|
2A48 Cobra
The 2A42 Cobra is an overhead-mount modular one-man gun turret designed by the ZTS Dubnica nad Váhom design bureau. It is specially designed to fit many different types of tracked and wheeled IFVs and APCs such as the BMP-1, BMD-1, BTR-70, BTR-80 and the OT-64 SKOT. Description The turret weights 1.05 tonnes without the equipment. The equipment provided for the turret meets modern combat requirements for protection of both the crew and the transported troops. It also allows accurate fire in all weather conditions, both by day and at night and while the vehicle is on the move. The turret is able to successfully operate in temperatures ranging from −30 °C up to +50 °C. The turret can turn through 360°, while the main gun and coaxial machine gun can be elevated or depressed between −4° and +50°. The weapons with which the turret is armed are externally mounted. The interior of the turret provides complete electrical equipment for operating the weapons, ammuniti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon and at the same time lets the weapon be aimed and fired in some degree of azimuth and elevation (cone of fire). Description Rotating gun turrets protect the weapon and its crew as they rotate. When this meaning of the word "turret" started being used at the beginning of the 1860s, turrets were normally cylindrical. Barbettes were an alternative to turrets; with a barbette the protection was fixed, and the weapon and crew were on a rotating platform inside the barbette. In the 1890s, armoured hoods (also known as "gun houses") were added to barbettes; these rotated with the platform (hence the term "hooded barbette"). By the early 20th Century, these hoods were known as turrets. Modern warships have gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
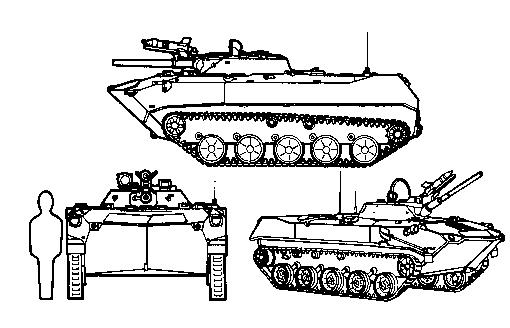
BMP-1
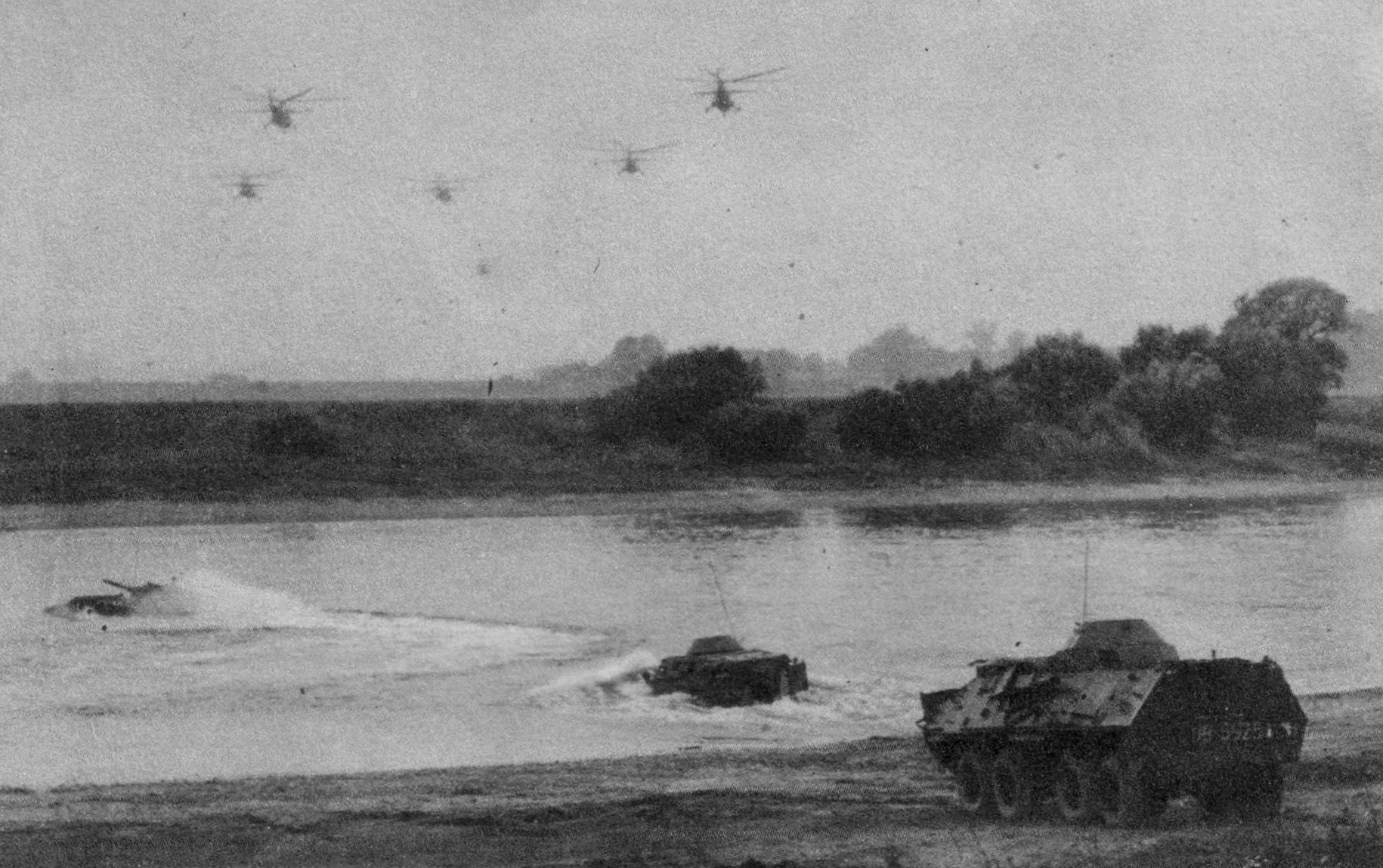
The BMP-1 is a Soviet amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle, in service 1966–present. BMP stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Pyekhoty 1'' (russian: link=no, Боевая Машина Пехоты 1; БМП-1), meaning "infantry fighting vehicle, 1st serial model". The BMP-1 was the first mass-produced infantry fighting vehicle (IFV) of the Soviet Union. It was called the M-1967, BMP and BMP-76PB by NATO before its correct designation was known. The Soviet military leadership saw any future wars as being conducted with nuclear, chemical and biological weapons. A new design, like the BMP, combining the properties of an armored personnel carrier (APC) and a light tank would allow infantry to operate from the relative safety of its armoured, radiation-shielded interior in contaminated areas and to fight alongside it in uncontaminated areas. It would increase infantry squad mobility, provide fire support to them, and also be able to fight alongside main battle tanks. The BMP- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMD-1
The BMD-1 is a Soviet airborne amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle, which was introduced in 1969 and first seen by the West in 1970. BMD stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Desanta'' (Боевая Машина Десанта, which literally translates to "Combat Vehicle of the Airborne"). It can be dropped by parachute and although it resembles the BMP-1 it is in fact much smaller. The BMD-1 was used as an IFV by the Soviet Army's airborne divisions. An improved variant of the BMD-1 was developed, the BMD-2. The BMD-1 also provided a basis for the BTR-D airborne multi-purpose tracked APC. Development In the wake of the Cuban Missile Crisis, the army was instructed to consider putting more emphasis on means to project power outside of the normal sphere of Soviet influence. As a result, there was a major effort to develop the VDV (Soviet airborne forces) as a rapid deployment force. Soviet studies of airborne operations had shown that lightly armed paratroops were unable to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BTR-70
The BTR-70 is an eight-wheeled armored personnel carrier (russian: бронетранспортер/ ''Bronetransporter'', or literally "Armoured Transporter") originally developed by the Soviet Union during the late 1960s under the manufacturing code GAZ-4905. On August 21, 1972, it was accepted into Soviet service and would later be widely exported. Large quantities were also produced under license in Romania as the ''TAB-77''. The BTR-70 was developed as a potential successor for the earlier BTR-60 series of Soviet wheeled armored personnel carriers, specifically the ''BTR-60PB'', which it most closely resembled. It evolved out of an earlier, unsuccessful project known as the ''GAZ-50'' to design a new wheeled infantry fighting vehicle on the chassis and drive train of a BTR-60PB. It initially received the NATO reporting name ''BTR M1970''. Development History In 1971, the Soviet Armed Forces began investigating the possibility of an updated BTR-60PB redesigned to make the veh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BTR-80
The BTR-80 (russian: бронетранспортёр, bronyetransportyor, literally "armoured transporter") is an 8×8 wheeled amphibious armoured personnel carrier (APC) designed in the USSR. It was adopted in 1985 and replaced the previous vehicles, the BTR-60 and BTR-70, in the Soviet Army. It was first deployed during the Soviet–Afghan War. The BTR-80 was developed into the larger BTR-90. Description The Soviets based the BTR-80 on the BTR-70 APC, which itself was based on the BTR-60. It has a single 260-hp V-8 turbocharged water-cooled diesel engine, an improvement over the twin gasoline engines installed in the BTR-60 and BTR-70 vehicles. The reconfigured rear portion of the hull accommodates the new, single engine. The Soviets removed the roof chamfers of the modified BTR-70, raised the rear, and squared off the rearward-sloping engine compartment. Standard equipment includes TNPO vision blocks, TNP-B and TKN-3 optical devices for the driver and commander, an OU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OT-64 SKOT
The OT-64 SKOT (Czech acronym for: ''Střední Kolový Obrněný Transportér'', and/or Polish Średni ''Kołowy Opancerzony Transporter'' – medium wheeled armoured transporter) is an amphibious, armored personnel carrier (8x8), developed jointly by Poland ( PRL) and Czechoslovakia ( ČSSR) well into the 1960s. Until the early 1970s Czechoslovakia and Poland produced around 4,500 OT-64 SKOTs of all variants, just under a third of which were exported.BURIAN, Michal; DÍTĚ, Josef; DUBÁNEK, Martin. OT-64 SKOT: historie a vývoj obrněného transportéru. 1. vyd. Praha: Grada, 2010.Kajetanowicz Jerzy, Transporter opancerzony SKOT i jego odmiany produkowane w Polsce, Zeszyty Naukowe WSOWL 2016, nr 2Kubiaczyk C., Transporter opancerzony SKOT, A. Karaś, W. Stefanowska (red.), J. Magnuski, Seria: Typy broni i uzbrojenia, vol. 9, Warszawa: Wydawnictwo Ministerstwa Obrony Narodowej, 1971 In 2002, the modernization of the SKOT transporter began in Poland. The work resulted in the KTO R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2A42
The Shipunov 2A42 is a Soviet/Russian 30 mm autocannon. It is built by the Tulamashzavod Joint Stock Company. Design The 30 mm 2A42 autocannon was developed as a replacement for 2A28 Grom and has a dual feed. One is for HE-T and the other for AP-T rounds. The gunner can select one of two rates of full automatic fire, low at 200 to 300 rds/min and high at 550 to 800 rds/min. According to the manufacturer, effective range when engaging ground targets such as light armoured vehicles is 1,500 m while soft-skinned targets can be engaged out to 4,000 m. Air targets can be engaged flying at low altitudes of up to 3,000 m at subsonic speeds and up to a slant range of 2,500 m. In addition to being installed in a two-person turret on the BMP-2 mechanised infantry combat vehicle, this gun is also fitted in the BMD-2 airborne combat vehicle, BMD-3 airborne combat vehicle and BTR-90 (or GAZ-5923) (8 × 8) armoured personnel carrier. A small number of these have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PKT Machine Gun
The PK (russian: Пулемёт Калашникова, transliterated as ''Pulemyot Kalashnikova'', or "Kalashnikov's machine gun"), is a belt-fed general-purpose machine gun, chambered for the 7.62×54mmR rimmed cartridge. Designed in the Soviet Union and currently in production in Russia, the original PK machine gun was introduced in 1961 and the improved PKM variant was introduced in 1969. The PKM was designed to replace the SGM and RP-46 machine guns that were previously in Soviet service. The weapon remains in use as a front-line infantry and vehicle-mounted weapon with Russia's armed forces and has also been exported extensively and produced in several other countries under license. History The Main Artillery Directorate of the Soviet Union (GRAU) adopted specification requirements for a new 7.62 mm general-purpose company and battalion-level machine gun that was to be chambered for a rifle cartridge in 1955. In 1958 a machine gun prototype, developed by G.I. Nik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-tank Guided Missile
An anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), anti-tank missile, anti-tank guided weapon (ATGW) or anti-armor guided weapon is a guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy heavily armored military vehicles. ATGMs range in size from shoulder-launched weapons, which can be transported by a single soldier, to larger tripod-mounted weapons, which require a squad or team to transport and fire, to vehicle and aircraft mounted missile systems. Earlier man-portable anti-tank weapons like anti-tank rifles and magnetic anti-tank mines, generally had very short range, sometimes on the order of metres or tens of metres. Rocket-propelled high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) systems appeared in World War II and extended range to the order of hundreds of metres, but accuracy was low and hitting targets at these ranges was largely a matter of luck. It was the combination of rocket propulsion and remote wire guidance that made the ATGM much more effective than these earlier weapons, and gave lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Weapon Stations
Remote may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Remote'' (1993 film), a 1993 movie * ''Remote'' (2004 film), a Tamil-language action drama film * ''Remote'' (album), a 1988 album by Hue & Cry * Remote (band), ambient chillout band * ''Remote'' (manga), a 2002 manga * Remote broadcast, commonly known in broadcasting as a person or a live remote Computing and technology * Remote (Apple software), software application made by Apple Inc. for the iOS * Remote control, commonly known as a remote * Remote control car, a car that can be controlled from a distance * Remote desktop or operating system, can be controlled by another system device * Remote operation Places * Remote, Oregon * Remote Peninsula, Canada * Remote Western Australia Other uses * Remote and isolated community, a community in a remote location * Remote learning, distance learning * Remote, to implement a remotion, withdrawal of a ''privatdozent'' academic teaching license See also * Remote access (disa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |