|
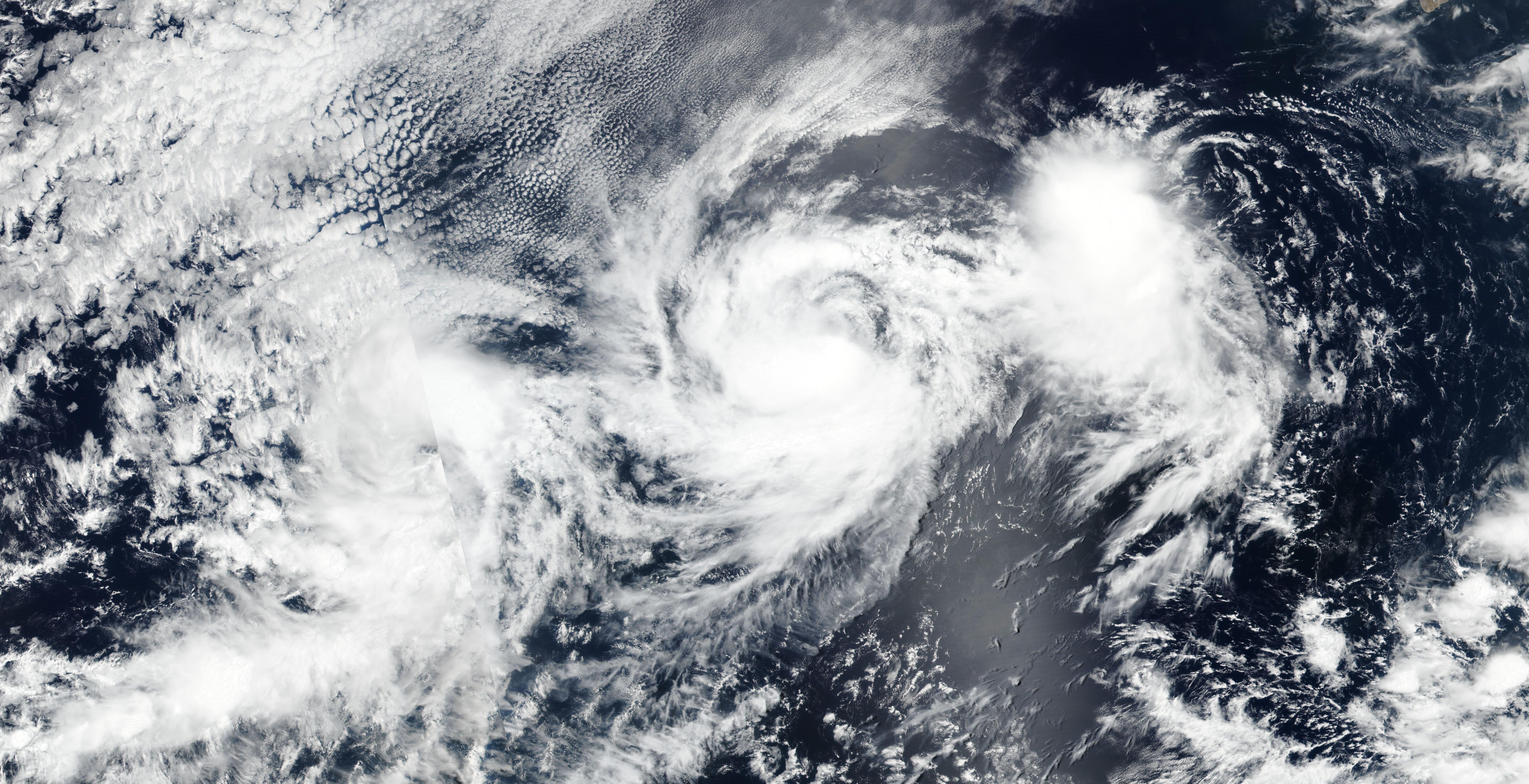
2017 Pacific Hurricane Season
The 2017 Pacific hurricane season was significantly less active than the previous three Pacific hurricane seasons, featuring eighteen named storms, nine hurricanes, and four major hurricanes. Despite the considerable amount of activity, most of the storms were weak and short-lived. The season officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the central Pacific; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the respective regions. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year, as illustrated in 2017 by the formation of the season's first named storm, Tropical Storm Adrian, on May 9. At the time, this was the earliest formation of a tropical storm on record in the eastern Pacific. The season saw near-average activity in terms of accumulated cyclone energy (ACE), in stark contrast to the extremely active seasons in 2014, 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2015 Pacific Hurricane Season
The 2015 Pacific hurricane season is the second-most active Pacific hurricane season on record, with 26 named storms, only behind the 1992 season. A record-tying 16 of those storms became hurricanes, and a record 11 storms further intensified into major hurricanes throughout the season. The Central Pacific, the portion of the Northeast Pacific Ocean between the International Date Line and the 140th meridian west, had its most active year on record, with 16 tropical cyclones forming in or entering the basin. Moreover, the season was the third-most active season in terms of accumulated cyclone energy, amassing a total of 287 units. The season officially started on May 15 in the Eastern Pacific and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Northeast Pacific basin. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charts the seas, conducts deep sea exploration, and manages fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the U.S. exclusive economic zone. Purpose and function NOAA's specific roles include: * ''Supplying Environmental Information Products''. NOAA supplies to its customers and partners information pertaining to the state of the oceans and the atmosphere, such as weather warnings and forecasts via the National Weather Service. NOAA's information services extend as well to climate, ecosystems, and commerce. * ''Providing Environmental Stewardship Services''. NOAA is a steward of U.S. coastal and marine environments. In coordination with federal, state, local, tribal and international authorities, NOAA manages the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal wind shear. Vertical wind shear is a change in wind speed or direction with a change in altitude. Horizontal wind shear is a change in wind speed with a change in lateral position for a given altitude. Wind shear is a microscale meteorological phenomenon occurring over a very small distance, but it can be associated with mesoscale or synoptic scale weather features such as squall lines and cold fronts. It is commonly observed near microbursts and downbursts caused by thunderstorms, fronts, areas of locally higher low-level winds referred to as low-level jets, near mountains, radiation inversions that occur due to clear skies and calm winds, buildings, wind turbines, and sailboats. Wind shear has significant effects on the control of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Mexico covers ,Mexico ''''. . making it the world's 13th-largest country by are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salina Cruz
Salina Cruz is a major seaport on the Pacific coast of the Mexican state of Oaxaca. It is the state's third-largest city and is the municipal seat of the municipality of the same name. It is part of the Tehuantepec District in the west of the Istmo Region. The city had a 2005 census population of 71,314, while its municipality, with an area of had a population of 76,219, the state's fourth-largest municipality in population. The port was developed in the late 19th century due to its location at the southern terminus of the Ferrocarril Transístmico, which carried freight across the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. History Salina Cruz, was founded by the Spanish in 1522 under whose command Pedro de Alvarado came. It was given the name "Salina de la Santa Cruz" as its official foundation day was the Catholic day of the holy cross. Salina Cruz is situated near the mouth of the Río Tehuantepec, on the open coast of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec on the Gulf of Tehuantepec, and has no nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the large-scale structure of its circulation remains fairly constant. The smaller scale weather systems – mid-latitude depressions, or tropical convective cells – occur chaotically, and long-range weather predictions of those cannot be made beyond ten days in practice, or a month in theory (see chaos theory and the butterfly effect). The Earth's weather is a consequence of its illumination by the Sun and the laws of thermodynamics. The atmospheric circulation can be viewed as a heat engine driven by the Sun's energy and whose energy sink, ultimately, is the blackness of space. The work produced by that engine causes the motion of the masses of air, and in that process it redistributes the energy absorbed by the Earth's surface near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-pressure Area
In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possible rain or storms), while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis force, Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In Meteorology#Dynamic meteorology, meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places: * The first is in the area on the east side of upper Trough (meteorology), troughs, which form half of a Rossby wave within the Westerlies (a trough (meteorology), trough with la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010 Pacific Hurricane Season
The 2010 Pacific hurricane season was the least active Pacific hurricane season since modern records, tied with 1977. The season saw only eight named storms, alongside a record-breaking low of three hurricanes. However, of those three, two of them became major hurricanes, and one hurricane, Celia, reached Category 5 intensity on the Saffir-Simpson scale. Also had the second-fewest ACE units on record, as many of the storms were weak and short-lived. The season officially began on May 15 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific basin. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year. Unlike the previous season, the first storm of the season, Agatha, formed during the month of May. Agatha developed on May 29 near the coast of Guatemala. In the second week of June, a sudden spre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm Andres (2021)
The 2021 Pacific hurricane season was a moderately active Pacific hurricane season, with above-average tropical activity in terms of named storms; but featured below-average activity in terms of major hurricanes and a near-normal accumulated cyclone energy (ACE). Five of the season's nineteen named storms made landfall in Mexico, the most since 2018. The season officially began on May 15 in the Eastern Pacific, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; both ending on November 30. These dates historically describe the period each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific basin and are adopted by convention. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year, as illustrated by the formation of Tropical Storm Andres on May 9, which became the earliest forming tropical storm in the northeastern Pacific proper (east of 140°W longitude) on record. In June, Tropical Storm Dolores made landfall near the border of the Mexican states of Colima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Depression One-E (2020)
The 2020 Pacific hurricane season was the least active Pacific hurricane season since 2011. The season was near average in terms of tropical storms, featuring a total of 17, but had a well below average number of hurricanes and major hurricanes, with only 4 hurricanes and 3 major hurricanes forming including one unnamed tropical storm which was operationally classified as a tropical depression, the first such occurrence since 2001. Despite this, it featured the earliest start to a season east of 140°W on record, with Tropical Depression One-E forming on April 25. The season officially began on May 15 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific and they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific basin. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year, as shown by the record-early formation of Tropical Depression One-E. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm Selma (2017)
Tropical Storm Selma was the first tropical storm on record to make landfall in El Salvador, and only the second Pacific tropical cyclone to attain tropical storm strength east of 90°W, the other being Alma of 2008. The twentieth tropical cyclone and eighteenth named storm of the 2017 Pacific hurricane season, Selma formed from a Central American gyre on October 27. The storm tracked northeastward and reached its peak intensity as a minimal tropical storm before making landfall east of San Salvador, El Salvador early on October 28. Selma rapidly weakened after making landfall, and its remnant circulation dissipated overland at 18:00 UTC on the same day. In anticipation of the storm's arrival, tropical storm warnings and watches were issued for the coast of El Salvador and the Pacific coast of Guatemala. Heavy rainfall associated with the storm and a cold front resulted in flash-flooding and mudslides that caused minor damage in El Salvador. The storm also caused 17 fatalities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |