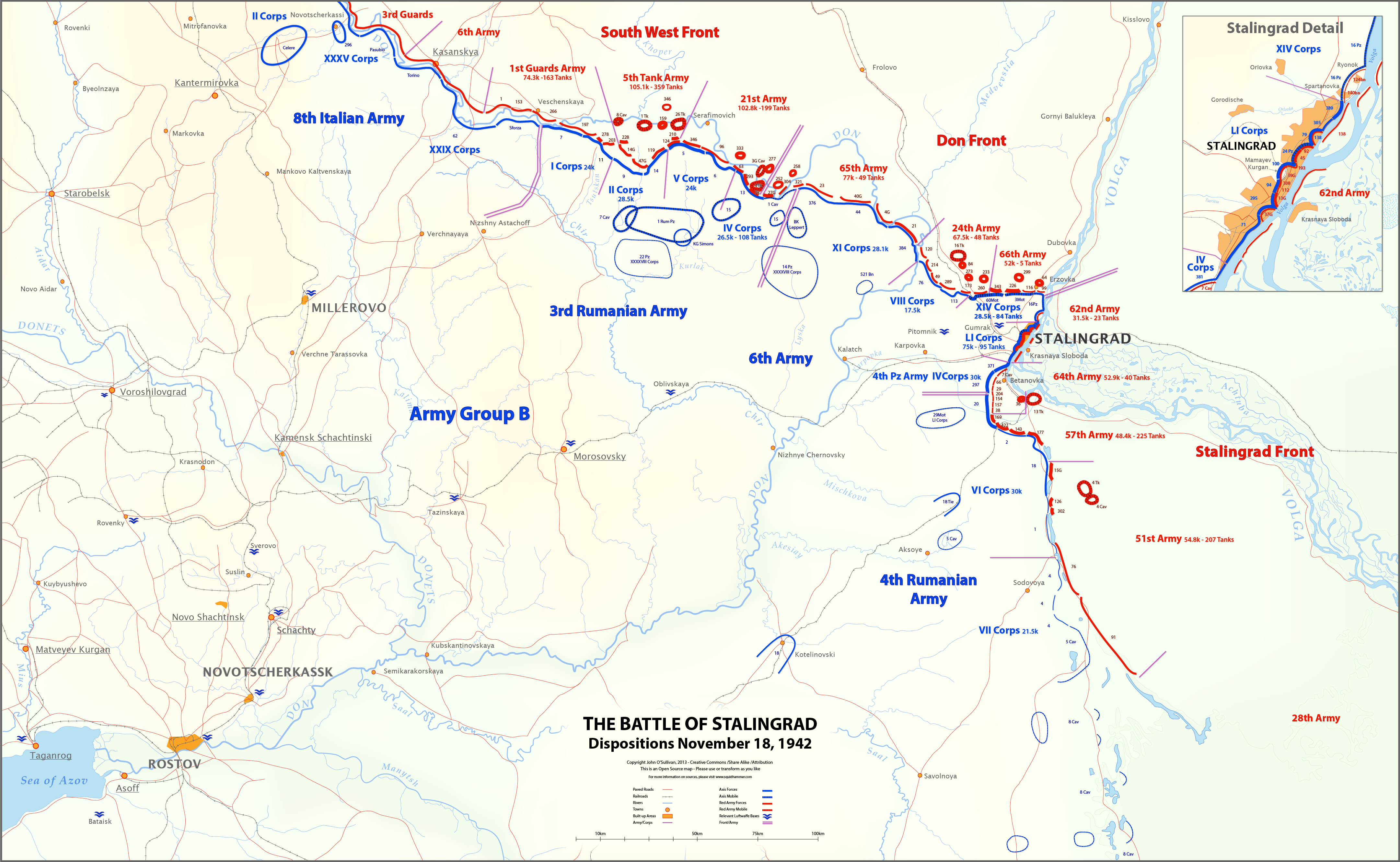
|
376th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 376th Infantry Division (german: 376. Infanterie-Division) was an infantry division of the German Army during World War II, active from 1942 to 1944 in two separate instances. The division was first formed in March 1942 in France and was sent to the Eastern Front, where it surrendered near the end of the Battle of Stalingrad. Reformed in the Netherlands in February 1943, the second 376th was also sent to the Eastern Front, where it was destroyed in fighting in Romania in August 1944. Operational history The 376th Infantry Division, part of the nineteenth wave of infantry divisions formed during the war, was formed near Angoulême in southwestern France on 21 March 1942 under the command of ''Generalleutnant'' Alexander Edler von Daniels. The division nominally fell within the responsibility of ''Wehrkreis'' VII (military district VII) and had a home station at Kempten. It included three infantry regiments: the 672nd, 673rd, and 767th, drawn respectively from the 337th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Army (Wehrmacht)
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the German Air Force, ''Luftwaffe'' (German Air Force). , the German Army had a strength of 62,766 soldiers. History Overview A German army equipped, organized, and trained following a single doctrine and permanently unified under one command in 1871 during the unification of Germany under the leadership of Prussia. From 1871 to 1919, the title ''German Army (German Empire), Deutsches Heer'' (German Army) was the official name of the German land forces. Following the German defeat in World War I and the end of the German Empire, the main army was dissolved. From 1921 to 1935 the name of the German land forces was the ''Reichswehr, Reichsheer'' (Army of the Empire) and from 1935 to 1945 the name ''German Army (We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
335th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 335th Infantry Division (german: 335. Infanterie-Division) was an infantry division of the German Army during the Second World War, active from 1940 to 1944. It saw active service in France and on the Eastern Front and was destroyed in fighting in Romania in August 1944. Operational history The 335th Infantry Division was formed in Konstanz in November 1940 under the command of ''Generalleutnant'' Max Dennerlein. The division nominally fell within the responsibility of Wehrkreis V. At its core were three infantry battalions transferred from the 298th Infantry Division while two battalions came from the 197th Infantry Division. The 87th Infantry Division, which had fought in the Battle of France, also transferred a battalion to the 335th. It was one of several static divisions raised for service in the occupied countries of Western Europe. It also had a strong Polish representation. In mid-1941, the 335th Infantry Division was posted to a position near the border betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Kissel
Hans Kissel (19 February 1897 – 30 November 1975) was a highly decorated Generalmajor in the Wehrmacht during World War II. He was also a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross. The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross was awarded to recognise extreme battlefield bravery or successful military leadership. Awards and decorations * Iron Cross (1914) ** 2nd Class ** 1st Class * Honour Cross of the World War 1914/1918 * Iron Cross (1939) ** 2nd Class ** 1st Class * Wound Badge (1939) ** in Black or Silver * Eastern Front Medal * German Cross in Gold (18 June 1942) * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 17 March 1944 as ''Oberst ''Oberst'' () is a senior field officer rank in several German-speaking and Scandinavian countries, equivalent to colonel. It is currently used by both the ground and air forces of Austria, Germany, Switzerland, Denmark, and Norway. The Swedish ...'' and commander of Grenadier-Regiment 683Fellgiebel 2000, p. 211. References Citations Bibliogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IV Army Corps (Wehrmacht)
IV Corps (IV. Armeekorps) was a corps level command of the German Army (Wehrmacht) before and during World War II. History The IV Army Corps was formed on 1 October 1934 in Wehrkreis IV (4th Military District) in Dresden by the expansion of the 4th Infantry Division of the Reichswehr. It was destroyed in the Battle of Stalingrad on 31 January 1943 and reformed on 20 July 1943. The Corps was again destroyed in August 1944 during the Soviet Jassy–Kishinev Offensive, and its commander killed. The Corps was redesignated as IV Panzer Corps on 10 October 1944 and as Panzer Corps Feldherrnhalle on 27 November 1944. Area of operations *Poland (September 1939 – May 1940) *France (May 1940 – June 1941) * Eastern Front, southern sector (June 1941 – October 1942) *Stalingrad (October 1942 – January 1943) * Eastern Front, southern sector (July 1943 – October 1944) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XIV Army Corps (Wehrmacht)
XIV Panzer Corps (also: XIV Army Corps or XIV. ''Armeekorps'') was a corps-level formation of the German Army which fought on both the Eastern Front and in the Italian Campaign. History The XIV Panzer Corps was originally formed as the XIV Motorised Corps in Magdeburg on 1 April 1938 to take command of units in the process of motorisation, where it was placed under the leadership of Gustav von Wietersheim. The Corps participated in the Invasion of Poland in 1939 where it fought in the Battle of Kock. The Corps later saw action in the Battle of France in 1940, as part of Panzer Group Kleist, where the 2nd Motorised Division, 13th Motorised Division and the 29th Motorised Division served under it. It was renamed the XIV Panzer Corps on 21 June 1942. In June 1941, it participated in Operation Barbarossa, where as part of Panzer Group 1, it served with Army Group South on the southern sector of the eastern front, advancing via Lviv, Ternopil and Zhytomyr to Kremenchuk and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Uranus
Operation Uranus (russian: Опера́ция «Ура́н», Operatsiya "Uran") was the codename of the Soviet Red Army's 19–23 November 1942 strategic operation on the Eastern Front of World War II which led to the encirclement of Axis forces in the vicinity of Stalingrad: the German Sixth Army, the Third and Fourth Romanian armies, and portions of the German Fourth Panzer Army. The Red Army carried out the operation at roughly the midpoint of the five-month long Battle of Stalingrad, aiming to destroy German forces in and around Stalingrad. Planning for Operation Uranus had commenced in September 1942, and developed simultaneously with plans to envelop and destroy German Army Group Center (Operation Mars) and German forces in the Caucasus. Due to the length of the front lines created by the German 1942 summer offensive, which had aimed at taking the Caucasus oil fields and the city of Stalingrad, German and other Axis forces were over-extended. The German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XI Army Corps (Wehrmacht)
German XI. Corps (XI. Armeekorps) was a corps in the German Army during World War II. Commanders * Artillery General (''General der Artillerie'') Emil Leeb, 1 September 1939 – 1 March 1940 * Infantry General (''General der Infanterie'') Joachim von Kortzfleisch, 1 March 1940 – 6 October 1941 * Infantry General (''General der Infanterie'') Eugen Ott, 6 October 1941 – 10 December 1941 * Infantry General (''General der Infanterie'') Joachim von Kortzfleisch, 10 December 1941 – 1 June 1942 * Colonel-General (''Generaloberst'') Karl Strecker, 1 June 1942 – 2 February 1943 After reformation * Colonel-General (''Generaloberst'') Erhard Raus, 10 February 1943 – 1 November 1943 * Artillery General (''General der Artillerie'') Wilhelm Stemmermann, 5 December 1943 – 18 February 1944 * Infantry General (''General der Infanterie'') Rudolf von Bünau, 20 March 1944 – 16 March 1945 * Artillery General (''General der Artillerie'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VIII Army Corps (Wehrmacht)
VIII Army Corps (VIII. Armeekorps) was a corps in the German Army during World War II. It was destroyed during the Battle of Stalingrad and reformed in mid-1943. Commanders * Cavalry General (''General der Kavallerie'') Paul Ludwig Ewald von Kleist, 21 May 1935 – 3 February 1938 * Infantry General (''General der Infanterie'') Ernst Busch, 3 February 1938 – 25 October 1939 * Colonel-General (''Generaloberst'') Walter Heitz, 25 October 1939 – 31 January 1943 After reformation * Infantry General (''General der Infanterie'') Gustav Höhne, 20 July 1943 – 1 April 1944 * Lieutenant General (''Generalleutnant'') Johannes Block, 1 April 1944 – 15 April 1944 * Lieutenant General (''Generalleutnant'') Hans Schlemmer, 15 April 1944 – 12 May 1944 * Infantry General (''General der Infanterie'') Gustav Höhne, 12 May 1944 – 10 September 1944 * Artillery General (''General der Artillerie'') Walter Hartmann, 10 September 1944 - 19 March ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don River (Russia)
The Don ( rus, Дон, p=don) is the fifth-longest river in Europe. Flowing from Central Russia to the Sea of Azov in Southern Russia, it is one of Russia's largest rivers and played an important role for traders from the Byzantine Empire. Its basin is between the Dnieper basin to the west, the lower Volga basin immediately to the east, and the Oka basin (tributary of the Volga) to the north. Native to much of the basin were Slavic nomads. The Don rises in the town of Novomoskovsk southeast of Tula (in turn south of Moscow), and flows 1,870 kilometres to the Sea of Azov. The river's upper half ribbles (meanders subtly) south; however, its lower half consists of a great eastern curve, including Voronezh, making its final stretch, an estuary, run west south-west. The main city on the river is Rostov-on-Don. Its main tributary is the Seversky Donets, centred on the mid-eastern end of Ukraine, thus the other country in the overall basin. To the east of a series of thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharkov
Kharkiv ( uk, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest city and municipality in Ukraine.Kharkiv "never had eastern-western conflicts" '''' (23 October 2014) Located in the northeast of the country, it is the largest city of the historic region. Kharkiv is the of |
Case Blue
Case Blue (German: ''Fall Blau'') was the German Armed Forces' plan for the 1942 strategic summer offensive in southern Russia between 28 June and 24 November 1942, during World War II. The objective was to capture the oil fields of the Caucasus for two purposes: to enable the Germans to re-supply their low fuel stock and also to deny their use to the Soviet Union, thereby bringing about the complete collapse of the Soviet war effort. After Operation Barbarossa failed to destroy the Soviet Union as a political and military threat the previous year, Adolf Hitler, the ''Führer'' of Nazi Germany, recognised that Germany was now locked in a war of attrition, and he was also aware that Germany was running low on fuel supply and would not be able to continue attacking deeper into enemy territory without more stock. With this in mind, Hitler ordered for the preparation of offensive plans for summer 1942 to secure the Soviet oil fields in the Caucasus. The operation involved a two-pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th Army (Wehrmacht)
The 6th Army was a field army unit of the German Wehrmacht during World War II (1939–1945). It was widely remembered for being the most highly decorated German army unit until its defeat by the Red Army at the Battle of Stalingrad in the winter of 1942–1943. It also acquired a reputation for the war crimes (such as the massacre of more than 30,000 Jews at Babi Yar in September 1941) that it committed under the command of Field Marshal Walther von Reichenau during Operation Barbarossa. Western campaigns Originally numbered as the 10th Army, this Army formed on 10 October 1939 with General Walther von Reichenau in command. Its primary mission was to guard the western defenses of Germany against British and French attacks during the Polish campaign. During the invasion of the Low Countries the 6th Army saw active service linking up with paratroopers and destroying fortifications at Eben Emael, Liège, and Namur during the Battle of Belgium. The 6th Army was then involved in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |