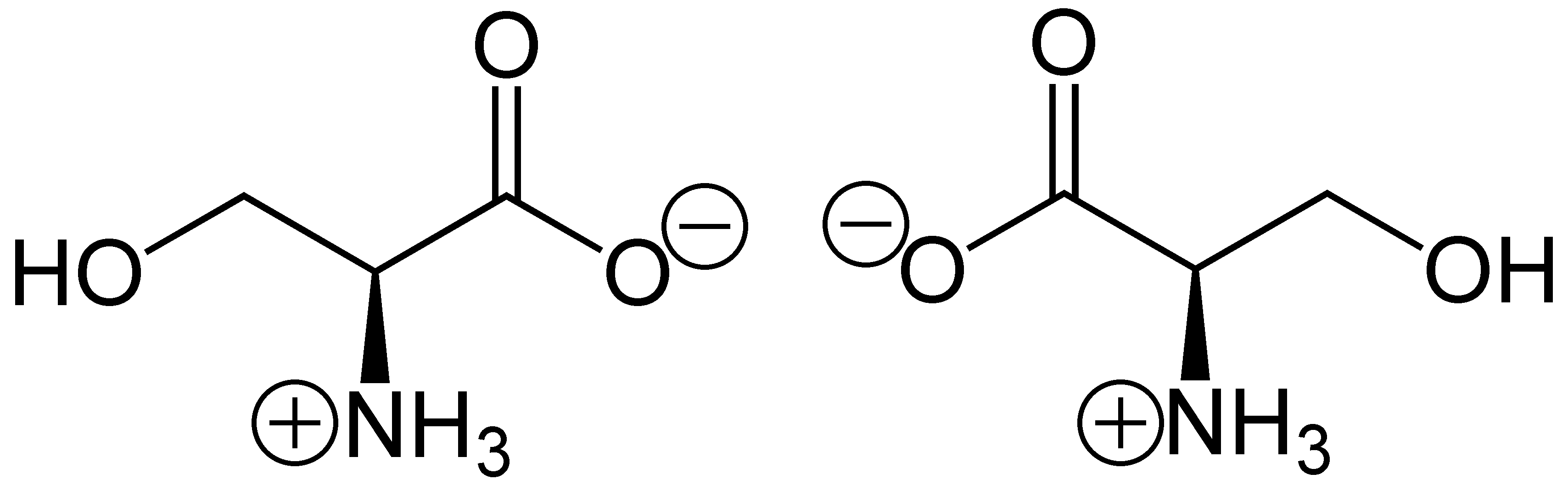|
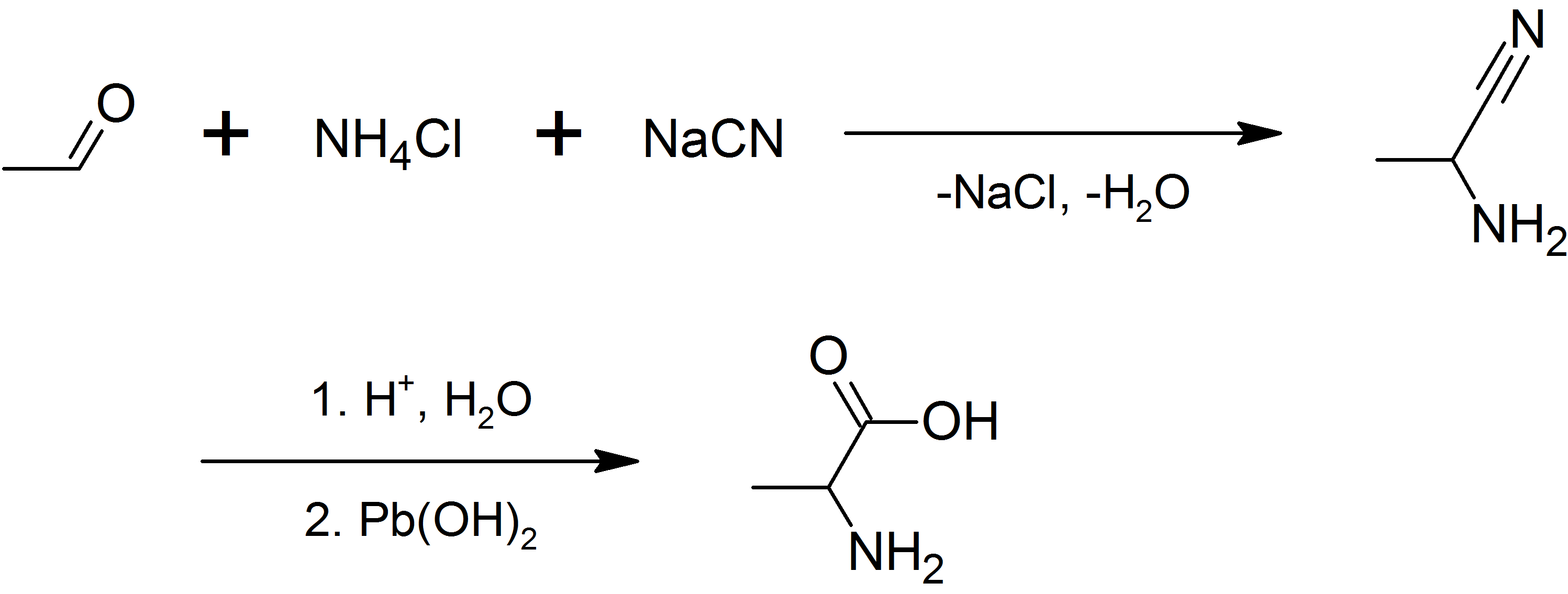
3CL Protease
The 3C-like protease (3CLpro) or main protease (Mpro), formally known as C30 endopeptidase or 3-chymotrypsin-like protease, is the main protease found in coronaviruses. It cleaves the coronavirus polyprotein at eleven conserved sites. It is a cysteine protease and a member of the PA clan of proteases. It has a cysteine-histidine catalytic dyad at its active site and cleaves a Gln–(Ser/Ala/Gly) peptide bond. The Enzyme Commission refers to this family as SARS coronavirus main proteinase (Mpro; ). The 3CL protease corresponds to coronavirus nonstructural protein 5 (nsp5). The "3C" in the common name refers to the 3C protease (3Cpro) which is a homologous protease found in picornaviruses. Function The 3C-like protease is able to catalytically cleave a peptide bond between a glutamine at position P1 and a small amino acid (serine, alanine, or glycine) at position P1'. The SARS coronavirus 3CLpro can for instance self-cleave the following peptides: The protease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a provisional name, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), and has also been called the human coronavirus 2019 (HCoV-19 or hCoV-19). First identified in the city of Wuhan, Hubei, China, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern on January 30, 2020, and a pandemic on March 11, 2020. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that is contagious in humans. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a virus of the species ''severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV), related to the SARS-CoV-1 virus that caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. Despite its close relation to SARS-CoV-1, its closest known relatives, with which it forms a sister group, are the derived SARS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to its compact form. For the same reason, it is the most abundant amino acid in collagen triple-helices. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a ''Clostridium tetani'' infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. History and etymology Glycine was discovered in 1820 by the French chemist He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1; or Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, SARS-CoV) is a strain of coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), the respiratory illness responsible for the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. It is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus that infects the epithelial cells within the lungs. The virus enters the host cell by binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. It infects humans, bats, and palm civets. On April 16, 2003, following the outbreak of SARS in Asia and secondary cases elsewhere in the world, the World Health Organization (WHO) issued a press release stating that the coronavirus identified by a number of laboratories was the official cause of SARS. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the United States and the National Microbiology Laboratory (NML) in Canada identified the SARS-CoV-1 genome in April 2003. Scientists at Erasmus University in Rotter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to its compact form. For the same reason, it is the most abundant amino acid in collagen triple-helices. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a ''Clostridium tetani'' infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. History and etymology Glycine was discovered in 1820 by the French chemist He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side chain. Consequently, its IUPAC systematic name is 2-aminopropanoic acid, and it is classified as a nonpolar, aliphatic α-amino acid. Under biological conditions, it exists in its zwitterionic form with its amine group protonated (as −NH3+) and its carboxyl group deprotonated (as −CO2−). It is non-essential to humans as it can be synthesised metabolically and does not need to be present in the diet. It is encoded by all codons starting with GC (GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG). The L-isomer of alanine (left-handed) is the one that is incorporated into proteins. L-alanine is second only to leucine in rate of occurrence, accounting for 7.8% of the primary structure in a sample of 1,150 proteins. The right-handed form, D-alanine, occurs in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L-stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, ''sericum''. Serine's structure was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral, polar amino acid. It is non-essential and conditionally essential in humans, meaning the body can usually synthesize sufficient amounts of it, but in some instances of stress, the body's demand for glutamine increases, and glutamine must be obtained from the diet. It is encoded by the codons CAA and CAG. In human blood, glutamine is the most abundant free amino acid. The dietary sources of glutamine include especially the protein-rich foods like beef, chicken, fish, dairy products, eggs, vegetables like beans, beets, cabbage, spinach, carrots, parsley, vegetable juices and also in wheat, papaya, Brussels sprouts, celery, kale and fermented foods like miso. Functions Glutamine plays a role in a variety of biochemical functions: * Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes including apoptosis, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or misfolded proteins in cells. Consequently, abnormality in the regulation of proteolysis can cause disease. Proteolysis can also be used as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, and it may also be used in industry, for example in food proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picornavirus
Picornaviruses are a group of related nonenveloped RNA viruses which infect vertebrates including fish, mammals, and birds. They are viruses that represent a large family of small, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses with a 30 nm icosahedral capsid. The viruses in this family can cause a range of diseases including the common cold, poliomyelitis, meningitis, hepatitis, and paralysis. Picornaviruses constitute the family ''Picornaviridae'', order ''Picornavirales'', and realm '' Riboviria''. There are 158 species in this family, assigned to 68 genera. Notable examples are genera ''Enterovirus'' (including ''Rhinovirus'' and ''Poliovirus''), '' Aphthovirus'', ''Cardiovirus'', and ''Hepatovirus''. Etymology The name "picornavirus" has a dual etymology. Firstly, the name derives from ''picorna''- which is an acronym for "''p''oliovirus, ''i''nsensitivity to ether, ''c''oxsackievirus, ''o''rphan virus, ''r''hinovirus, and ribo''n''ucleic ''a''cid". Secondly, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Homology
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer event (xenologs). Homology among DNA, RNA, or proteins is typically inferred from their nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarity. Significant similarity is strong evidence that two sequences are related by evolutionary changes from a common ancestral sequence. Alignments of multiple sequences are used to indicate which regions of each sequence are homologous. Identity, similarity, and conservation The term "percent homology" is often used to mean "sequence similarity”, that is the percentage of identical residues (''percent identity''), or the percentage of residues conserved with similar physicochemical properties (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picornain 3C
Picornain 3C () is a protease found in picornaviruses, which cleaves peptide bonds of non-terminal sequences. Picornain 3C’s endopeptidase activity is primarily responsible for the catalytic process of selectively cleaving Gln-Gly bonds in the polyprotein of poliovirus and with substitution of Glu for Gln, and Ser or Thr for Gly in other picornaviruses. Picornain 3C are cysteine proteases related by amino acid sequence to trypsin-like serine proteases. Picornain 3C is encoded by enteroviruses, rhinoviruses, aphtoviruses and cardioviruses. These genera of picoviruses cause a wide range of infections in humans and mammals. Picornavirus belongs to the family ''Picornaviridae''. Picornavirus virions are nonenveloped and the +ssRNA nonsegmented genome is encapsulated in an icosahedral protein structure made from four capsid proteins encoded by the virus. Picornavirus viral replication typically takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Picornavirus +ssRNA genome then gets translated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




2(OH2).png)