|
37th Guards Motor Rifle Brigade
The 37th Separate Guards Motor Rifle Don Cossack Budapest Red Banner Order of the Red Star Brigade named after Ye. A. Shchadenko is a motor rifle brigade of the Russian Ground Forces (Military Unit Number 69647). It is stationed at Kyakhta in Buryatia, part of the 36th Combined Arms Army of the Eastern Military District. The brigade fought in the War in Donbas and the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. Components Due to its location in Kiakhta in Buryatia, this brigade has a high percentage of Buryat and other ethnic minority servicemen, many of whom adhere to Tibetan Buddhism. As a result, by 2021 it was the only Russian military unit with a Buddhist lama serving as a military chaplain. The brigade included more than 200 tracked vehicles and more than 100 wheeled vehicles in 2013. According to 2015 data, the brigade was equipped with 40 T-72B3, 1 T-72BK, 120 BMP-2, 15 MT-LB, 18 BM 2B17-1 Tornado-G, 36 2S3M Akatsiya 152mm howitzers, 18 120mm mortar 2S12 Sani, 6 100 mm MT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanized Infantry
Mechanized infantry are infantry units equipped with armored personnel carriers (APCs) or infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs) for transport and combat (see also mechanized force). As defined by the United States Army, mechanized infantry is distinguished from motorized infantry in that its vehicles provide a degree of armor protection and armament for use in combat, whereas motorized infantry are provided with "soft-skinned" wheeled vehicles for transportation only.Infantry Division Transportation Battalion and Transportation, Tactical Carrier Units. (1962). United States: Headquarters, Department of the Army. p. 15 Most APCs and IFVs are fully tracked or are all-wheel drive vehicles (6×6 or 8×8), for mobility across rough ground. Some nations distinguish between mechanized and armored (or armoured) infantry, designating troops carried by APCs as mechanized and those in IFVs as armored. The support weapons for mechanized infantry are also provided with motorized transport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Chaplain
A military chaplain ministers to military personnel and, in most cases, their families and civilians working for the military. In some cases they will also work with local civilians within a military area of operations. Although the term '' chaplain'' originally had Christian roots, it is generally used today in military organizations to describe all professionals specially trained to serve any spiritual need, regardless of religious affiliation. In addition to offering pastoral care to individuals, and supporting their religious rights and needs, military chaplains may also advise the executive on issues of religion, and ethics, morale and morals as affected by religion. They may also liaise with local religious leaders in an effort to understand the role of religion as a factor both in hostility and war and in reconciliation and peace. On the role of chaplains in multinational operations. Military chaplains normally represent a specific religion or faith group but work w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th Guards Tank Division
The 5th Guards Tank Division was an armored division of the Soviet Ground Forces and Russian Ground Forces, active from 1945 to 2009, in two different formations. First Formation The 5th Guards "Stalingradsko-Kievskaya Order of Lenin Red Banner orders of Suvorov and Kutuzov" Tank Division was formed in September 1945 at Sherlovaya Gora, Chita Oblast, from the 5th Guards Tank Corps. In mid 1957 it became the 122nd Guards Motor Rifle Division. Half a century later, in June 2009, the descendant formation became the 35th Separate Guards Motor Rifle Brigade. Second Formation The second formation drew its heritage from an illustrious Soviet World War II cavalry formation, the 5th Guards Cavalry Corps (Honorifics Don-Budapest Red Banner). After the end of World War II, the corps relocated from Ploiești in Romania, where it was part of the Southern Group of Forces, to Novocherkassk in Rostov Oblast, by the fall of 1945. The corps was reorganised as the 5th Guards Cavalry Division on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZSU-23-4 Shilka
The ZSU-23-4 "Shilka" is a lightly armored Soviet self-propelled, radar-guided anti-aircraft weapon system ( SPAAG). Etymology The acronym "ZSU" stands for ''Zenitnaya Samokhodnaya Ustanovka'' (russian: Зенитная Самоходная Установка), meaning "anti-aircraft self-propelled system"; the "23" signifies the bore diameter in millimeters; the "4" signifies the number of gun barrels. It is named after the Shilka River in Russia. Afghan soldiers nicknamed it the "sewing machine" due to the sound of firing guns. It is also referred to by its nickname of "Zeus", derived from the Russian acronym. History The previous Soviet self-propelled anti-aircraft gun ( SPAAG), the ZSU-57-2, was armed with two 57 mm autocannons; it was aimed optically using a basic tracking and lead calculating system. The ZSU-57-2 was not particularly successful despite its very powerful autocannons; given their large caliber, it could only carry 300 rounds, was inaccurate as it lack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9K35 Strela-10
The 9K35 ''Strela-10'' (russian: 9К35 «Стрела-10»; en, arrow) is a Soviet highly mobile, short-range surface-to-air missile system. It is visually aimed, and utilizes optical/ infrared-guidance. The system is primarily intended to engage low-altitude threats, such as helicopters. "9K35" is its GRAU designation; its NATO reporting name is SA-13 "Gopher". Development The 9K35 is the successor of the 9K31 Strela-1 and can also use the Strela-1's missiles in place of the 9M37. Development of the 9K37 Strela-10SV system was initiated July 24, 1969. The decision to begin the development of a new non-all-weather system was taken despite the simultaneous development of an all-weather hybrid gun/missile system 9K22 "Tunguska" mainly as an economical measure. It was also seen as advantageous to have a system capable of fast reaction times and immunity to heavy radio-frequency jamming. Rather than being mounted on an amphibious but lightly armoured BRDM chassis like the 9K31, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9K33 Osa
The 9K33 ''Osa'' (, literally "wasp"; NATO reporting name SA-8 ''Gecko'') is a highly mobile, low-altitude, short-range tactical surface-to-air missile system developed in the Soviet Union in the 1960s and fielded in 1972. Its export version name is Romb. Development Design work on an entirely new, self-propelled air defense guided missile system began in 1960 and was assigned to the Moscow-based () research and design institute under lead designer M.M. Kosichkin. The program initially suffered numerous delays and setbacks due to poorly formulated performance and tactical requirements, as this was a pioneering battlefield air defense system with no equivalents in existence at the time, and no doctrinal experience with such a weapon. P.M. Chukadov was assigned project leader in 1965 after a thorough review of the stalled program. The Osa had service acceptance in 1972 after a period of trials. Description The Osa was the first mobile air defense missile system incorporating it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BTR-80
The BTR-80 (russian: бронетранспортёр, bronyetransportyor, literally "armoured transporter") is an 8×8 wheeled amphibious armoured personnel carrier (APC) designed in the USSR. It was adopted in 1985 and replaced the previous vehicles, the BTR-60 and BTR-70, in the Soviet Army. It was first deployed during the Soviet–Afghan War. The BTR-80 was developed into the larger BTR-90. Description The Soviets based the BTR-80 on the BTR-70 APC, which itself was based on the BTR-60. It has a single 260-hp V-8 turbocharged water-cooled diesel engine, an improvement over the twin gasoline engines installed in the BTR-60 and BTR-70 vehicles. The reconfigured rear portion of the hull accommodates the new, single engine. The Soviets removed the roof chamfers of the modified BTR-70, raised the rear, and squared off the rearward-sloping engine compartment. Standard equipment includes TNPO vision blocks, TNP-B and TKN-3 optical devices for the driver and commander, an OU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9K114 Shturm
9K114 ''Shturm'' - Weaponsystems.net (russian: 9К114 «Штурм» - "Assault", borrowed from German "Sturm" - Storm/Assault) - is a radio guided system of the . Its designation is 9K114. Its |
MT-12 Rapira
2A19 or T-12 was a revolutionary Soviet 100-mm anti-tank gun. It was the first (anti-) tank gun to adopt a smoothbore barrel, and to introduce modern armor piercing shot, like the APFSDS. It uses long projectiles that are more powerful than its caliber suggests. The T-12 served as the primary towed anti-tank artillery in the Soviet and Bulgarian armies from the early 1960s to the late 1980s. History The T-12 was designed by the construction bureau of the Yurga Machine-Building Plant as a replacement for the BS-3 100 mm gun. The first serial examples were produced in 1955, but the T-12 entered service only in 1961. Its special feature was the use of a smoothbore gun. The T-12 was typically deployed in the anti-tank units of armored and motor rifle regiments to protect flanks against counter-attacks during rapid advances. In 1971 a new variant was introduced, T-12A or MT-12 "Rapira" (2A29). This has the same barrel, but has a redesigned carriage and gun shield. This allows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2S12 Sani
The 2S12 "Sani" ("sleigh") (GRAU index 2S12) is a 120 mm heavy mortar system used by the Russian Army and other former Soviet states. First fielded in 1981, the 2S12 is a continued development on the towed mortars first used in World War II. Design 2S12 is in fact the designator for the combination of the 2B11 "Sani" heavy mortar with its transport vehicle 2F510, a GAZ-66-15 4×4 truck. The 2B11 weighs nearly 200 kg (500 lb) when fully assembled, and thus must be mounted to the 2×1 wheeled chassis 2L81 and towed to the emplacement site by the truck. The GAZ-66 prime mover also transports the ammo load: 24 crates of 120mm HE mortar bombs, 2 bombs per crate, for a total of 48 available rounds. Once on site, it is unloaded from the transport chassis and manually emplaced by the crew of 5. It is the largest caliber indirect artillery employed at the battalion level. There is also an improved model, the 2B11M, that can fire the laser-guided round "Gran" with a range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
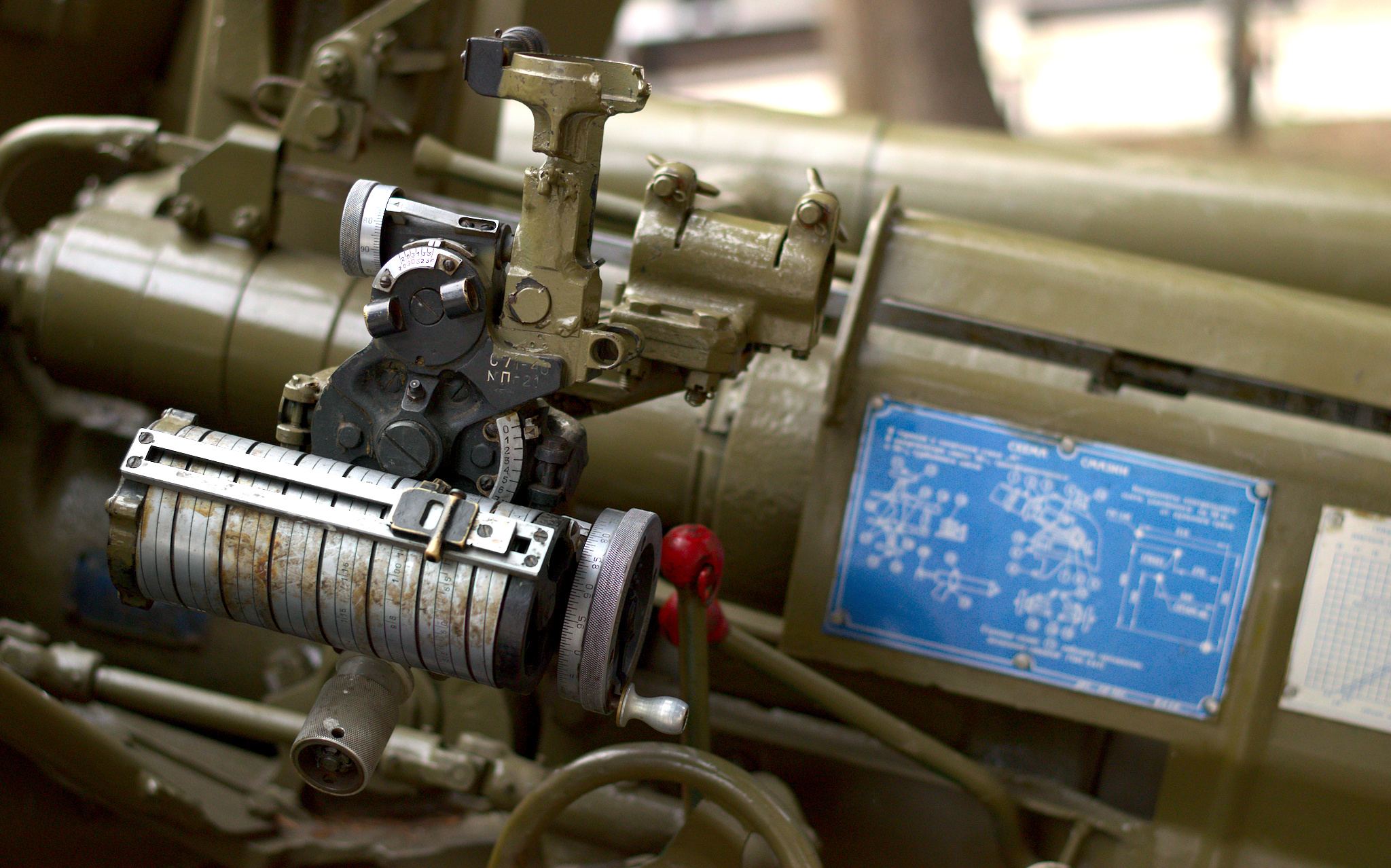
2S3 Akatsiya
The SO-152 (Russian: СО-152) is a Soviet 152.4 mm self-propelled gun developed in 1968, as a response to the American 155 mm M109 howitzer. Development began in 1967, according to the Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union from July 4, 1967. In 1968, the SO-152 was completed and in 1971 entered service. Its GRAU designation is 2S3 (2С3). The fighting vehicle also received the added designation ''Akatsiya'' (Акация), which is Russian for Acacia. Description The ''Akatsiya'' is armed with a 152.4 mm howitzer based on the Soviet 152.4 mm D-20 howitzer and is sometimes confused with the M109 self-propelled artillery. The artillery system was developed at the design bureau No. 9 of Sverdlovsk. The factory designation of the howitzer is D-22 and the GRAU designation, 2A33. The chassis was developed by Uraltransmash. The driver's and engine-transmission compartments are located in the front part of a hull, the fighting compartment with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tornado-G
The Tornado is a family of related multiple rocket launchers developed by NPO Splav for the Russian Ground Forces. Variants of the system, which include the Tornado-G and Tornado-S models, have different capabilities and different battlefield roles. Variants The 9A52-4 Tornado system is a lightweight rocket launcher. There are two other systems. A modular MLRS based on the MZKT-79306 truck, which can carry two BM-27 Uragan or BM-30 Smerch launcher modules, and one based on the Kamaz 6×6 truck. The "Tornado-G" system is an upgrade package for the existing BM-21 Grad. The Russian government ordered 36 new "Tornado-G" based on the Kamaz 6x6 chassis, instead of the old systems based on the Ural-4320 truck. Systems in the Tornado family: * 9A53-G Tornado (2 × 15; 1×40 122 mm Upgraded BM-21 Grad Multiple Rocket Launcher Module, based on a Kamaz Truck or on a Ural-4320). * 9A53-S Tornado (2 × 6; 2×4 300 mm Upgraded BM-30 Smerch Multiple Rocket Launcher Modules, based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_for_2S3_Akatsiya.jpg)
