|
254mm 45 Caliber Pattern 1891
The 254 mm 45 caliber Pattern 1891 was a Russian naval gun developed in the years before the Russo-Japanese War that armed coastal defense ships and pre-dreadnought battleships during the Russo-Japanese War and World War I. Guns salvaged from scrapped ships found a second life as coastal artillery. It is believed none were in service during World War II. History The 254 mm 45 caliber Pattern 1891 was the product of an agreement between the Imperial Russian Army and Navy to standardize calibers and ammunition during 1892. The gun originally envisioned in 1892 was a 45 caliber gun, with a shell, a muzzle velocity of and a brown powder propellant charge. In 1893 a new scaled up 45 caliber gun, weighing , with a Army shell, a muzzle velocity of and a smokeless powder propellant charge was specified. The weights and dimensions of the new gun were expected to be as close to the original specifications as possible to remain compatible with the ships they were inten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
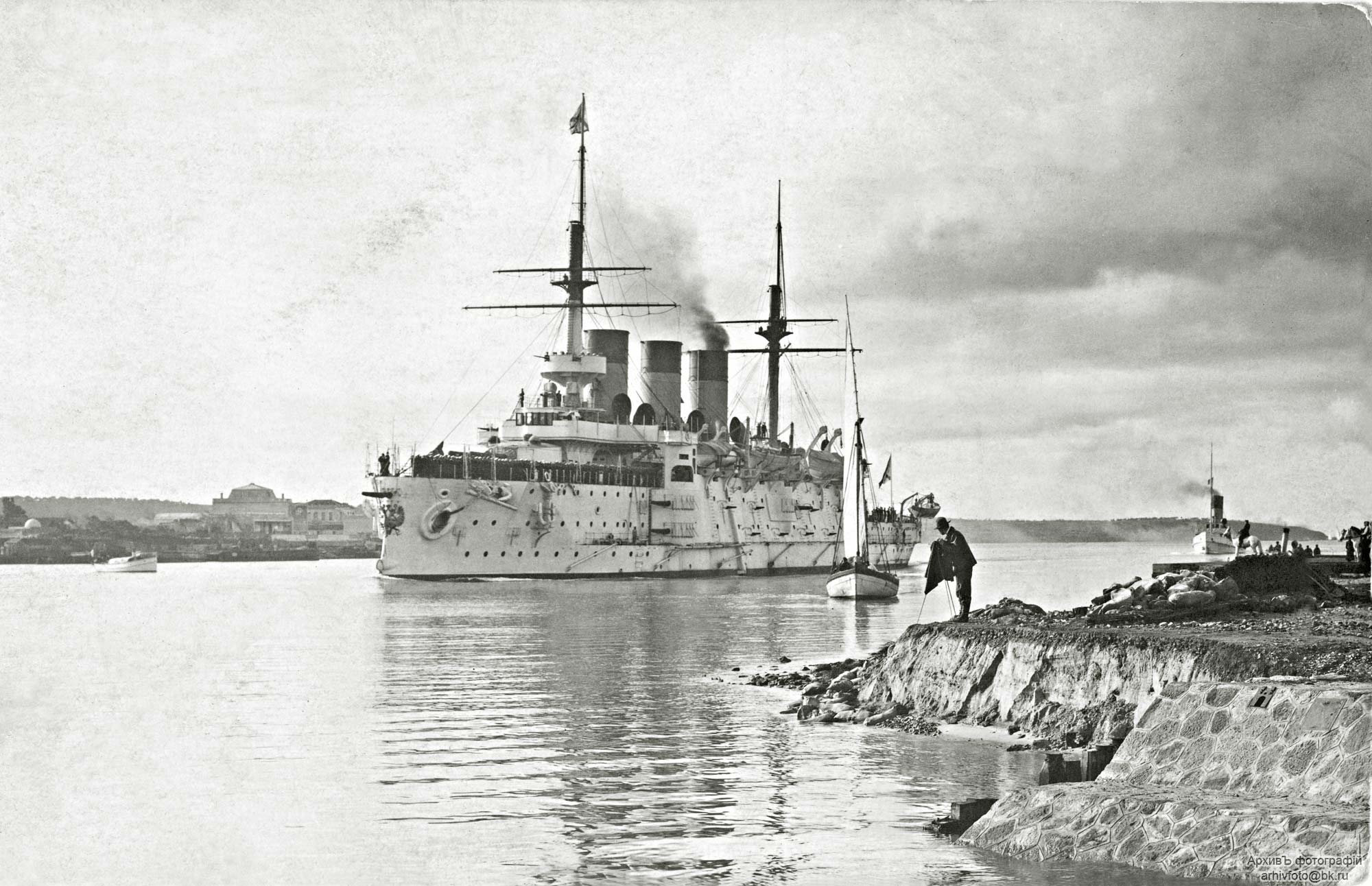
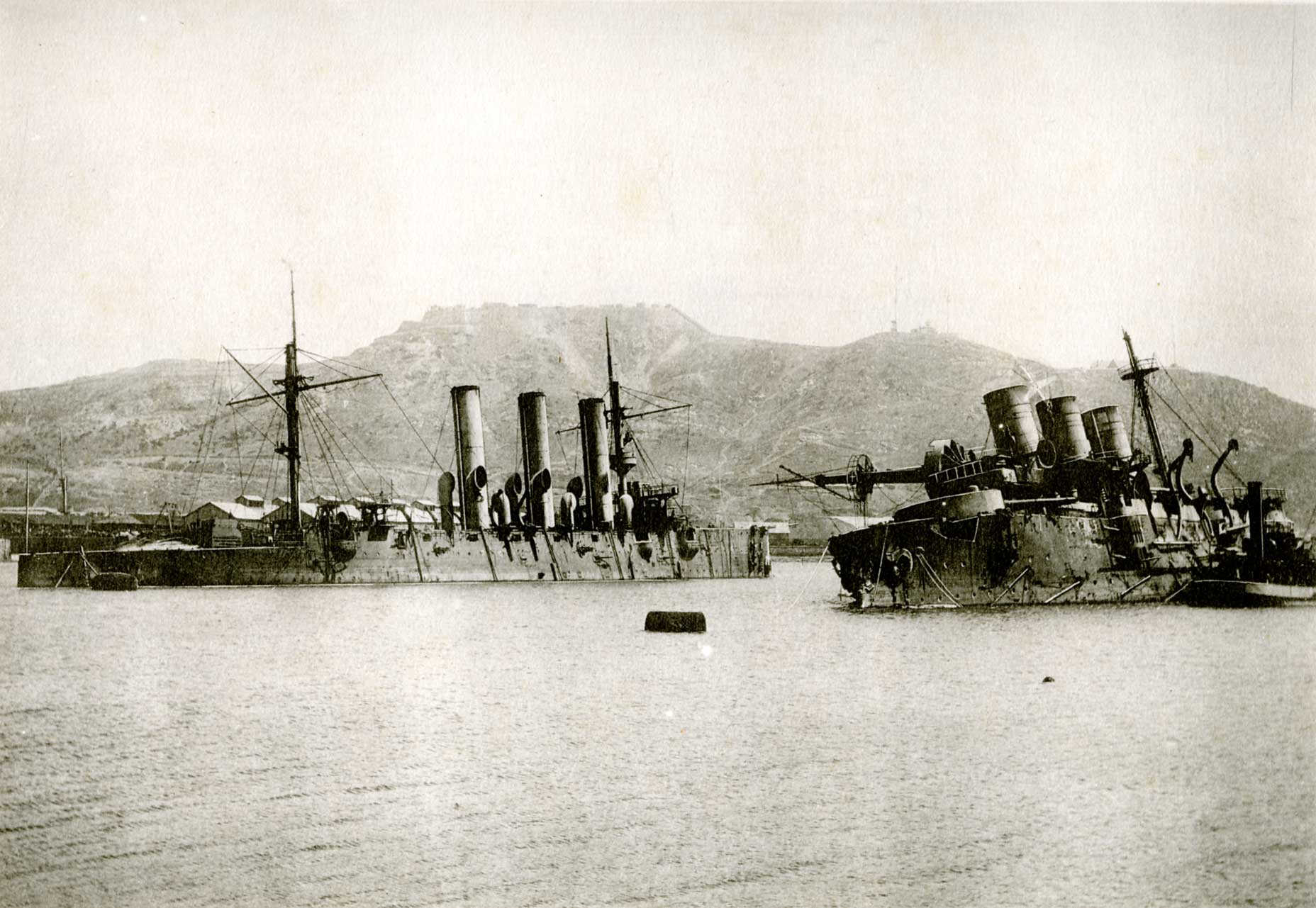
Russian Battleship Rostislav
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including: *Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries *Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and people of Russia, regardless of ethnicity *Russophone, Russian-speaking person (, ''russkogovoryashchy'', ''russkoyazychny'') *Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages *Russian alphabet *Russian cuisine *Russian culture *Russian studies Russian may also refer to: *Russian dressing *''The Russians'', a book by Hedrick Smith *Russian (comics), fictional Marvel Comics supervillain from ''The Punisher'' series *Russian (solitaire), a card game * "Russians" (song), from the album ''The Dream of the Blue Turtles'' by Sting *"Russian", from the album ''Tubular Bells 2003'' by Mike Oldfield *"Russian", from the album '' '' by Caravan Palace *Nik Russian, the perpetrator of a con committed in 2002 *The South African name for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Russian Navy
The Imperial Russian Navy () operated as the navy of the Russian Tsardom and later the Russian Empire from 1696 to 1917. Formally established in 1696, it lasted until dissolved in the wake of the February Revolution of 1917. It developed from a smaller force that had existed prior to Tsar Peter the Great's founding of the modern Russian navy during the Second Azov campaign in 1696. It expanded in the second half of the 18th century and reached its peak strength by the early part of the 19th century, behind only the British and French fleets in terms of size. The Imperial Navy drew its officers from the aristocracy of the Empire, who belonged to the state Russian Orthodox Church. Young aristocrats began to be trained for leadership at a national naval school. From 1818 on, only officers of the Imperial Russian Navy were appointed to the position of Chief Manager of the Russian-American Company, based in Russian America (present-day Alaska) for colonization and fur-trade developme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhu
Muhu (also called Muhumaa in Estonian), is an island in the West Estonian archipelago of the Baltic Sea. With an area of it is the third largest island belonging to Estonia, after Saaremaa and Hiiumaa. Together with neighbouring smaller islands of Kesselaid, Viirelaid, Võilaid and Suurlaid it forms Muhu Parish ( et, Muhu vald), the rural municipality within Saare County. The municipality has a population of 1,697 (as of 19 April 2010) and covers an area of . The population density is . History and geography The German names for the island are Mohn and Moon. Moon is also the Swedish name for the island. The most important villages in Muhu are Kuivastu, Liiva (where the school can be found) and Koguva. In Pädaste, an internationally renowned luxury hotel and spa operates in the restored manor house. The island is divided from mainland Estonia by the Suur Strait (''Moonsund'') and from Saaremaa by the Väike Strait. It is linked by ferry to Virtsu in the mainland, and to S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lüshunkou District
Lüshunkou District (also Lyushunkou District; ) is a district of Dalian, Liaoning province, China. Also formerly called Lüshun City () or literally Lüshun Port (), it was formerly known as both Port Arthur (russian: Порт-Артур, translit=Port-Artur) and Ryojun ( ja, 旅順). The district's area is and its permanent population is 324,773. Lüshunkou is located at the extreme southern tip of the Liaodong Peninsula. It has an excellent natural harbor, the possession and control of which became a '' casus belli'' of the Russo-Japanese War (1904–05). Japanese and then Russian administration was established in 1895 and continued until 1905 when control was ceded to Japan. During that period, it was world-famous and was more significant than the other port on the peninsula, Dalian proper. Toponym In English-language diplomatic, news, and historical writings, it was known as Port Arthur after a British Royal Navy Lieutenant named William Arthur who surveyed the harbor i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian 12 Inch 40 Caliber Naval Gun
The 12-inch 40-caliber naval gun was the standard main weapon of the pre-dreadnought battleships of the Imperial Russian Navy. Sixty-eight guns of the first production run were built in 1895–1906 by the Obukhov Works in Saint Petersburg. They were installed on seventeen battleships starting with ''Sissoi Veliky'' and ''Tri Sviatitelia'' and ending with the ''Andrei Pervozvanny'' class. A second production run was ordered to Russian and British gunmakers during World War I. History In 1886 the Imperial Russian Navy adopted the 12-inch 35 caliber Krupp gun. The first batch of six German-made guns was installed on ''Chesma''. Local production of the modified Krupp gun began in 1891.Shirokorad, p. 32. Eleven Obukhov guns were installed on ''Navarin'', ''Chesma'' and ''Georgii Pobedonosets''. The low firing rate of these guns made them a temporary, intermediate weapon. In the same 1891 the Naval Technical Committee ordered the Obukhov Works to design a new gun with improved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Battleship Oslyabya
''Oslyabya'' (russian: Ослябя) was the second of the three second-class pre-dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Russian Navy at the end of the nineteenth century, although construction delays meant that she was the last to be completed. The ship was part of the Pacific Fleet (Russia), Second Pacific Squadron sent to the Far East during the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–05, and served as the flagship of Rear Admiral Baron Dmitry von Fölkersam. ''Oslyabya'' was sunk on 27 May 1905 at the Battle of Tsushima, and was the first all-steel battleship to be sunk by naval gunfire alone.Forczyk, p. 62 Sources differ on the exact number of casualties, but over half her crew went down with the ship. Design and description The design of the ''Peresvet'' class was inspired by the Royal Navy, British second-class battleships of the . The British ships were intended to defeat commerce-raiders like the Russian armored cruisers and ; the ''Peresvet''-class ships were designed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Battleship Peresvet
''Peresvet'' (russian: Пересвет, link=no) was the lead ship of the three pre-dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Russian Navy at the end of the nineteenth century. The ship was transferred to the Pacific Squadron upon completion and based at Port Arthur from 1903. During the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905, she participated in the Battle of Port Arthur and was seriously damaged during the Battle of the Yellow Sea and again in the siege of Port Arthur. The ship was scuttled before the Russians surrendered, then salvaged by the Japanese and placed into service with the name . Partially rearmed, ''Sagami'' was reclassified by the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) as a coastal defense ship in 1912. In 1916, the Japanese sold her to the Russians, their allies since the beginning of World War I. En route to the White Sea in early 1917, she sank off Port Said, Egypt, after striking mines laid by a German submarine. Design and description The design of the ''Peresve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Battleship Pobeda
''Pobeda'' (russian: Победа, lit=Victory) was the last of the three pre-dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Russian Navy at the end of the nineteenth century. The ship was assigned to the Pacific Squadron upon completion and based at Port Arthur from 1903. During the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905, she participated in the battles of Port Arthur and the Yellow Sea. Having escaped serious damage in these engagements, ''Pobeda'' was sunk by gunfire during the siege of Port Arthur, and then salvaged by the Japanese and placed into service under the name . Rearmed and re-boilered by the Japanese, ''Suwo'' was reclassified by the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) as a coastal defense ship in 1908 and served as a training ship for several years. She was the flagship of the Japanese squadron that participated in the Battle of Tsingtao at the beginning of World War I and continued in that role until she became a gunnery training ship in 1917. The ship was disarmed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
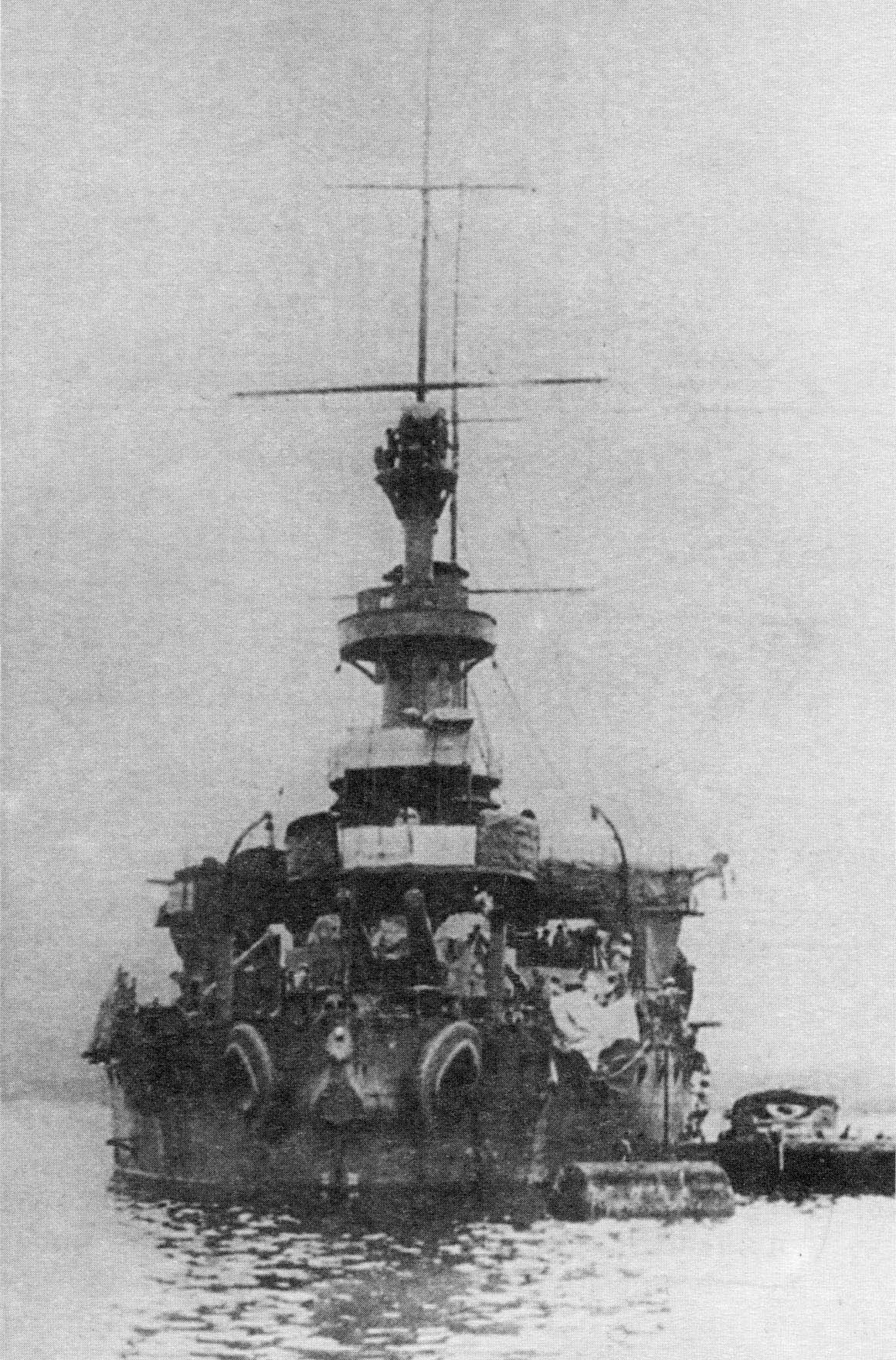
Russian Coast Defense Ship General Admiral Graf Apraksin
''General-Admiral Apraksin'' (russian: Генералъ-Адмиралъ Апраксинъ), sometimes transliterated as ''Apraxin'', was a member of the s of the Imperial Russian Navy. She was named after General Admiral Fyodor Matveyevich Apraksin, the first commander of Russian Baltic Fleet. She was one of eight Russian pre-dreadnought battleships captured by the Imperial Japanese Navy during the Russo-Japanese War of 1904-1905. She subsequently served in the Japanese Navy as until removed from service in 1922. She had only three guns (a single gun turret aft, as shown in the photograph), instead of her sister ships, which were equipped with four guns. Russian service In November 1899, shortly after entering service with the Baltic Fleet, ''General-Admiral Apraksin'' ran aground on Hogland Island in the Gulf of Finland. It was hoped that she could be salvaged, as a similar incident in 1897 had cost the Russian Navy another battleship, . ''General-Admiral Apraksin''s cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Coast Defense Ship Admiral Seniavin
''Admiral Seniavin'' (russian: Адмирал Сенявин), was a built for Imperial Russian Navy during the 1890s. She was one of eight Russian pre-dreadnought battleships captured by the Imperial Japanese Navy from the Russians during the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905. She subsequently served in the Japanese Navy under the name until sunk as a target in 1936. In Russian service Initially assigned to the Russian Baltic Fleet, she was later reclassed as a coastal defence ship. The three obsolete ''Ushakov''s (, , and ''Admiral Senyavin'') were rejected for inclusion in the Second Pacific Squadron assembled by Admiral Zinovy Rozhestvensky to reinforce the existing Russian squadron based at Port Arthur after the outbreak of the Russo-Japanese War as Rozhestvensky felt they were unsuitable for such an extreme blue-water operation. Nevertheless, all three were selected to form part of Admiral Nebogatov's Third Pacific Squadron which was subsequently sent out to reinforce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Coast Defense Ship Admiral Ushakov
''Admiral Ushakov'' was the lead ship in her class of armoured warships (coastal battleships) of the Imperial Russian Navy, and named after Admiral Fyodor Fyodorovich Ushakov the Russian naval commander of the 18th century. Service life ''Admiral Ushakov'' was part of the Baltic Fleet at the beginning of the Russo-Japanese war. ''Admiral Ushakov'' was chosen to form part of Admiral Nikolai Nebogatov's Third Pacific Squadron which was sent out to reinforce Admiral Zinovy Rozhestvensky on his journey to the Far East. The ship was obsolete and was not considered suitable for a voyage to the Pacific.Hore (2005), p. 115 However the Admiralty insisted on including ''Admiral Ushakov'' and her sister ships and to bolster their force. Journeying via the Suez Canal and across the Indian Ocean, they linked up with Rozhestvensky's fleet off Cam Ranh Bay in Indochina and proceeded together to the Straits of Tsushima. At the Battle of Tsushima The Battle of Tsushima (Japanese:対馬 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon and at the same time lets the weapon be aimed and fired in some degree of azimuth and elevation (cone of fire). Description Rotating gun turrets protect the weapon and its crew as they rotate. When this meaning of the word "turret" started being used at the beginning of the 1860s, turrets were normally cylindrical. Barbettes were an alternative to turrets; with a barbette the protection was fixed, and the weapon and crew were on a rotating platform inside the barbette. In the 1890s, armoured hoods (also known as "gun houses") were added to barbettes; these rotated with the platform (hence the term "hooded barbette"). By the early 20th Century, these hoods were known as turrets. Modern warships have gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |