|
3D Printing Speed
3D printing speed measures the amount of manufactured material over a given time period (\text / \text), where the unit of time is measured in Seconds, and the unit of manufactured material is typically measured in units of either kg, mm or cm3, depending on the type of additive manufacturing technique. The following table compares the speeds of commercially relevant 3D printing technologies. 3D printing speed refers to only the build stage, a subcomponent of the entire 3D printing process. However, the entire process spans from pre-processing to post-processing stages. The time required for printing a completed part from a data file (. stl or .obj) is calculated as the sum of time for the following stages: #The pre-processing stage, which spans the preparation process of both part and printer. This is required before the actual printing starts. It is calculated as the sum of the time required for the following processes: #* Positioning and orienting of the part to be printed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Printing
3D printing or additive manufacturing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer control, with material being added together (such as plastics, liquids or powder grains being fused), typically layer by layer. In the 1980s, 3D printing techniques were considered suitable only for the production of functional or aesthetic prototypes, and a more appropriate term for it at the time was rapid prototyping. , the precision, repeatability, and material range of 3D printing have increased to the point that some 3D printing processes are considered viable as an industrial-production technology, whereby the term ''additive manufacturing'' can be used synonymously with ''3D printing''. One of the key advantages of 3D printing is the ability to produce very complex shapes or geometries that would be otherwise impossible to construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
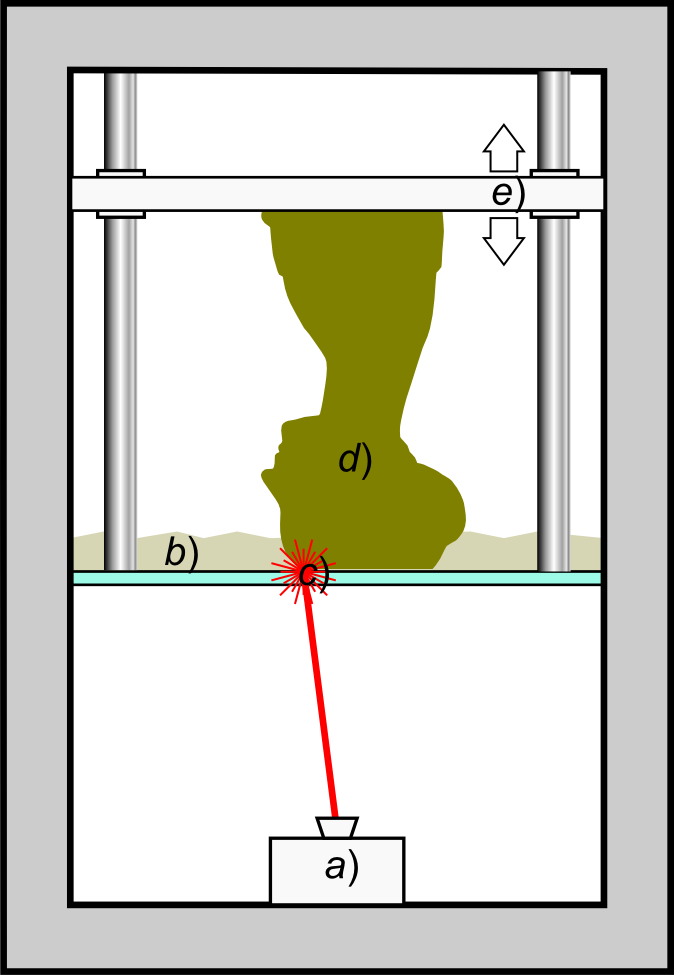
Stereolithography
Stereolithography (SLA or SL; also known as vat photopolymerisation, optical fabrication, photo-solidification, or resin printing) is a form of 3D printing technology used for creating models, prototypes, patterns, and production parts in a layer by layer fashion using photochemical processes by which light causes chemical monomers and oligomers to cross-link together to form polymers. U.S. Patentbr>4,575,330(“Apparatus for Production of Three-Dimensional Objects by Stereolithography”) Those polymers then make up the body of a three-dimensional solid. Research in the area had been conducted during the 1970s, but the term was coined by Chuck Hull in 1984 when he applied for a patent on the process, which was granted in 1986. Stereolithography can be used to create prototypes for products in development, medical models, and computer hardware, as well as in many other applications. While stereolithography is fast and can produce almost any design, it can be expensive. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fused Filament Fabrication
Fused filament fabrication (FFF), also known as fused deposition modeling (with the trademarked acronym FDM), or called ''filament freeform fabrication'', is a 3D printing process that uses a continuous filament of a thermoplastic material. Filament is fed from a large spool through a moving, heated printer extruder head, and is deposited on the growing work. The print head is moved under computer control to define the printed shape. Usually the head moves in two dimensions to deposit one horizontal plane, or layer, at a time; the work or the print head is then moved vertically by a small amount to begin a new layer. The speed of the extruder head may also be controlled to stop and start deposition and form an interrupted plane without stringing or dribbling between sections. "Fused filament fabrication" was coined by the members of the RepRap project to give an acronym (FFF) that would be legally unconstrained in its use. Fused filament printing is now the most popular process (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STL (file Format)
STL is a file format native to the stereolithography CAD software created by 3D Systems. STL has several backronyms such as "Standard Triangle Language" and "Standard Tessellation Language". This file format is supported by many other software packages; it is widely used for rapid prototyping, 3D printing and computer-aided manufacturing. STL files describe only the surface geometry of a three-dimensional object without any representation of color, texture or other common CAD model attributes. The STL format specifies both ASCII and binary representations. Binary files are more common, since they are more compact. An STL file describes a raw, unstructured triangulated surface by the unit normal and vertices (ordered by the right-hand rule) of the triangles using a three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system. In the original specification, all STL coordinates were required to be positive numbers, but this restriction is no longer enforced and negative coordinates are commonl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object File
An object file is a computer file containing object code, that is, machine code output of an assembler or compiler. The object code is usually relocatable, and not usually directly executable. There are various formats for object files, and the same machine code can be packaged in different object file formats. An object file may also work like a shared library. In addition to the object code itself, object files may contain metadata used for linking or debugging, including: information to resolve symbolic cross-references between different modules, relocation information, stack unwinding information, comments, program symbols, debugging or profiling information. Other metadata may include the date and time of compilation, the compiler name and version, and other identifying information. The term "object program" dates from at least the 1950s: A computer programmer generates object code with a compiler or assembler. For example, under Linux, the GNU Compiler Collection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAD Model
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software are helpful in protecting products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used. Its use in designing electronic systems is known as ''electronic design automation'' (''EDA''). In mechanical design it is known as ''mechanical design automation'' (''MDA''), which includes the process of creating a technical drawing with the use of computer software. CAD software for mechanical design uses either vector-based graphics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Slicing (1)
Adaptation, in biology, is the process or trait by which organisms or population better match their environment Adaptation may also refer to: Arts * Adaptation (arts), a transfer of a work of art from one medium to another ** Film adaptation, a story from another work, adapted into a film ** Literary adaptation, a story from a literary source, adapted into another work ** ** Theatrical adaptation, a story from another work, adapted into a play * ''Adaptation'' (film), a 2002 film by Spike Jonze * "Adaptation" (''The Walking Dead''), a television episode *''Adaptation'', a 2012 novel by Malinda Lo Biology and medicine * Adaptation (eye), the eye's adjustment to light ** Chromatic adaptation, visual systems' adjustments to changes in illumination for preservation of colors ** Prism adaptation, sensory-motor adjustments after the visual field has been artificially shifted * Cellular adaptation, changes by cells/tissues in response to changed microenvironments * High-altitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Printing Filament
3D printing filament is the thermoplastic feedstock for fused deposition modeling 3D printers. There are many types of filament available with different properties. Filament comes in a range of diameters, most commonly 1.75 mm and 2.85 mm, with the latter often being confused with the less common 3 mm. Filament consists of one continuous slender plastic thread spooled into a reel. Production Commercially produced filament 3D printing filament is created using a process of heating, extruding and cooling plastic to transform nurdles into the finished product. However Unlike a 3D printer the filament is pulled rather than pushed through the nozzle to create the filament, the diameter of the filament is defined by the process that takes place after the plastic has been heated rather than the diameter of the extruder nozzle. A different force and speed is applied to the filament as it is pulled out of the extruder to define the width of the filament, most commonly 1.75 mm o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shape Optimization
Shape optimization is part of the field of optimal control theory. The typical problem is to find the shape which is optimal in that it minimizes a certain cost functional while satisfying given constraints. In many cases, the functional being solved depends on the solution of a given partial differential equation defined on the variable domain. Topology optimization is, in addition, concerned with the number of connected components/boundaries belonging to the domain. Such methods are needed since typically shape optimization methods work in a subset of allowable shapes which have fixed topological properties, such as having a fixed number of holes in them. Topological optimization techniques can then help work around the limitations of pure shape optimization. Definition Mathematically, shape optimization can be posed as the problem of finding a bounded set \Omega, minimizing a functional :\mathcal(\Omega), possibly subject to a constraint of the form :\mathcal(\Omega)=0. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accoustic Fabrication
Acoustic may refer to: Music Albums * ''Acoustic'' (Above & Beyond album), 2014 * ''Acoustic'' (Deine Lakaien album), 2007 * ''Acoustic'' (Everything but the Girl album), 1992 * ''Acoustic'' (John Lennon album), 2004 * ''Acoustic'' (Love Amongst Ruin album), 2011 * ''Acoustic'' (Nitty Gritty Dirt Band album), 1994 * ''Acoustic'' (Nouvelle Vague album), 2009 * ''Acoustic'' (Simple Minds album), 2016 * ''The Acoustic'', by Ektomorf, 2012 * ''Acoustic'', by Oumou Sangaré, 2020 EPs and singles * ''Acoustic'' (Bayside EP), 2006 * ''Acoustic'' (Britt Nicole EP), 2010 * ''Acoustic'' (Coldplay EP), 2000 * ''Acoustic'' (Lights EP), 2010 * ''Acoustic'' (Second Coming EP), an acoustic version of ''13'', 2003 * ''Acoustic'', by Brandi Carlile, 2004 * ''Acoustic'', by Gabrielle Aplin, 2010 * ''Acoustic'', by Press to Meco, 2019 * "Acoustic" (single), "Follow You Home" and "Refugees", by Embrace, 2014 Companies * ''Acoustic'' (magazine) * ''Acoustic Guitar'' (magazine) * Acous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoimprint Lithography
Nanoimprint lithography (NIL) is a method of fabricating nanometer scale patterns. It is a simple nanolithography process with low cost, high throughput and high resolution. It creates patterns by mechanical deformation of imprint resist and subsequent processes. The imprint resist is typically a monomer or polymer formulation that is cured by heat or UV light during the imprinting. Adhesion between the resist and the template is controlled to allow proper release. History The term "nanoimprint lithography" was coined in the scientific literature in 1996, when Prof. Stephen Chou and his students published a report in ''Science'', although hot embossing (now taken as a synonym of NIL) of thermoplastics had been appearing in the patent literature for a few years already. Soon after the ''Science'' paper, many researchers developed different variations and implementations. At this point, nanoimprint lithography has been added to the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Continues Inhibition Patterning
Rapids are sections of a river where the river bed has a relatively steep gradient, causing an increase in water velocity and turbulence. Rapids are hydrological features between a ''run'' (a smoothly flowing part of a stream) and a ''cascade''. Rapids are characterized by the river becoming shallower with some rocks exposed above the flow surface. As flowing water splashes over and around the rocks, air bubbles become mixed in with it and portions of the surface acquire a white color, forming what is called "whitewater". Rapids occur where the bed material is highly resistant to the erosive power of the stream in comparison with the bed downstream of the rapids. Very young streams flowing across solid rock may be rapids for much of their length. Rapids cause water aeration of the stream or river, resulting in better water quality. Rapids are categorized in classes, generally running from I to VI. A Class 5 rapid may be categorized as Class 5.1-5.9. While Class I rapids are ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)



.jpg)
