|
2015 Finnish Parliamentary Election
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 19 April 2015, with advance voting taking place from 8 to 14 April. The 200 members of the Parliament of Finland were elected with the proportional D'Hondt method. There were 4,463,333 people entitled to vote in Finland and abroad. Background Previous government coalition The incumbent government was a four-party coalition composed of the National Coalition Party, Social Democratic Party, Swedish People's Party and the Christian Democrats as well as independent Member of Parliament Elisabeth Nauclér. The Left Alliance and the Green League were initially also part of the governing coalition, but both left in 2014. On 22 June 2011, the parliament elected Jyrki Katainen as prime minister by a vote of 118–72; two Left Alliance MPs voted against Katainen, for which they were formally reprimanded by the Left Alliance parliamentary group. They were subsequently expelled from the group, reducing the government majority from 126 MPs to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of Finland
The Parliament of Finland ( ; ) is the unicameral and supreme legislature of Finland, founded on 9 May 1906. In accordance with the Constitution of Finland, sovereignty belongs to the people, and that power is vested in the Parliament. The Parliament consists of 200 members, 199 of whom are elected every four years from 13 multi-member districts electing 7 to 36 members using the proportional D'Hondt method. In addition, there is one member from Åland. Legislation may be initiated by either the Government or one of the members of Parliament. The Parliament passes legislation, decides on the state budget, approves international treaties, and supervises the activities of the government. It may bring about the resignation of the Finnish Government, override presidential vetoes, and alter the constitution. To make changes to the constitution, amendments must be approved by two successive parliaments, with an election cycle in between, or passed as an emergency law with a 167/20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Democrats (Finland)
The Christian Democrats ( fi, Suomen Kristillisdemokraatit, sv, Kristdemokraterna i Finland; KD) is a Christian democracy, Christian-democratic list of political parties in Finland, political party in Finland. It was founded in May 1958, chiefly by the Christian faction of the National Coalition Party (Finland), National Coalition Party. It entered parliament in 1970. The party leader since 28 August 2015 has been Sari Essayah. The Christian Democrats have five seats in the Parliament of Finland, Finnish Parliament. It is positioned on the Centre-right politics, centre-right on the political spectrum. The party name was for a long time abbreviated to SKL (standing for , , ''Finnish Christian League''), until 2001, when the party changed its name to the current ''Christian Democrats'' and its abbreviation to ''KD''.The KD was a minor party in the Centre-right politics, centre-right coalition government led by Prime Minister of Finland, Prime Minister Esko Aho between 1991 and 199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savonia-Karelia (electoral District)
The Savo-Karelia constituency (Finnish: ''Savo-Karjalan vaalipiiri'', Swedish: ''Savolax-Karelens valkrets'') is a Finnish constituency represented in eduskunta. It covers the regions of North Karelia and Northern Savonia. The Savo-Karelia district currently elects 16 members of the ''Eduskunta''. The district was formed in 2013 by merging the electoral districts of Northern Savonia and North Karelia into one. Members of parliament 2015–2019 * Markku Eestilä (NCP) *Sari Essayah ( CD) * Hannakaisa Heikkinen (Centre) *Hannu Hoskonen (Centre) *Elsi Katainen (Centre) * Kimmo Kivelä (Finns) * Kari Kulmala (Finns) *Seppo Kääriäinen (Centre) *Krista Mikkonen ( Greens) * Riitta Myller ( SDP) * Merja Mäkisalo-Ropponen (SDP) * Pentti Oinonen (Finns) * Sari Raassina (NCP) * Markku Rossi (Centre) * Matti Semi (Left) * Anu Vehviläinen (Centre) 2019–2023 *Sanna Antikainen (Finns) * Markku Eestilä (NCP) *Seppo Eskelinen (SDP) *Sari Essayah (CD) * Hannakaisa Heikkinen (Centre) *Hannu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Karelia (electoral District)
North Karelia (formerly Kuopio East) was an electoral district represented in the Finnish ''Eduskunta'' (parliament). In 2013 it was merged with Northern Savonia electoral district to form the Savonia-Karelia electoral district. It covered the administrative region of North Karelia, with a population of 169,722 (). North Karelia elected six members of the ''Eduskunta'', when in 2005 there were still seven seats. The constituency was largely rural, centred on the city of Joensuu. The largest party in the Finnish parliamentary elections has traditionally been the Centre Party. The reduction of seats caused the Green League leader Tarja Cronberg to lose her seat in 2007 elections, even she got 11,7% and second the most votes in constituency. Members of parliament 2017–2021 2003–2007 * Tarja Cronberg ( VIHR) * Hannu Hoskonen ( Kesk.) * Lauri Kähkönen ( SDP) * Esa Lahtela (SDP) * Esko Mononen ( vas.) * Eero Reijonen (Kesk.) * Säde Tahvanainen (SDP) * Matti Väistö ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Savonia (electoral District)
Northern Savonia (formerly Kuopio) was an electoral district represented in the Finnish ''Eduskunta'' (parliament). Since 2013 it has been part of the Savonia Karelia electoral district. It covered the administrative region of Northern Savonia, with a population of about 251,000 (). Northern Savonia currently elects ten members of the ''Eduskunta''. The constituency is largely rural, and the only major city in the area is Kuopio. The largest party in the 1999, 2003 and 2007 elections was the Centre Party. 2015–2019 members of parliament * Markku Eestilä (NCP) * Sari Essayah (CD) * Hannakaisa Heikkinen (Centre) * Hannu Hoskonen (Centre) * Elsi Katainen (Centre) * Kimmo Kivelä (Finns) * Kari Kulmala (Finns) * Seppo Kääriäinen (Centre) * Krista Mikkonen (Greens) * Riitta Myller (SDP) * Merja Mäkisalo-Ropponen (SDP) * Pentti Oinonen (Finns) * Sari Raassina (NCP) * Markku Rossi (Centre) * Matti Semi (Left) * Anu Vehviläinen (Centre) 2019–2023 members of par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
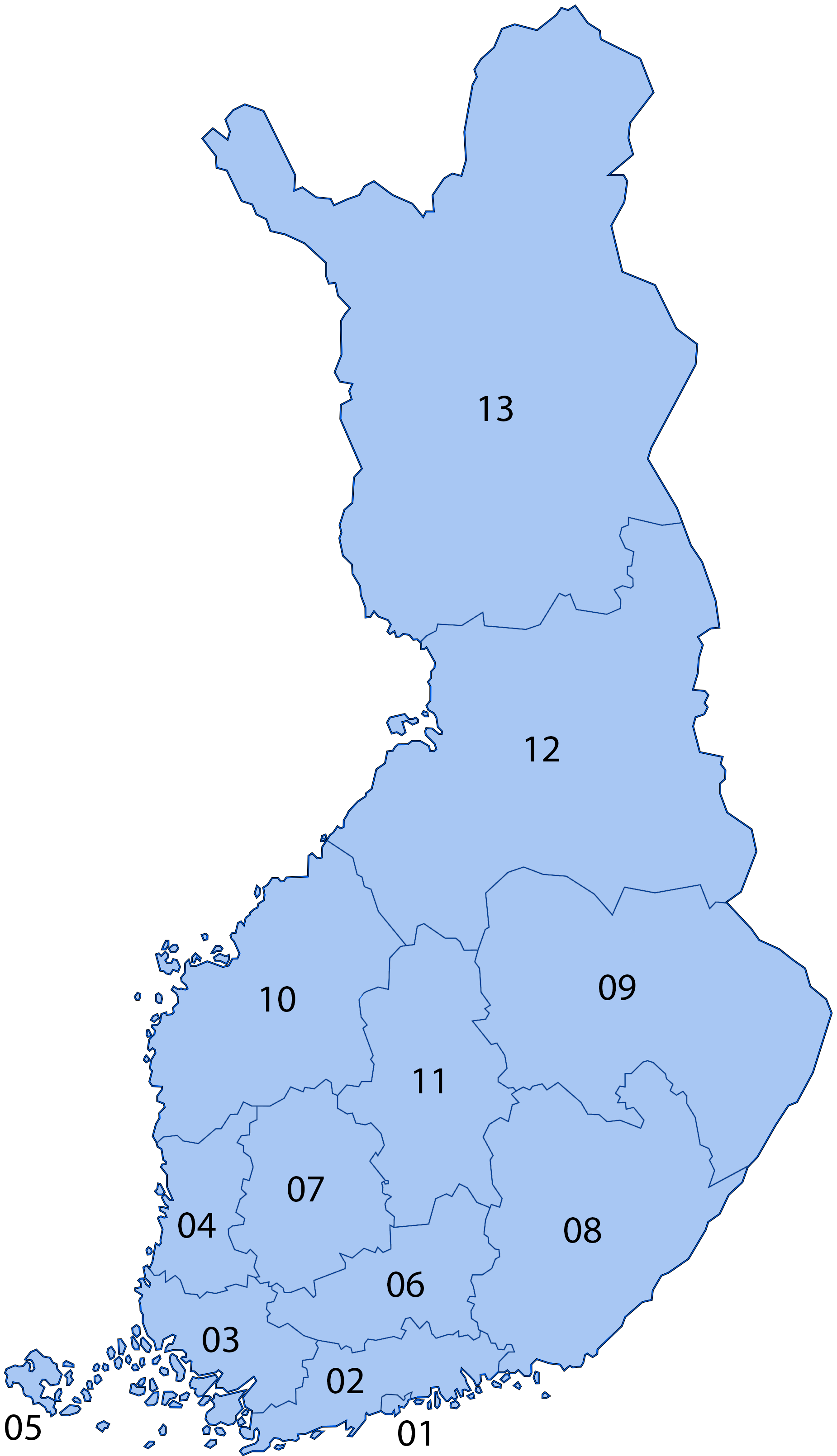
Electoral Districts Of Finland
There are thirteen constituencies in Finland, nowadays called electoral districts by the Finnish Parliament. (The English word "constituency" is confusing due to its various meanings.) The citizens of each electoral district elect from 6 to 35 MPs (members of parliament), depending on the population of the district, but 05 Åland only elects one. The boundaries of the electoral districts are based on the province division in use from 1634 to 1997 and has remained basically the same since the first parliamentary election in 1907. In 1939, the constituency of Northern Oulu was divided between the constituencies of Lapland and Oulu. The constituency of Southern Oulu was renamed to Oulu in the process. After the Continuation War, the electoral districts of Eastern and Western Viipuri, which lost much of their territories to the Soviet Union, were united to the new constituency of Kymi. At the same time, Åland became a distinct constituency. In 1954, Helsinki was cut from the consti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral Constituencies Of Finland 2013-2020
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office. Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated since the 17th century. Elections may fill offices in the legislature, sometimes in the executive and judiciary, and for regional and local government. This process is also used in many other private and business organisations, from clubs to voluntary associations and corporations. The global use of elections as a tool for selecting representatives in modern representative democracies is in contrast with the practice in the democratic archetype, ancient Athens, where the elections were considered an oligarchic institution and most political offices were filled using sortition, also known as allotment, by which officeholders were chosen by lot. Electoral reform describes the process of introducing fair electoral systems where they are no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speaker Of The Parliament Of Finland
The speaker of the Parliament of Finland (Finnish ''eduskunnan puhemies'', Swedish ''riksdagens talman''), along with two deputy speakers, is elected by Parliament during the first plenary session each year. Speakers are chosen for a year at a time. In addition to their preparing the work in plenary sessions the speakers also play a key role in Parliament's international co-operation, which includes visits by speakers and international delegations as well as participation in numerous interparliamentary organisations. The speaker and two deputy speakers are elected by parliament from among its members by secret ballot. After the election the speaker and deputy speakers each make the following solemn affirmation before Parliament: :''"I, ..., affirm that in my office as speaker I will to the best of my ability defend the rights of the people, parliament and the government of Finland according to the Constitution."'' Formally, the speaker ranks second in the protocol, after the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyhäjoki
Pyhäjoki (; literally the " Holy River") is a municipality of Finland. It is located in the defunct province of Oulu, which was split in two regions; Pyhäjoki is part of the Northern Ostrobothnia region. It is located southwest of the city of Oulu. The municipality is located on the Gulf of Bothnia at the mouth of the river Pyhäjoki. It has a population of () and covers an area of of which is water. The population density is . The municipality is unilingually Finnish. The subject of the coat of arms of Pyhäjoki refers to the large boulder of Hanhikivi ("Goose Rock") near the mouth of the Pyhäjoki river, which was considered by the Russians at the end of the 15th century as the landmark of the Treaty of Nöteborg from 1323; a crown and cross pattern is carved into the stone as a landmark. The coat of arms was designed by Olof Eriksson and approved by the Pyhäjoki Municipal Council at its meeting on June 18, 1965. The Ministry of the Interior confirmed the use of the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanhikivi Nuclear Power Plant
The Hanhikivi Nuclear Power Plant ( fi, Hanhikiven ydinvoimalaitos, sv, Hanhikivi kärnkraftverk) was a project to build a nuclear power plant on the Finnish Hanhikivi peninsula, in the municipality of Pyhäjoki. It was planned to house one Russian-designed VVER-1200 pressurised water reactor, with a capacity of 1200 MW. It was estimated that the reactor would supply 10% of Finland's energy demand by 2024. The power company Fennovoima announced in April 2021 that construction of the plant would begin in 2023 and commercial operation would start in 2029. In May 2022, in the wake of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, Fennovoima terminated its contract with Rosatom to build the power plant. Description On 21 April 2010, the Finnish Government decided to grant a permit (decision-in-principle) to Fennovoima for construction of a nuclear reactor. The decision was approved by the Parliament on 1 July 2010. The chosen plant model was Rosatom's pressurised water reactor AES-2006 w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fennovoima
Fennovoima Ltd ( fi, Fennovoima Oy) is a nuclear power company established by Russian state's nuclear company Rosatom and a consortium of Finnish state-owned power and industrial companies. The company does not own any nuclear capacities; however, it is preparing to build the 1200 MW Hanhikivi 1 nuclear power plant at Pyhäjoki. Fennovoima Board The Chairman of Fennovoima's Board is Juhani Pitkäkoski, Senior Vice President of M&A of Caverion Corporation while the Vice Chairman is Anastasia Zoteeva, Deputy Director General for Business Development of Rusatom Energy International. Other board members are Esa Lager, former CFO of Outokumpu Plc; Juha Mäkitalo, Attorney-at-Law; Stefan Storholm, CEO of Katternö Group; Seppo Siljama, and CEO of Rusatom Energy International Nikita Konstantinov. Deputy Members of the Board are Ilkka Salonen, CEO of Garmoshka Ltd, Djurica Tankosic, President of Global Nuclear of Worley Parsons; Jussi Lehto, CEO of Keravan and Pekka Erkkil� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jyrki Katainen
Jyrki Tapani Katainen (born 14 October 1971) is a Finnish politician who served as the European Commission's Vice-President for Jobs, Growth, Investment and Competitiveness from 2014 until 2019. Katainen was previously Prime Minister of Finland from 2011 to 2014 and chairman of the National Coalition Party from 2004 to 2014. He was succeeded by Alexander Stubb as chairman of Finland's National Coalition Party. After stepping down as Prime Minister, Katainen was elected as European Commission Vice-President in July 2014. Education and personal life Katainen was born in Siilinjärvi, a town in Finland. He graduated from Siilinjärvi Senior High School in 1990. He obtained a Master's degree in political science from the University of Tampere, spending one year at the University of Leicester as an Erasmus exchange student. Jyrki Katainen has two children: Saara (born in 2005) and Veera (2009). In addition to Finnish, Katainen speaks English, French and Swedish. Katainen is an accom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |