|
3-Methyl-3-pentanol
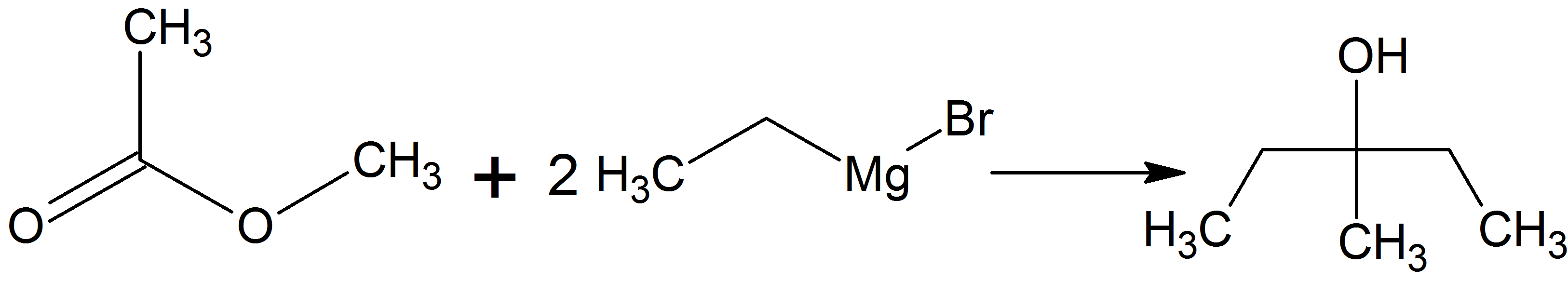
3-Methyl-3-pentanol (IUPAC name: 3-methylpentan-3-ol) is an organic chemical compound and a tertiary hexanol. It is used in the synthesis of the tranquilizer emylcamate, and has similar sedative and anticonvulsant actions itself. Synthesis It can be prepared by reacting ethylmagnesium bromide with methyl acetate in the so-called Grignard reaction using dried diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran as solvent. It can be prepared also by reacting ethylmagnesium bromide with butanone Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH3. This colourless liquid ketone has a sharp, sweet odor reminiscent of acetone. It is produced industrially on a large scale, but occurs in ... in the same conditions already mentioned. References Tertiary alcohols Hexanols {{alcohol-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-Methyl-3-pentanol Chemical Equation
3-Methyl-3-pentanol (IUPAC name: 3-methylpentan-3-ol) is an organic chemical compound and a tertiary hexanol. It is used in the synthesis of the tranquilizer emylcamate, and has similar sedative and anticonvulsant actions itself. Synthesis It can be prepared by reacting ethylmagnesium bromide with methyl acetate in the so-called Grignard reaction using dried diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran as solvent. It can be prepared also by reacting ethylmagnesium bromide with butanone Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH3. This colourless liquid ketone has a sharp, sweet odor reminiscent of acetone. It is produced industrially on a large scale, but occurs in n ... in the same conditions already mentioned. References Tertiary alcohols Hexanols {{alcohol-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexanol
Hexanol may refer to any of the following isomeric organic compounds with the formula C6H13OH: : See also * Cyclohexanol * Amyl alcohol An amyl alcohol is any of eight alcohols with the formula C5H12O. A mixture of amyl alcohols (also called amyl alcohol) can be obtained from fusel alcohol. Amyl alcohol is used as a solvent and in esterification, by which is produced amyl acetate ... {{Chemistry index Fatty alcohols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexanol
Hexanol may refer to any of the following isomeric organic compounds with the formula C6H13OH: : See also * Cyclohexanol * Amyl alcohol An amyl alcohol is any of eight alcohols with the formula C5H12O. A mixture of amyl alcohols (also called amyl alcohol) can be obtained from fusel alcohol. Amyl alcohol is used as a solvent and in esterification, by which is produced amyl acetate ... {{Chemistry index Fatty alcohols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miscible
Miscibility () is the property of two substances to mix in all proportions (that is, to fully dissolve in each other at any concentration), forming a homogeneous mixture (a solution). The term is most often applied to liquids but also applies to solids and gases. For example, water and ethanol are miscible because they mix in all proportions. By contrast, substances are said to be immiscible if there are certain proportions in which the mixture does not form a solution. For one example, oil is not soluble in water, so these two solvents are immiscible. As another example, butanone (methyl ethyl ketone) is significantly soluble in water, but these two solvents are also immiscible because in some proportions the mixture will separate into two phases. Organic compounds In organic compounds, the weight percent of hydrocarbon chain often determines the compound's miscibility with water. For example, among the alcohols, ethanol has two carbon atoms and is miscible with water, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Anticonvulsants suppress the excessive rapid firing of neurons during seizures. Anticonvulsants also prevent the spread of the seizure within the brain. Conventional antiepileptic drugs may block sodium channels or enhance γ-aminobutyric acid ( GABA) function. Several antiepileptic drugs have multiple or uncertain mechanisms of action. Next to the voltage-gated sodium channels and components of the GABA system, their targets include GABAA receptors, the GAT-1 GABA transporter, and GABA transaminase. Additional targets include voltage-gated calcium channels, SV2A, and α2δ. By blocking sodium or ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butanone
Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH3. This colourless liquid ketone has a sharp, sweet odor reminiscent of acetone. It is produced industrially on a large scale, but occurs in nature only in trace amounts.Wilhelm Neier, Guenter Strehlke "2-Butanone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2002. It is partially soluble in water, and is commonly used as an industrial solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, tetrahydrofuran. Production Butanone may be produced by oxidation of 2-butanol. The dehydrogenation of 2-butanol is catalysed by copper, zinc, or bronze: :CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3 → CH3C(O)CH2CH3 + H2 This is used to produce approximately 700 million kilograms yearly. Other syntheses that have been examined but not implemented include Wacker oxidation of 2-butene and oxidation of isobutylbenzene, which is analogous to the industrial production of acetone. The cumene process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is mainly used as a precursor to polymers. Being polar and having a wide liquid range, THF is a versatile solvent. Production About 200,000 tonnes of tetrahydrofuran are produced annually. The most widely used industrial process involves the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 1,4-butanediol. Ashland/ISP is one of the biggest producers of this chemical route. The method is similar to the production of diethyl ether from ethanol. The butanediol is derived from condensation of acetylene with formaldehyde followed by hydrogenation. DuPont developed a process for producing THF by oxidizing ''n''-butane to crude maleic anhydride, followed by catalytic hydrogenation. A third major industrial route entails hydroformylation of allyl alcohol followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grignard Reaction
The Grignard reaction () is an organometallic chemical reaction in which alkyl, allyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides ( Grignard reagent) is added to a carbonyl group in an aldehyde or ketone. This reaction is important for the formation of carbon–carbon bonds. The reaction of an organic halide with magnesium is ''not'' a Grignard reaction, but provides a Grignard reagent. : Grignard reactions and reagents were discovered by and are named after the French chemist François Auguste Victor Grignard (University of Nancy, France), who published it in 1900 and was awarded the 1912 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work. Reaction mechanism Because carbon is more electronegative than magnesium, the carbon attached to magnesium functions as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon atom that is present within the polar bond of a carbonyl group. The addition of the Grignard reagent to the carbonyl typically proceeds through a six-membered ring transition state. Based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Acetate
Methyl acetate, also known as MeOAc, acetic acid methyl ester or methyl ethanoate, is a carboxylate ester with the formula CH3COOCH3. It is a flammable liquid with a characteristically pleasant smell reminiscent of some glues and nail polish removers. Methyl acetate is occasionally used as a solvent, being weakly polar and lipophilic, but its close relative ethyl acetate is a more common solvent being less toxic and less soluble in water. Methyl acetate has a solubility of 25% in water at room temperature. At elevated temperature its solubility in water is much higher. Methyl acetate is not stable in the presence of strong aqueous bases or aqueous acids. Methyl acetate is not considered a VOC in the USA. Preparation and reactions Methyl acetate is produced industrially via the carbonylation of methanol as a byproduct of the production of acetic acid. Methyl acetate also arises by esterification of acetic acid with methanol in the presence of strong acids such as sulfuric ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylmagnesium Bromide
Ethylmagnesium bromide is a Grignard reagent with formula C2H5MgBr. It is widely used in the laboratory synthesis of organic compounds. Reactions Apart from acting as the synthetic equivalent of an ethyl anion synthon for nucleophilic addition, ethylmagnesium bromide may be used as a strong base to deprotonate various substrates such as alkynes: :RC≡CH + EtMgBr → RC≡CMgBr + EtH In this application, ethylmagnesium bromide has been supplanted by the wide availability of organolithium reagents. Preparation Ethylmagnesium bromide is commercially available, usually as a solution in diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran. It may be prepared in the normal manner of Grignard reagents — by reacting bromoethane with magnesium in diethyl ether Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound in the ether class with the formula , sometimes abbreviated as (see Pseudoelement symbols). It is a colourless, highly volatile, sweet-smelling ("ethereal odour"), extremel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emylcamate
Emylcamate (marketed as Striatran by Merck) is an anxiolytic and muscle relaxant. It was patented in the US in 1961 (US Patent 2,972,564) and advertised for the treatment of anxiety and tension. It was claimed to be superior to meprobamate Meprobamate—marketed as Miltown by Wallace Laboratories and Equanil by Wyeth, among others—is a carbamate derivative used as an anxiolytic drug. It was the best-selling minor tranquilizer for a time, but has largely been replaced by the be ..., which was the market leader at the time. It is no longer prescribed. A study of the drug's effects in mice was done in 1959. It concluded that at 50 mg/kg emylcamate gave a 63% decrease in motor activity compared with meprobamate's 32% decrease, a doubling in effective potency. The therapeutic index in mice was also established: Emylcamate also has a faster intra-parenteral onset than meprobamate, 3 minutes compared with 35. References Further reading * External links * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedative
A sedative or tranquilliser is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement. They are CNS depressants and interact with brain activity causing its deceleration. Various kinds of sedatives can be distinguished, but the majority of them affect the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). In spite of the fact that each sedative acts in its own way, most produce relaxing effects by increasing GABA activity. This group is related to hypnotics. The term ''sedative'' describes drugs that serve to calm or relieve anxiety, whereas the term ''hypnotic'' describes drugs whose main purpose is to initiate, sustain, or lengthen sleep. Because these two functions frequently overlap, and because drugs in this class generally produce dose-dependent effects (ranging from anxiolysis to loss of consciousness) they are often referred to collectively as ''sedative-hypnotic'' drugs. Sedatives can be used to produce an overly-calming effect ( alcohol being the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |