|
381st Training Group
The United States Air Force 381st Training Group at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California provides training for the United States Air Force's intercontinental ballistic missile forces and missile maintenance forces. This Air Education and Training Command (AETC) organization is a tenant unit located on an site at Vandenberg. The group was activated in the fall of 1994, when it replaced a provisional group as missile training activities at Vandenberg were transferred to AETC. During World War II, the group's first predecessor, the 381st Bombardment Group was an Eighth Air Force Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress unit, which flew strategic bombing missions from RAF Ridgewell. The group had the highest losses of all groups on first Schweinfurt–Regensburg mission on 17 August 1943. It flew 296 combat missions, earning two Distinguished Unit Citations. It flew its last mission on 25 April 1945 before returning to the United States, where it was inactivated. The group was activated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. Russia, the United States, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, and North Korea are the only countries known to have operational ICBMs. Early ICBMs had limited precision, which made them suitable for use only against the largest targets, such as cities. They were seen as a "safe" basing option, one that would keep the deterrent force close to home where it would be difficult to attack. Attacks against military targets (especially hardened ones) still demanded th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Ridgewell
Royal Air Force Ridgewell or more simply RAF Ridgewell is a former Royal Air Force station located at Ridgewell, north west of Halstead, Essex, England. During the Second World War, the airfield was used by the Royal Air Force and the United States Army Air Forces Eighth Air Force. History RAF Ridgewell was an early example of stations completed to Class A heavy bomber airfield design for the RAF, and had three intersecting runways of 6,500 ft each in length, thirty-six hardstands, two T-2 hangars and accommodation for 2,900 men in temporary buildings. RAF Bomber Command use The airfield was opened in December 1942 and was first used by No. 90 Squadron of RAF Bomber Command, equipped with Short Stirling Bombers until May 1943, the station being at that time a satellite of RAF Stradishall. USAAF use RAF Ridgewell was the only long-term heavy bomber airfield of the Eighth Air Force in Essex. For United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) use, the number of hardstandings was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Mans
Le Mans (, ) is a city in northwestern France on the Sarthe River where it meets the Huisne. Traditionally the capital of the province of Maine, it is now the capital of the Sarthe department and the seat of the Roman Catholic diocese of Le Mans. Le Mans is a part of the Pays de la Loire region. Its inhabitants are called ''Manceaux'' (male) and ''Mancelles'' (female). Since 1923, the city has hosted the 24 Hours of Le Mans, the world's oldest active endurance sports car race. History First mentioned by Claudius Ptolemy, the Roman city ''Vindinium'' was the capital of the Aulerci, a sub tribe of the Aedui. Le Mans is also known as ''Civitas Cenomanorum'' (City of the Cenomani), or ''Cenomanus''. Their city, seized by the Romans in 47 BC, was within the ancient Roman province of Gallia Lugdunensis. A 3rd-century amphitheatre is still visible. The ''thermae'' were demolished during the crisis of the third century when workers were mobilized to build the city's defensive walls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Nazaire
Saint-Nazaire (; ; Gallo: ''Saint-Nazère/Saint-Nazaer'') is a commune in the Loire-Atlantique department in western France, in traditional Brittany. The town has a major harbour on the right bank of the Loire estuary, near the Atlantic Ocean. The town is at the south of the second-largest swamp in France, called "la Brière". Given its location, Saint-Nazaire has a long tradition of fishing and shipbuilding. The Chantiers de l'Atlantique, one of the largest shipyards in the world, constructed notable ocean liners such as , , and the cruise ship , the largest passenger ship in the world until 2022. Saint-Nazaire was a small village until the Industrial Revolution but became a large town in the second half of the 19th century, thanks to the construction of railways and the growth of the seaport. Saint-Nazaire progressively replaced upstream Nantes as the main haven on the Loire estuary. As a major submarine base for the Kriegsmarine, Saint-Nazaire was subject to a successful Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amiens
Amiens (English: or ; ; pcd, Anmien, or ) is a city and commune in northern France, located north of Paris and south-west of Lille. It is the capital of the Somme department in the region of Hauts-de-France. In 2021, the population of Amiens was 135,429. A central landmark of the city is Amiens Cathedral, the largest Gothic cathedral in France. Amiens also has one of the largest university hospitals in France, with a capacity of 1,200 beds. The author Jules Verne lived in Amiens from 1871 until his death in 1905, and served on the city council for 15 years. Incumbent French president Emmanuel Macron was born in Amiens. The town was fought over during both World Wars, suffering significant damage, and was repeatedly occupied by both sides. The 1918 Battle of Amiens was the opening phase of the Hundred Days Offensive which directly led to the Armistice with Germany. The Royal Air Force heavily bombed the town during the Second World War. In the aftermath, the city was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McConnell Air Force Base
McConnell Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located four miles (6 km) southeast of the central business district of Wichita, a city in Sedgwick County, Kansas, United States., effective 2007-12-20 The airbase was named in honor of the brothers Fred and Thomas McConnell of Wichita, who had both been Air Force pilots and veterans of World War II. It is the home of Air Mobility Command's 22d Air Refueling Wing (22 ARW), Air Force Reserve Command's 931st Air Refueling Wing (931 ARW), and the Kansas Air National Guard's 184th Intelligence Wing (184 IW). McConnell's primary mission is to provide global reach by conducting air refueling and airlift where and when needed. History McConnell Air Force Base was known during the first part of its existence as the Wichita Municipal Airport. Although the field was designed originally to serve only municipal civil airport needs, it had an Air Force connection almost from the beginning. Origins McConnell's history be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was both a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile components of the United States military's strategic nuclear forces from 1946 to 1992. SAC was also responsible for the operation of strategic reconnaissance aircraft and airborne command post aircraft as well as most of the USAF's aerial refueling fleet, including aircraft from the Air Force Reserve (AFRES) and Air National Guard (ANG). SAC primarily consisted of the Second Air Force (2AF), Eighth Air Force (8AF) and the Fifteenth Air Force (15AF), while SAC headquarters (HQ SAC) included Directorates for Operations & Plans, Intelligence, Command & Control, Maintenance, Training, Communications, and Personnel. At a lower echelon, SAC headquarters divisions included Aircraft Engineering, Missile Concept, and Strategic Communicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
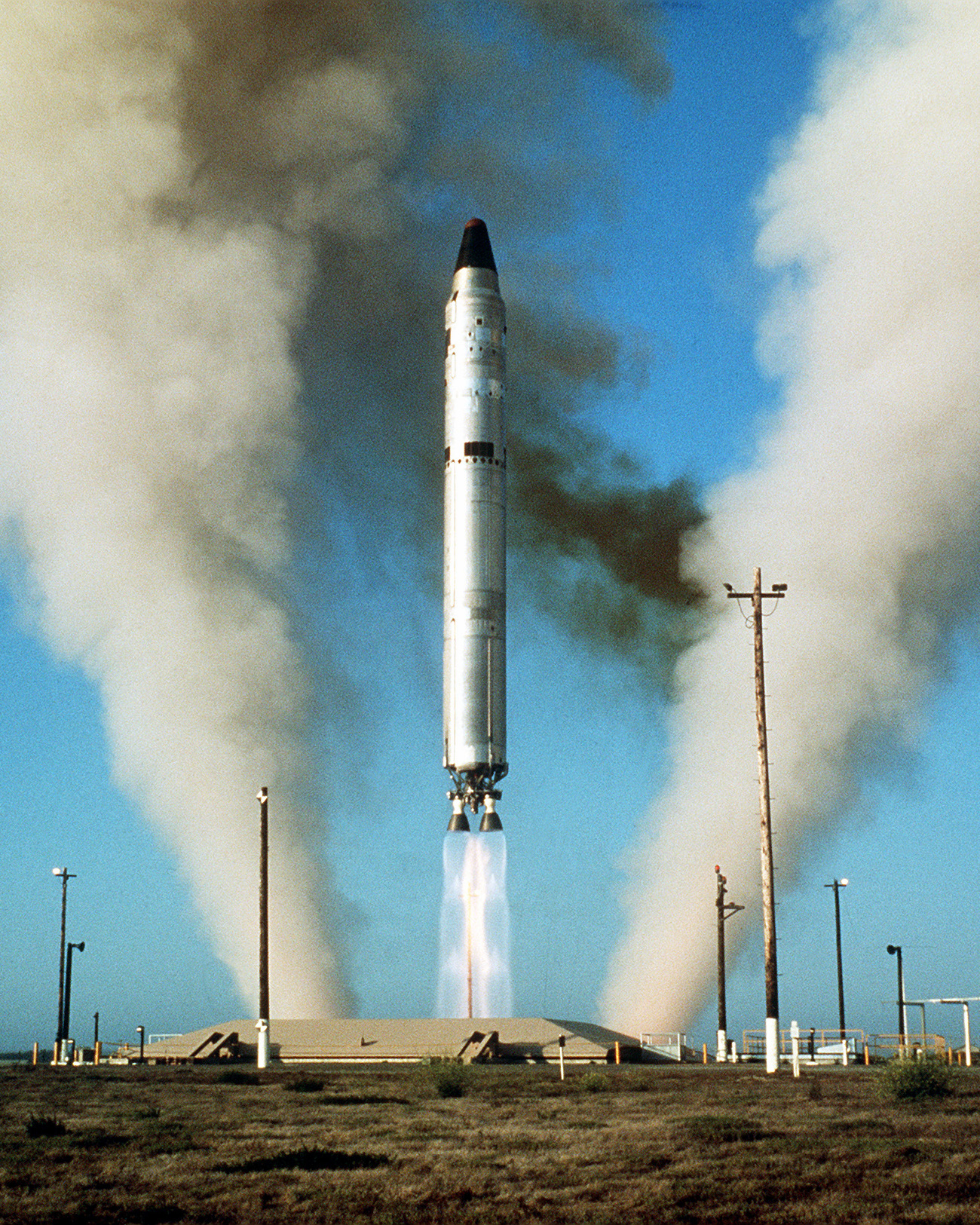
LGM-25C Titan II
The Titan II was an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the Glenn L. Martin Company from the earlier Titan I missile. Titan II was originally designed and used as an ICBM, but was later adapted as a medium-lift space launch vehicle (these adaptations were designated Titan II GLV and Titan 23G) to carry payloads to Earth orbit for the United States Air Force (USAF), National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Those payloads included the USAF Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP), NOAA weather satellites, and NASA's Gemini crewed space capsules. The modified Titan II SLVs (Space Launch Vehicles) were launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, up until 2003. Titan II missile The Titan II ICBM was the successor to the Titan I, with double the payload. Unlike the Titan I, it used hydrazine-based hypergolic propellant which was storable and reliably ignited. This red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
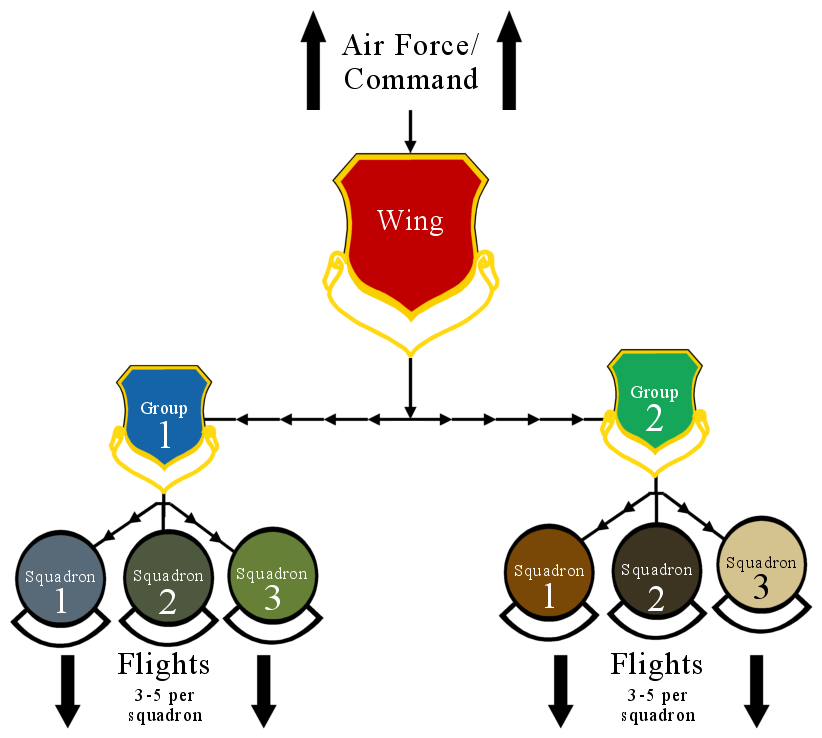
Wing (military Aviation Unit)
In military aviation, a wing is a unit of command. In most military aviation services, a wing is a relatively large formation of planes. In Commonwealth countries a wing usually comprises three squadrons, with several wings forming a group (around 10 squadrons). Each squadron will contain around 20 planes. Commonwealth usage Origins On its establishment in 1912, the British Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was intended to be an inter-service, combined force of the British Army and Royal Navy. Given the rivalry that existed between the army and navy, new terminology was used, in order to avoid marking the corps out as having an army or navy ethos. While the term "wing" had been used in the cavalry, its more general use predominated. Accordingly, the word "wing", with its allusion of flight, was chosen as the term of subdivision and the corps was split into a "Military Wing" (i.e. an army wing) and a "Naval Wing". Each wing consisted of a number of squadrons (the term "squadro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.gif)