|
291st Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The German 291st Infantry Division, was an infantry division of the Wehrmacht and served in World War II. It was formed on February 10th 1940 as a division of the 8th Wave at the Troop training ground Arys im WK I (Prussia). 291. Infanterie Division was formed in Insterburg in the military training area of Arys (south-east of Königsberg, East Prussia) in February 1940 as part of the 8th Wave. Created by using cadres from previously existing units, it took part in the attack on France but played no noticeable role there. During the expansion of the Heer in the autumn the division lost 3 Btns. of Infantry (I /504th, I /505th and I /506th.) and one of Artillery (III /291st.) to the newly raised 306. Infanterie Division, but these units were replaced before the division was assigned to Heeresgruppe Nord in early 1941 as 18. Armee's reserve as they prepared for the launching of Barbarossa. The "Elch" (Moose) division managed to advance 44 miles in the first 34 hours of the campaign i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Shock Army
The 2nd Shock Army (russian: 2-я Ударная армия) was a field army of the Soviet Union during the Second World War. This type of formation was created in accordance with prewar doctrine that called for Shock Armies to ''overcome difficult defensive dispositions in order to create a tactical penetration of sufficient breadth and depth to permit the commitment of mobile formations for deeper exploitation.'' However, as the war went on, Shock Armies lost this specific role and reverted, in general, to ordinary frontline formations. Formation The 2nd Shock Army was formed from the Volkhov Front's 26th Army in December 1941 and initially consisted of the 327th Rifle Division and eight separate rifle brigades. During the Lyuban offensive operation in early 1942, the 2nd Shock Army broke through German lines, was cut off from reinforcement along the Volkhov River by a German counter-attack, and was not permitted to retreat. When the order for retreat finally came in, the 2nd w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
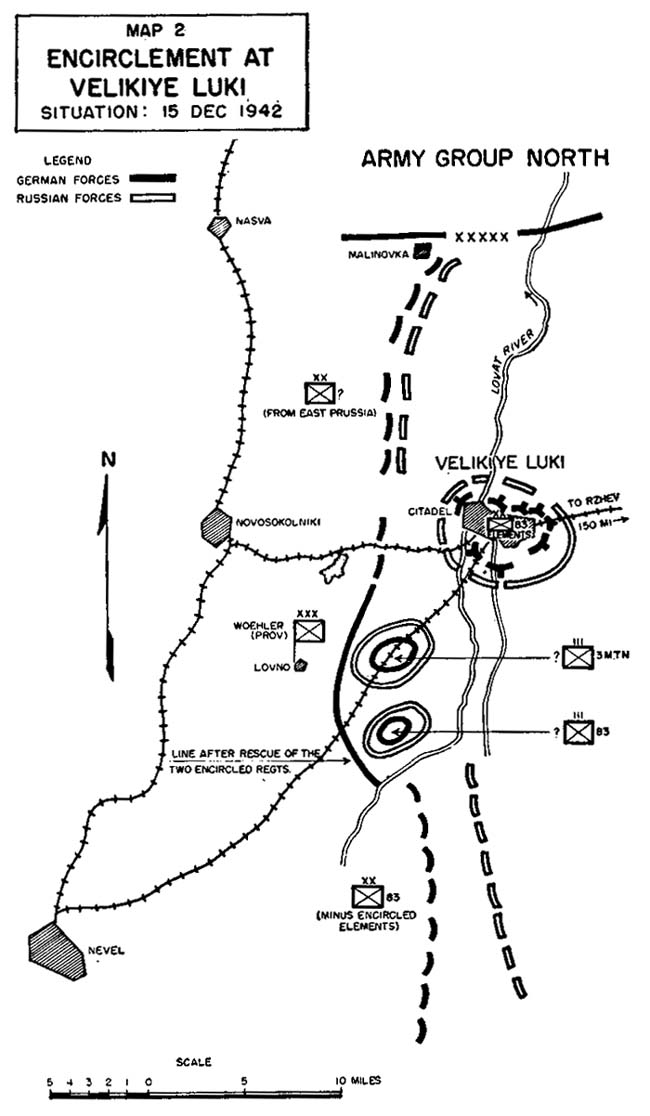
Infantry Divisions Of Germany During World War II
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets '' infant''. The individual-soldier term ''infantry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Finger
__NOTOC__ Arthur Finger (18 January 1898 – 27 January 1945) was a German general ( Generalmajor) in the Wehrmacht during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross of Nazi Germany. Finger was killed on 27 January 1945 near Tschenstochau, Poland during the Soviet Vistula–Oder Offensive. Awards and decorations * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 16 November 1943 as ''Oberst ''Oberst'' () is a senior field officer rank in several German-speaking and Scandinavian countries, equivalent to colonel. It is currently used by both the ground and air forces of Austria, Germany, Switzerland, Denmark, and Norway. The Swedish ...'' and commander of Artillerie-Regiment 306 Fellgiebel 2000, p. 151. References Citations Bibliography * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Finger, Arthur 1898 births 1945 deaths Major generals of the German Army (Wehrmacht) German Army personnel of World War I German police officers Recipients of the clasp to the Iron Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oskar Eckholt
__NOTOC__ Oskar Eckholt (4 November 1894 – 12 August 1982) was a German general ( Generalmajor) in the Wehrmacht during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross of Nazi Germany. Eckholt surrendered to American troops in May 1945. He was released in 1947. Awards and decorations * German Cross in Gold on 18 May 1942 as ''Oberstleutnant'' in Artillerie-Regiment 178 * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 9 April 1943 as ''Oberst ''Oberst'' () is a senior field officer rank in several German-speaking and Scandinavian countries, equivalent to colonel. It is currently used by both the ground and air forces of Austria, Germany, Switzerland, Denmark, and Norway. The Swedish ...'' and commander of Artillerie-Regiment 178Fellgiebel 2000, p. 142. References Citations Bibliography * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Eckholt, Oskar 1894 births 1982 deaths Military personnel from Essen Major generals of the German Army (Wehrmacht) German Army personnel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Werner Goeritz
__NOTOC__ Werner Goeritz (9 March 1892 – 27 May 1958) was a German general during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross of Nazi Germany. Awards and decorations * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 6 November 1943 as ''Generalleutnant is the Germanic variant of lieutenant general, used in some German speaking countries. Austria Generalleutnant is the second highest general officer rank in the Austrian Armed Forces (''Bundesheer''), roughly equivalent to the NATO rank of ...'' and commander of 291. Infanterie-DivisionFellgiebel 2000, p. 165. References Citations Bibliography * {{DEFAULTSORT:Goeritz, Werner 1892 births 1958 deaths Lieutenant generals of the German Army (Wehrmacht) German Army personnel of World War I Recipients of the clasp to the Iron Cross, 1st class Recipients of the Gold German Cross Recipients of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross German prisoners of war in World War II Military person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurt Herzog
__NOTOC__ Kurt Herzog (27 March 1889, Quedlinburg – 8 May 1948) was a German general during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves. A war criminal, Herzog surrendered to the Soviet troops in May 1945 and died in captivity on 8 May 1948. Awards and decorations * Iron Cross (1914) 2nd Class (26 October 1914) & 1st Class (6 November 1916)Thomas 1997, p. 277. * Clasp to the Iron Cross (1939) 2nd Class (10 September 1939) & 1st Class (29 September 1939) * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves ** Knight's Cross on 18 October 1941 as ''Generalleutnant'' and commander of 291. Infanterie-Division **Oak Leaves on 12 January 1945 as ''General der Artillerie General der Artillerie ( en: General of the artillery) may mean: 1. A rank of three-star general, comparable to modern armed forces OF-8 grade, in the Imperial German Army and its contingency armies of Prussia, Bavaria, Saxony and Württembe ...'' and commander of X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Ukrainian Front
The 1st Ukrainian Front (Russian: Пéрвый Украи́нский фронт), previously the Voronezh Front (Russian: Воронежский Фронт) was a major formation of the Soviet Army during World War II, being equivalent to a Western army group. Background During the first months of the war, officers from 16 regions of Ukraine conscripted about 2.5 million people from military enlistment offices. 1.3 million militiamen from the left-bank and southern regions of Ukraine fought against the enemy. In 1941, about 3.185 million citizens of the Ukrainian SSR were sent to the Soviet Red Army and Navy. Replenishing mostly the units of the Southern and Southwestern fronts, the Ukrainian people formed the basis of the 37th, 38th, and 40th armies; and the 13th and 17th rifle divisions. Due to the conscription of civilians, the proportion of Ukrainian citizens fighting in south-west Ukraine reached 50%. This significantly exceeded the percentage of Ukrainians from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd Guards Tank Army (Soviet Union)
The 3rd Guards Tank Army (russian: 3-я гвардейская танковая армия) was a tank army established by the Soviet Union's Red Army during World War II. The 3rd Tank Army was created in 1942 and fought in the southern areas of the Soviet Union and Poland, then in Germany and Czechoslovakia until the defeat of Germany in 1945. Postwar, the army served as occupation troops in East Germany, went through several name changes, and was finally deactivated in 1969. History Second World War First Formation The 3rd Tank Army was formed as part of the Reserve of the Supreme High Command (RVGK, Stavka reserve) on the basis of the 58th Army in the Moscow Military District in May 1942. It was placed under the command of Lieutenant General Prokofy Romanenko. Its initial composition was 12th and 15th Tank Corps, one motor rifle division, and two rifle divisions. As part of the Soviet Western Front, the 3rd Tank Army successfully counter-attacked the German Second Panz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th SS Polizei Panzergrenadier Division
The 4th SS Polizei Panzergrenadier Division (4. SS-Polizei-Panzergrenadier-Division) or SS Division Polizei was one of the thirty-eight divisions fielded as part of the Waffen-SS during World War II. Formation The division was formed in October 1939, when thousands of members of the ''Ordnungspolizei'' (Orpo) were drafted to fill the ranks of the new SS division. These men were not enrolled in the SS and remained policemen, retaining their Orpo rank structure and insignia. They did not have to meet the racial and physical requirements imposed for the SS. Himmler's purpose in forming the division was to get around the recruitment caps the Wehrmacht had succeeded in placing on the SS, it also provided a means for his policemen to satisfy their military obligation and avoid army conscription. The first commander was ''Generalleutnant der Polizei'' (Major-General) Karl Pfeffer-Wildenbruch, a career police commander who had been a general staff officer during World War I; simultaneous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrey Vlasov
Andrey Andreyevich Vlasov (russian: Андрéй Андрéевич Влáсов, – August 1, 1946) was a Soviet Red Army general and Nazi collaborator. During World War II, he fought in the Battle of Moscow and later was captured attempting to lift the siege of Leningrad. After being captured, he defected to Nazi Germany and headed the Russian Liberation Army (''Russkaya osvoboditel'naya armiya'', ROA). Initially this army only existed on paper and was used by Germans to goad the Red Army troops to surrender; only in 1944 did Heinrich Himmler, knowing that Germany was running out of manpower, arrange Vlasov to form a real Russian pro-Nazi army. At the war's end, Vlasov changed sides again and ordered the ROA to aid the Prague uprising against the Germans. He and the ROA then tried to escape to the Western Front, but were captured by Soviet forces. Vlasov was tortured, tried for treason and hanged. Early career Born in Lomakino, Nizhny Novgorod Governorate, Russia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |