|
349th Night Fighter Squadron
The 349th Night Fighter Squadron (349th NFS) is an inactive United States Air Force unit which specialized in training airmen to utilize night fighters as nighttime interceptors. Its last assignment was with the 481st Night Fighter Operational Training Group, based at Hammer Field, California. First activated in October 1942, the unit was inactivated on 31 March 1944. The squadron was one of the first dedicated Night Fighter Operational Training Squadron of the Air Force. The squadron trained newly activated night fighter squadrons who were deployed overseas into combat until its inactivation in March 1944 due to a re-alignment of training unit designations.Northrop P-61 Black Widow—The Complete History and Combat Record, Garry R. Pape, John M. Campbell and Donna Campbell, Motorbooks International, 1991. History The squadron was formed in October 1942 from elements of the 81st Fighter Squadron as part of the Army Air Force School of Applied Tactics (AAFSAT) Fighter Command S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
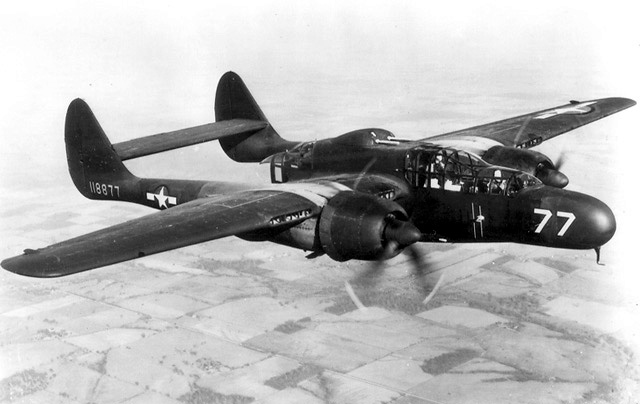
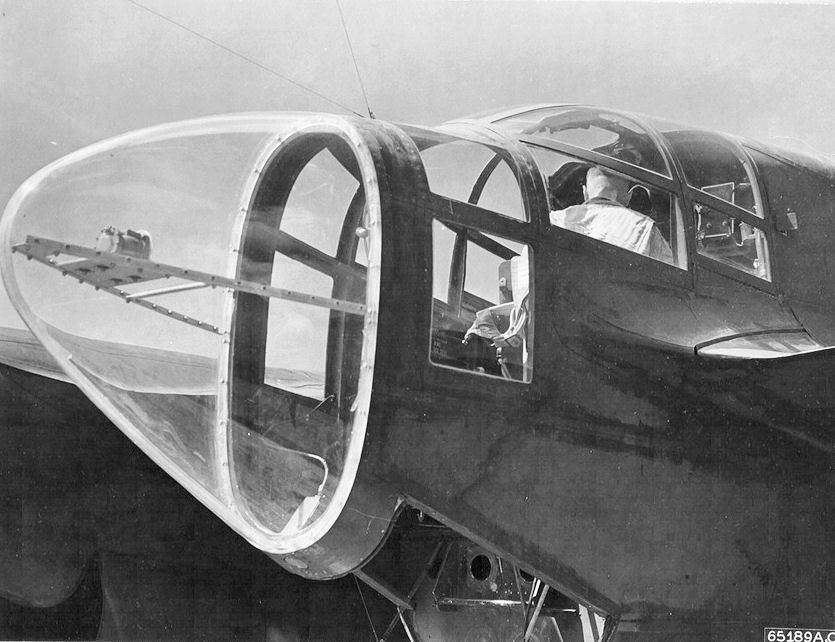
P-61 Black Widow
The Northrop P-61 Black Widow is a twin-engine United States Army Air Forces fighter aircraft of World War II. It was the first operational U.S. warplane designed as a night fighter, and the first aircraft designed specifically as a night fighter. Named for the North American spider ''Latrodectus mactans'', it was an all-metal, twin-engine, twin-boom design armed with four forward-firing 20 mm (.79 in) Hispano M2 autocannon in the lower fuselage, and four M2 Browning machine guns in a dorsal gun turret. Developed during the war, the first test flight was made on May 26, 1942, with the first production aircraft rolling off the assembly line in October 1943. Although not produced in the large numbers of its contemporaries, the Black Widow was operated effectively as a night fighter by United States Army Air Forces squadrons in the European Theater, Pacific Theater, China Burma India Theater, and Mediterranean Theater during World War II. It replaced earlier British-d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
481st Night Fighter Operational Training Group
The 481st Night Fighter Operational Training Group (481 NFOTG) was a unit of the United States Army Air Forces. It was inactivated on 31 March 1944 at Hammer Field, California. The group was the primary night fighter Operational Training Unit (OTU)/Replacement Training Unit (RTU) of the Army Air Forces during World War II. Its mission was to train either new graduates of Training Command advanced flying schools or transition experienced pilots into the P-61 Black Widow night fighter. It trained them in the flight characteristics of the aircraft and also night fighter interceptor techniques prior to the operational squadrons or replacement pilots being deployed to one of the overseas combat theaters. History Origins Specialized training in night fighter interceptor tactics began in March 1942 upon the return of Air Corps observers from England prior to the United States' entry into World War II. During World War I, the 1st Pursuit Group 185th Aero Squadron had flown night inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operational - Replacement Training Units
Operational Training Units (OTU) and Replacement Training Units (RTU) were training organizations of the United States Army Air Forces during World War II. Unlike the schools of the Army Air Forces Training Command (AAFTC), OTU-RTU units were operational units of the four domestic numbered air forces along with I Troop Carrier Command and Air Transport Command, with the mission of final phase training new pilots or crews. Most were disbanded in the Spring of 1944 and replaced by combat crew replacement centers assigned to base units. History When the Army Air Corps began its great expansion program in 1939, no provision for operational training existed outside the combat groups themselves. Graduates of the flying schools were assigned either to fill the requirements of existing combat squadrons or to round out the cadre taken from an older unit to form a new one. Each combat squadron was responsible for training its own personnel in order to meet proficiency standards set by trai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YP-61 Black Widow
The Northrop P-61 Black Widow is a twin-engine United States Army Air Forces fighter aircraft of World War II. It was the first operational U.S. warplane designed as a night fighter, and the first aircraft designed specifically as a night fighter. Named for the North American spider ''Latrodectus mactans'', it was an all-metal, twin-engine, twin-boom design armed with four forward-firing 20 mm (.79 in) Hispano M2 autocannon in the lower fuselage, and four M2 Browning machine guns in a dorsal gun turret. Developed during the war, the first test flight was made on May 26, 1942, with the first production aircraft rolling off the assembly line in October 1943. Although not produced in the large numbers of its contemporaries, the Black Widow was operated effectively as a night fighter by United States Army Air Forces squadrons in the European Theater, Pacific Theater, China Burma India Theater, and Mediterranean Theater during World War II. It replaced earlier British- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-18 Bolo
The Douglas B-18 Bolo is an American heavy bomber which served with the United States Army Air Corps and the Royal Canadian Air Force (as the Digby) during the late 1930s and early 1940s. The Bolo was developed by the Douglas Aircraft Company from their DC-2, to replace the Martin B-10. By 1940 standards, it was slow, had an inadequate defensive armament, and carried too small a bomb load. A B-18 was one of the first USAAF aircraft to sink a German U-boat, on 22 August 1942 in the Caribbean. By 1942, surviving B-18s were relegated to antisubmarine, training and transport duties. Design and development In 1934, the United States Army Air Corps requested for a twin-engine heavy bomber with double the bomb load and range of the Martin B-10 then entering service. During the evaluation at Wright Field the following year, Douglas offered its DB-1. It was competing against the Boeing Model 299 (later developed into the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress) and Martin 146. While the Boeing de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Burma India Theater
China Burma India Theater (CBI) was the United States military designation during World War II for the China and Southeast Asian or India–Burma (IBT) theaters. Operational command of Allied forces (including U.S. forces) in the CBI was officially the responsibility of the Supreme Commanders for South East Asia or China. However, US forces in practice were usually overseen by General Joseph Stilwell, the Deputy Allied Commander in China; the term "CBI" was significant in logistical, material and personnel matters; it was and is commonly used within the US for these theaters. U.S. and Chinese fighting forces in the CBI included the Chinese Expeditionary Force, the Flying Tigers, transport and bomber units flying the Hump, including the Tenth Air Force, the 1st Air Commando Group, the engineers who built the Ledo Road, the 5307th Composite Unit (Provisional), popularly known as "Merrill's Marauders", and the 5332d Brigade, Provisional or 'Mars Task Force', which assumed the Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asiatic-Pacific Theater
The Asiatic-Pacific Theater was the theater of operations of U.S. forces during World War II in the Pacific War during 1941–1945. From mid-1942 until the end of the war in 1945, two U.S. operational commands were in the Pacific. The Pacific Ocean Areas (POA), divided into the Central Pacific Area, the North Pacific Area and the South Pacific Area, were commanded by Fleet Admiral Chester W. Nimitz, Commander-in-Chief Pacific Ocean Areas. The South West Pacific Area (SWPA) was commanded by General of the Army Douglas MacArthur, Supreme Allied Commander South West Pacific Area. During 1945, the United States added the United States Strategic Air Forces in the Pacific, commanded by General Carl A. Spaatz. Because of the complementary roles of the United States Army and the United States Navy in conducting war, the Pacific Theater had no single Allied or U.S. commander (comparable to General of the Army Dwight D. Eisenhower in the European Theater of Operations). No actual comma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IV Fighter Command
The IV Fighter Command is a disbanded United States Air Force unit. It was activated under Fourth Air Force at March Field, California in June 1941, when it replaced a provisional organization. It was responsible for training fighter units and for the air defense of the southern portion of the Pacific Coast. Following the attack on Pearl Harbor, the command's units were placed on alert. In 1942, its air defense responsibility was expanded to include the entire Pacific coast of the continental United States and the command moved its headquarters from southern California to Oakland Airport, California, which was more centrally located. As the threat to the Pacific decreased, it was disbanded on 31 March 1944. History Background GHQ Air Force (GHQ AF) had been established with two major combat functions, to maintain a striking force against long range targets, and the air defense of the United States. In the spring of 1941, the War Department established four strategic defense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Air Force School Of Applied Tactics
The Army Air Forces Tactical Center was a major command and military training organization of the United States Army Air Forces during World War II. It trained cadres from newly formed units in combat operations under simulated field conditions around which new combat groups would be formed. It was established as the Army Air Forces School of Applied Tactics (AAFSAT) in 1942 and redesignated the following year. In addition to its training function, the school also developed as a tactical doctrine development center, assuming the functions formerly assigned the Air Corps Tactical School. In June 1946, the center became the Army Air Forces Proving Ground Command. History Background As the threat of entry of the United States into World War II increased, the United States Army decided to close the Air Corps Tactical School in 1940 in order to use its experienced personnel at headquarters, and in expanded training and tactical units. As a result, the responsibility for the devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
81st Fighter Squadron
The 81st Fighter Squadron (81 FS) is a training squadron of the United States Air Force's Air Education and Training Command (AETC), stationed at Moody Air Force Base, Georgia. It is a Geographically Separate Unit of the 14th Operations Group, 14th Flying Training Wing at Columbus Air Force Base, Mississippi, and operates the A-29B Super Tucano aircraft conducting close air support training for allied nations. The 81st FS is AETC's only combat mission ready fighter squadron. History World War II The squadron was first activated on 15 January 1942, at Key Field, Mississippi, as the 81st Pursuit Squadron flying the P-40 Warhawk. The squadron was assigned to the 50th Fighter Group to replace the 11th Pursuit Squadron, which had been transferred after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor to reinforce the air defenses of Alaska. In May 1942 the 50th Group was assigned to the Fighter Command School of the Army Air Forces School of Applied Tactics and the 81st became the 81st Fight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammer Field
Fresno Yosemite International Airport is a joint military/public airport in Fresno, California, United States. It is the primary commercial airport for the San Joaquin Valley and three national parks: Yosemite, Sequoia and Kings Canyon. It offers scheduled passenger flights to several major airline hubs in the United States and international service to Mexico. The facility opened in June 1942 as Hammer Field, a military airfield. The airport is owned and operated by the city of Fresno and operates two runways on a property spanning . Its airport code 'FAT' stands for Fresno Air Terminal, a former name for the airport. Due to its central location within the state, the airport is home to several military, law enforcement, firefighting, and medical air units. The Fresno Air National Guard Base on the southeast corner of the airport is home to the 144th Fighter Wing of the California Air National Guard. The Fresno Air Attack Base on the eastern side of the airport supports aeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interceptor Aircraft
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are capable of being or are employed as both ‘standard’ air superiority fighters and as interceptors are sometimes known as fighter-interceptors. There are two general classes of interceptor: light fighters, designed for high performance over short range; and heavy fighters, which are intended to operate over longer ranges, in contested airspace and adverse meteorological conditions. While the second type was exemplified historically by specialized night fighter and all-weather interceptor designs, the integration of mid-air refueling, satellite navigation, on-board radar and beyond visual range (BVR) missile systems since the 1960s has allowed most frontline fighter designs to fill the roles once reserved for specialised night/all-weathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)




.jpg)