|
36th Infantry Division
36th Division or 36th Infantry Division may refer to: Infantry divisions * 36th Division (German Empire) * 36th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht) * 36th Infantry Division Forlì, Italy * 36th Infantry Division (Poland) * 36th Rifle Division (Soviet Union) * 36th Guards Rifle Division, Soviet Union, fought in the Battle of Stalingrad * 36th (Ulster) Division, British Army, World War I * 36th Infantry Division (United Kingdom), World War II * 36th Infantry Division (United States) *36th Division (Imperial Japanese Army) Cavalry divisions * 36th Division (National Revolutionary Army), Republic of China Armoured divisions * 36th Division (Israel) * 36th Tank Division (Soviet Union), with 17th Mechanized Corps, June 1941 See also * 36th Brigade (other) * 36th Regiment (other) * 36 Squadron (other) 36 Squadron or 36th Squadron may refer to: *No. 36 Squadron RAF *No. 36 Squadron RAAF United States * 36th Airlift Squadron * 36th Electronic Warfare Squadron, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
36th Division (German Empire)
The 36th Division (''36. Division'') was a unit of the Prussian/German Army. It was formed on April 1, 1890, and was headquartered in Danzig (now Gdańsk, Poland). The division was subordinated in peacetime to the XVII Army Corps (''XVII. Armeekorps''). The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I. The division was recruited primarily in West Prussia. Combat chronicle The 36th Infantry Division began World War I on the Eastern Front. It fought in the battles of Gumbinnen and Tannenberg, and in the First Battle of the Masurian Lakes. In 1915, it participated in the Gorlice-Tarnów Offensive. In October 1915, it was transferred to the Western Front. In 1916, it fought in the Battle of the Somme. In 1917, it participated in the Battle of Arras and the Battle of Passchendaele. In 1918, the division fought in the German spring offensive, including the Battle of St. Quentin, also known as the First Battle of the Somme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
36th Infantry Division (United States)
The 36th Infantry Division ("Arrowhead"), also known as the "Panther Division", "Lone Star Division", history.army.mil, last updated 20 May 2011, last accessed 23 January 2017 "The Texas Army", or the "T-patchers", is an of the and part of the Texas Army National Guard. It was organized during |
36th Brigade (other)
36th Brigade or 36th Infantry Brigade may refer to: * 36 Canadian Brigade Group of the Canadian Army * 36th Indian Brigade of the British Indian Army in the First World War * 36th Indian Infantry Brigade of the British Indian Army in the Second World War * 36th Engineer Brigade (United States) of the United States Army * Task Force Mustang, formally known as the 36th Combat Aviation Brigade, of the United States Army * 36th Separate Guards Motor Rifle Brigade of the Russian Army * 36th Separate Marine Brigade of the Ukrainian Naval Infantry ;United Kingdom * 36th Infantry Brigade (United Kingdom) * Artillery Brigades ** 36th Brigade Royal Field Artillery XXXVI Brigade, Royal Field Artillery was a brigade of the Royal Field Artillery which served in the First World War World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in his ... See also * 36th Division (other) * 36th Regiment (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th Mechanized Corps (Soviet Union)
The 17th Mechanized Corps (Military Unit Number 9406) was a mechanised unit of the Red Army. Formed in March 1941, the corps was destroyed in the Battle of Białystok–Minsk and reduced in size to the 147th Tank Brigade. History Formation The 17th Mechanized Corps was formed in March 1941 at Baranovichi under the command of Mikhail Petrovich Petrov. It was part of the Western Special Military District's reserve at Slonim. The corps included the 27th and 36th Tank Divisions, and the 209th Motorized Division. The 17th Mechanized Corps was a cadre-strength formation equipped with only 36 tanks, which included 24 BT tanks, a T-26 tank, and eleven T-37, T-38, and T-40 amphibious tanks. Battle of Białystok–Minsk Following the German invasion of the Soviet Union, the 17th Mechanized corps fought in the Battle of Białystok–Minsk. The corps was initially stationed in the rear but was moved forward to Baranovichi to stop the German advance. On 26 June it fought in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
36th Division (Israel)
The 36th Armored Division, also known as the Ga'ash Formation ("Rage"), is the largest regular-service armored division in the Armored Corps of the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). It was subordinate to the Northern Regional Command until February 2014. The division was established in September 1954 and until 1958 was led by ''Aluf'' Avraham Yoffe. At the time, divisional commands were mission-based commands without organic forces, but rather with troops apportioned according to given missions. It was led by ''Aluf'' Zvi Zamir from 1958 until he was succeeded by ''Aluf'' Uzi Narkiss in 1962, who led until 1965. In the years 1965–1969, it was led by ''Aluf'' Elad Peled. During the 1967 Six-Day War, the division led the battles in the northern West Bank, commanding the Barak Armored Brigade (then the 45th Armored Brigade), the 37th Brigade and forces from the 1st Brigade. Later, it oversaw the occupation of the southern Golan Heights. After the war, from 1969 to 1972, the division wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
36th Division (National Revolutionary Army)
The New 36th Division was a cavalry division in the National Revolutionary Army. It was created in 1932 by the Kuomintang for General Ma Zhongying, who was also its first commander. It was made almost entirely out of Hui Muslim troops, all of its officers were Hui, with a few thousand Uighurs forced conscripts in the rank and file. It was commonly referred to as the "KMT 36th Division", or "Tungan 36th Division". Original organization General Ma Zhongying, a Muslim who had trained under Chiang Kai-shek at Whampoa Military Academy in Nanjing in 1929, was the new 36th Division commander. Kamal Kaya Efendi, a Turk and a former Ottoman military officer was chief-of-staff to Ma Zhongying. The 1st Brigade was commanded by General Ma Ju-lung. The 2nd Brigade was commanded by General Ma Sheng-kuei. Cavalry regiments were divided into 2,000 men each, by horse color, black, brown, or white. Infantry then followed cavalry. Su Chin-shou was General Ma Zhancang's chief of staff. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
36th Division (Imperial Japanese Army)
The was an infantry division of the Imperial Japanese Army. The division was formed in 1939 and was disbanded in 1945. Its call sign was the . The ''36th Division'' was activated at Hirosaki 7 February 1939, simultaneously with 32nd, 33rd, 34th, 35th and 37th divisions. Action The ''36th division'' was initially assigned to 1st army garrison duty in North China. The division was assigned to 2nd army, ordered to move south in October 1943 and reformed to seaborne division 5 November 1943, with infantry regiments absorbing artillery and engineering units. Soon the ''36th division'' has departed Shanghai, briefly stopped at Halmahera and finally landed in Sarmi on New Guinea island. The majority of the 222nd infantry regiment was sent to Biak (forming ''Biak Detachment'') where it was annihilated in Battle of Biak by 17 August 1944. On New Guinea, the US forces have landed in Aitape 22 April 1944 and in Sarmi 17 May 1944, squeezing ''36th division'' to the coastal strip south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
36th Infantry Division (United Kingdom)
The 36th Indian Infantry Division was an infantry division of the Indian Army during the Second World War. The division was subsequently redesignated as a British Army formation, the 36th Infantry Division in September 1944. It served in India and during the Burma Campaign. After the end of the war it was disbanded and its remaining British units were transferred to the British 2nd Infantry Division. History 36th Indian Division The division was formed in India on 15 December 1942. Its constituent formations were the 29th Infantry Brigade Group (under command from 26 January 1943), which had already fought as an independent brigade in the Battle of Madagascar, and 72nd Indian Infantry Brigade confusingly composed of entirely British combat units. 72nd Indian Infantry Brigade was re-designated the new 72nd Infantry Brigade (the previous 72 Inf Bde had become 5th Parachute Brigade on 28 April 1943). Most of the division's engineer, medical and service units were Indian. The div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
36th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 36th Infantry Division was a German infantry formation of World War II. It was formed in Kaiserslautern on 1 October 1936. During World War II it was mobilized in August 1939, as part of the first wave. It was later reorganized and re-designated the 36th Infantry Division (mot) in November 1940. It was then de-motorized, reorganized and re-designated the 36th Infantry Division on 1 May 1943. The division was destroyed at Bobruysk in June 1944 during the Soviet Operation Bagration. It was reformed on 3 August 1944 as the 36th Grenadier Division and renamed the 36th Volksgrenadier Division in October 1944. Operational history The division was formed in October 1936 with men from Kaiserslautern, and consisted largely of Bavarian Palatinates. France During the German invasion of France the 36th Infantry Division was part of Army Group A's 16th Army, where it served with VII Corps. Crossing into France through the Chiers, the corps' objective was a commune by the name of La Fert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
36th (Ulster) Division
The 36th (Ulster) Division was an infantry division of the British Army, part of Lord Kitchener's New Army, formed in September 1914. Originally called the ''Ulster Division'', it was made up of mainly members of the Ulster Volunteer Force, who formed thirteen additional battalions for three existing regiments: the Royal Irish Fusiliers, the Royal Irish Rifles and the Royal Inniskilling Fusiliers. However, regular Officers and Soldiers and men from all around the United Kingdom made up the strength of the Division. The division served from October 1915 on Western Front as a formation of the British Army during the Great War. The division's insignia was the Red Hand of Ulster. History Formation The Ulster Volunteers were a unionist militia founded in 1912 to block Home Rule for Ireland. In 1913 they organised themselves into the Ulster Volunteer Force to give armed resistance to the prospective Third Home Rule Act (enacted in 1914). Many Ulster Protestants feared being gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
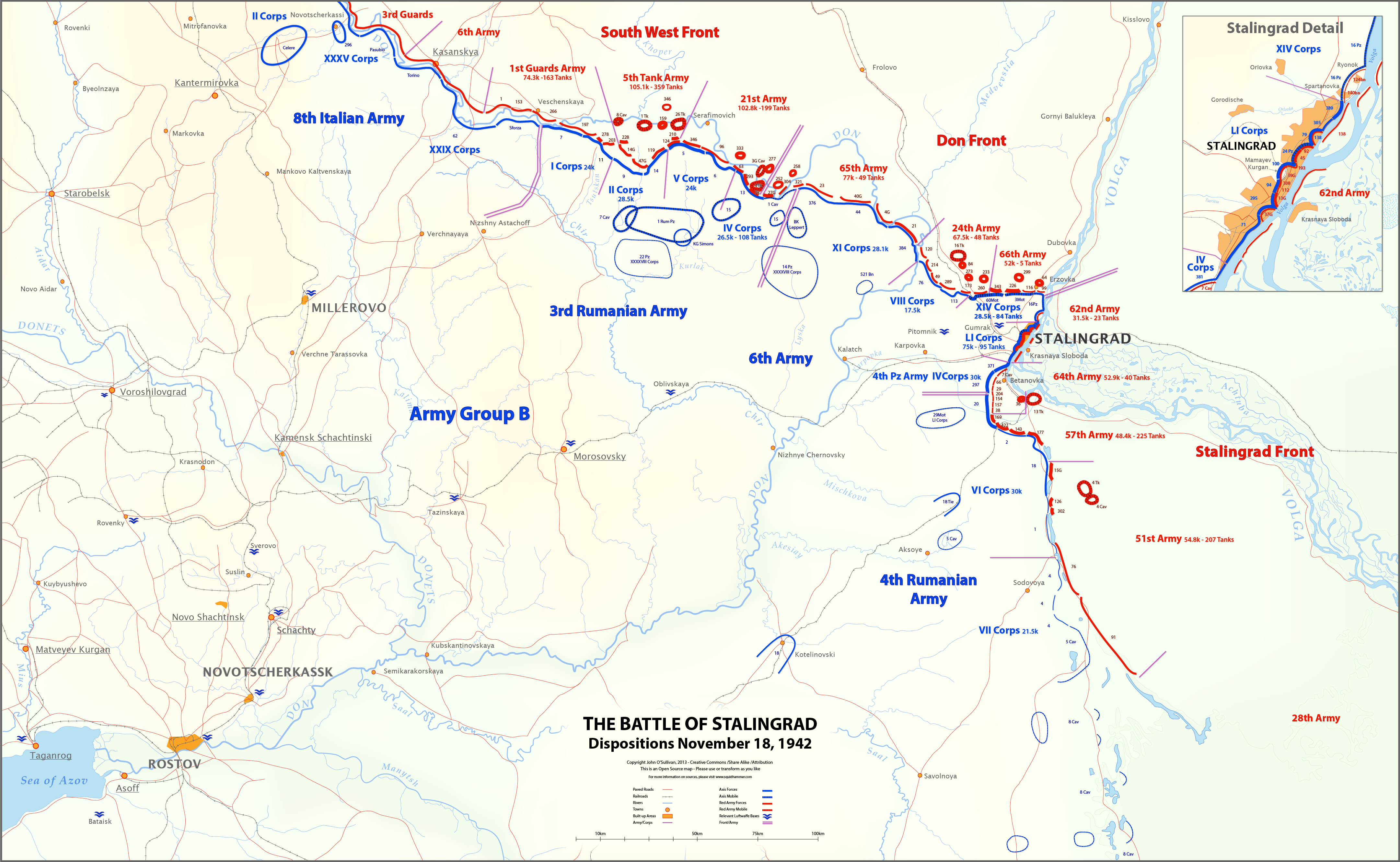
Soviet Order Of Battle For The Battle Of Stalingrad
The Soviet order of battle for Operation Uranus details the combat units of the Soviet forces that fought in Operation Uranus, the Soviet strategic counteroffensive that led to the encirclement of the German troops in Stalingrad. The order of battle lists units present on 19 November 1942, the day the operation began, from north to south. High command Stavka representatives * Army General G.K. Zhukov * Colonel-General of Artillery N.N. Voronov * Colonel-General A.M. VasilevskyBeevor (1998) Voronezh Front The Voronezh Front was commanded by Colonel General Filipp Golikov and included four field armies. Its massed armor component was the 25th Tank Corps. Air support was provided by the single division and regiment from 2nd Air Army that were kept under front control during the operation while the rest of the air army was placed under Southwestern Front control. * 38th Army (Lieutenant General Nikandr Chibisov) ** 161st Rifle Division ** 167th Rifle Division ** 237th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |