freight haulage. Design The 38 class were first conceived in the 1930s when the NSWGR established there was a need for a locomotive to eliminate the complications of double heading on a number of fast intrastate passenger trains. The design was influenced by the fashion for streamlining at the time, including elements of the class J locomotives of the Norfolk and Western Railway and of some of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clyde Engineering
Clyde Engineering was an Australian manufacturer of locomotives, rolling stock, and other industrial products. It was founded in September 1898 by a syndicate of Sydney businessmen buying the Granville factory of timber merchants Hudson Brothers. The company won contracts for railway rolling stock, a sewerage system, trams and agricultural machinery. In 1907 it won its first contract for steam locomotives for the New South Wales Government Railways. By 1923 it had 2,200 employees. After contracting during the depression it became a major supplier of munitions during World War II. In 1950 it was awarded the first of many contracts for diesel locomotives by the Commonwealth Railways after it was appointed the Australian licensee for Electro-Motive Diesel products. Apart from building locomotives and rolling stock, Clyde Engineering diversified into telephone and industrial electronic equipment, machine tools, domestic aluminium ware, road making and earth making equipmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powerhouse Museum
The Powerhouse Museum is the major branch of the Museum of Applied Arts & Sciences (MAAS) in Sydney, the others being the historic Sydney Observatory at Observatory Park, Sydney, Observatory Hill, and the newer Museums Discovery Centre at Castle Hill, New South Wales, Castle Hill. Although often described as a science museum, the Powerhouse has a diverse collection encompassing all sorts of technology including decorative arts, science, communication, transport, costume, furniture, mass media, media, computer technology, space technology and steam engines. The museum has existed in various guises for over 125 years, previously named the Technological, Industrial and Sanitary Museum of New South Wales (1879–1882) and the Technological Museum (August 1893 – March 1988). the collection contains over 500,000 objects collected over the last 135 years, many of which are displayed or housed at the site it has occupied since 1988, and for which it is named – a converted electric t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roundhouse (periodical)
In 2013, Transport Heritage NSW was established by the Government of New South Wales to manage the State’s rail heritage collection and provide support to the broader transport (bus, tram, rail) heritage sector in NSW following an independent review. History In May 2013, Minister for Transport Gladys Berejiklian acknowledged the importance of steam locomotive 3801, stating it would be a priority of Transport Heritage NSW to return it to service. On 10 December 2013, a majority of the members of the New South Wales Rail Transport Museum voted in support of the creation of Transport Heritage NSW. Other transport heritage groups also expressed concern for their future existence. Peter Lowry was appointed as chairperson of the board and the nominated chief executive of Transport Heritage NSW, Andrew Killingsworth has been seen as a political appointment. In February 2016, Andrew Moritz was appointed as the new chief executive following the resignation of Andrew Killingsworth. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirit Of Progress
The ''Spirit of Progress'' was the premier express passenger train on the Victorian Railways in Australia, running from Melbourne to the New South Wales border at Albury, and later through to Sydney. Route From its introduction in November 1937 until April 1962, the train service ran on broad gauge line from Melbourne's Spencer Street station to Albury, on the New South Wales / Victorian border, where passengers changed to a New South Wales Government Railways train (the ''Melbourne Limited Express''), running on standard gauge track to complete the journey to Sydney. Following the completion of the standard gauge line between Melbourne and Albury in April 1962, the ''Spirit of Progress'' was extended to Sydney. Broad gauge service (1937–1962) The ''Spirit of Progress'' ushered in a standard of passenger train speed and comfort not previously seen in Australia. Its introduction in November 1937 marked the culmination of many years of preparatory work by the Victori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Railway Station, Sydney
Central is a heritage-listed railway station located in the centre of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. The station is the largest and busiest railway station in Australia and serves as a major transport interchange for NSW TrainLink inter-city rail services, Sydney Trains commuter rail services, Sydney light rail services, bus services, and private coach transport services. The station is also known as Sydney Terminal (Platforms 1 to 12). The property was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License It recorded 85.4 million passenger movements in 2018. Central station occupies a large city block separating , and the central business district, bounded by Railway Square and Pitt Street in the west, Eddy Avenue in the north, Elizabeth Street in the east and the Devonshire Street Tunnel in the south. Parts of the station and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enfield Locomotive Depot
The Enfield Locomotive Depot was operated by the New South Wales Government Railways in Strathfield South, Sydney. It was part of the Enfield Marshalling Yards, which covers a considerable area in the west of the modern suburb of Strathfield South. The site is now part of the Enfield Intermodal Logistics Centre. History The Enfield Locomotive Depot was the largest locomotive depot on the New South Wales Government Railways' network, being located within the confines of Enfield yard. It would eventually comprise three roundhouses. The Enfield rail yard is in the suburb of Strathfield South, and was named after the former Municipality of Enfield, which governed this area between 1889 and 1949. The modern suburb of Enfield is some distance away to the east. With dieselisation, a new depot for diesel locomotives, Delec Locomotive Depot opened in 1958. As the steam era grew to a close, the depot gradually closed. In August 1969, the New South Wales Rail Transport Museum moved into R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wyong Railway Station
Wyong railway station is located on the Main Northern line in New South Wales, Australia. It serves the northern Central Coast suburb of Wyong. History Wyong station was opened on 15 August 1887. In 1912, the line was duplicated. In 1937, the eastern platform was converted to an island platform. A pair of passing loops were added south of the station in 1948. In the 1950s, a new bridge was built over Wyong Creek immediately south of the station, with the old railway bridge becoming part of the Pacific Highway. Between April 1982 and June 1984, Wyong was the northern extremity of the electrified network. A brick building on Platforms 1 and 2 was replaced by the current structure in the 1990s. On 1 November 1993, an upgraded footbridge with a new ticket office and lifts was opened by Minister for Transport Bruce Baird. Platforms & services Wyong has three platforms, one island with two faces and one side platform. It is serviced by NSW TrainLink Central Coast & Newcastle li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trainworks Railway Museum
The NSW Rail Museum is the main railway museum in New South Wales, Australia. A division of Transport Heritage NSW, it was previously known as the New South Wales Rail Transport Museum (NSWRTM), Rail Heritage Centre and Trainworks. Transport Heritage NSW has divisions located in Thirlmere, New South Wales, where the NSW Rail Museum is dedicated to displaying locomotives, passenger cars, and freight rolling stock formerly operated by the New South Wales Government Railways (NSWGR) and various private operators. The Blue Mountains division is located at the Valley Heights Locomotive Depot Heritage Museum. * At Thirlmere, the NSW Rail Museum operates steam heritage trains on the Picton – Mittagong railway line between Picton, Thirlmere and Buxton. It also hosts the Thirlmere Festival of Steam in March each year. * In addition to this, Transport Heritage NSW regularly operates mainline tours under the ''NSW Rail Museum'' branding. These can consist of day or extended tours, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maitland Railway Station
Maitland railway station is located on the Main Northern line in New South Wales, Australia. It serves the city of Maitland opening on in 1880 as West Maitland being renamed on 1 April 1949. It is the junction station for the Main Northern and North Coast lines. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999. History The Great Northern Railway was built through Maitland in the 1850s and extended to Lochinvar in July 1860. Maitland was serviced by Victoria Street, East Maitland and High Street when it opened however it was not until 1880 that what is now Maitland's principal station opened as West Maitland. Initially the station comprised only one platform, the present Platform 1. The station expanded with an island platform and footbridge constructed in 1914 followed in 1933 by another island platform. In April 1949 in recognition of its position as Maitland's primary station it received its present name. A bay platform was located at the easte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moss Vale Railway Station
Moss Vale railway station is a heritage-listed railway station on the Main South line in New South Wales, Australia. It serves the town of Moss Vale. It opened on 2 December 1867 as Sutton Forest, being renamed in 1877. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999. History Moss Vale station opened as Suttons Forest on 2 December 1867. It was the terminus of the line until the extension to Marulan on 6 August 1868. The station was renamed to Moss Vale in 1877. In March 1999, a refuelling and stabling facility for Endeavour railcars was built to the north of the station. Platforms & services Moss Vale has an island platform with two sides. It is serviced by NSW TrainLink Southern Highlands Line services from Campbelltown, morning services to Sydney Central and 1 early morning & evening services to Goulburn. It is also serviced by NSW TrainLink Xplorer and XPT long-distance services from Sydney to Canberra, Griffith and Melbourne. Tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enfield, New South Wales
Enfield is a suburb in the Inner West of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It is 11 kilometres south-west of the Sydney central business district in the Local government in Australia, local government area of Municipality of Burwood. History The suburb is named after Enfield Town, a suburb of London, England. Aboriginal culture Before the arrival of the First Fleet in 1788, the Enfield area belonged to the Wangal people, a clan of the Eora tribe, which covered most of Sydney. In the early years, the Eora people were badly affected by smallpox, which arrived with the British. Many of the clans became unsustainably small and the survivors formed new bands who lived where they could. While it would be wrong to say that the local indigenous population gave no resistance to British land claims (Pemulwuy being a notable example), within thirty years or so of the colony's establishment, most of the land in the inner-west had been conceded to British settlers. Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


