|
2012 Carterton Hot Air Balloon Crash
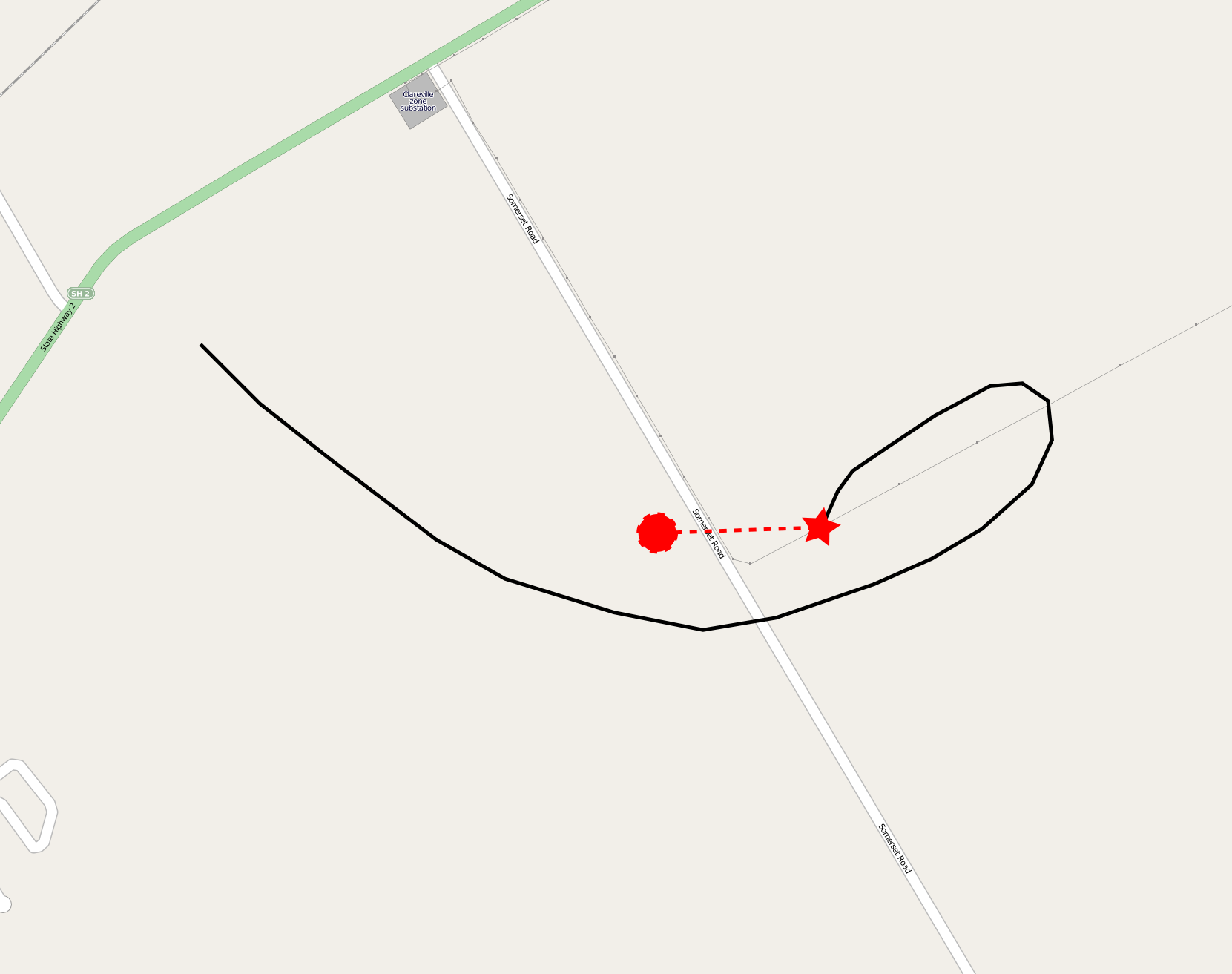
On 7 January 2012, a scenic hot air balloon flight from Carterton, New Zealand, collided with a high-voltage power line while attempting to land, causing it to catch fire, disintegrate and crash just north of the town, killing all eleven people on board. An inquiry into the accident by the Transport Accident Investigation Commission (TAIC) concluded that the balloon pilot had made an error of judgement when contact with the power lines became imminent, trying to outclimb the power lines rather than using the rapid descent system to drop the balloon quickly to the ground below. Toxicology analysis of the balloon pilot, Lance Hopping, after the accident tested positive for tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), suggesting he may have been under the influence of cannabis at the time of the crash, which ultimately led to the error in judgement. The crash was the sixth transport accident in ten years the TAIC had investigated which involved key people testing positive for drugs or alcohol, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilot Error
Pilot error generally refers to an Aviation accidents and incidents, accident in which an action or decision made by the Aircraft pilot#Airline, pilot was the cause or a contributing factor that led to the accident, but also includes the pilot's failure to make a correct decision or take proper action. Errors are intentional actions that fail to achieve their intended outcomes. Chicago Convention on International Civil Aviation, Chicago Convention defines accident as "An occurrence associated with the operation of an aircraft [...] in which [...] a person is fatally or seriously injured [...] ''except when the injuries are [...] inflicted by other persons."'' Hence the definition of the "pilot error" does not include deliberate crash (and such crash is not an accident). The causes of pilot error include psychological and physiological human limitations. Various forms of threat and error management have been implemented into pilot training programs to teach crew members how t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellington
Wellington ( mi, Te Whanganui-a-Tara or ) is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the second-largest city in New Zealand by metro area, and is the administrative centre of the Wellington Region. It is the world's southernmost capital of a sovereign state. Wellington features a temperate maritime climate, and is the world's windiest city by average wind speed. Legends recount that Kupe discovered and explored the region in about the 10th century, with initial settlement by Māori iwi such as Rangitāne and Muaūpoko. The disruptions of the Musket Wars led to them being overwhelmed by northern iwi such as Te Āti Awa by the early 19th century. Wellington's current form was originally designed by Captain William Mein Smith, the first Surveyor General for Edward Wakefield's New Zealand Company, in 1840. The Wellington urban area, which only includes urbanised ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Civil Aviation Authority
The Civil Aviation Authority of New Zealand (CAA; Māori: ''Te Mana Rererangi Tūmatanui o Aotearoa'') is the government agency tasked with establishing civil aviation safety and security standards in New Zealand. The CAA also monitors adherence to those standards and is responsible for enforcement proceedings. The authority "investigates and reviews accident and incident investigations in its capacity as the responsible safety and security authority, subject to the limitations set out in section 14(3) of the Transport Accident Investigation Commission Act 1990" (TAIC). CAA is also responsible for managing civilian pilot, aerodrome and aircraft licensing in New Zealand. The CAA has its headquarters in the Asteron Centre in Featherston Street, Wellington. Ministers of Civil Aviation Before a Civil Aviation portfolio was created in 1946, ministerial authority had rested with the Minister of Defence. The position of Minister for Civil Aviation was abolished just before the 1990 elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellington Hospital, New Zealand
Wellington Hospital, also known as Wellington Regional Hospital, is the main hospital in Wellington, New Zealand, located south of the city centre in the suburb of Newtown. It is the main hospital run by Capital & Coast District Health Board (C&CDHB), which serves Wellington City, Porirua and the Kapiti Coast District. Lower Hutt and Upper Hutt have a separate district health board, the Hutt Valley DHB, and a separate hospital, Hutt Hospital, in the Lower Hutt suburb of Boulcott. Wellington Hospital is the Wellington Region's main tertiary hospital, with services such as complex specialist and acute (or "tertiary") services, procedures and treatments such as the Intensive Care Unit, cardiac surgery, cancer care, cardiology procedures, neurosurgery, and renal care. The hospital is a tertiary referral centre for the lower half of the North Island and the top of the South Island (specifically the Hawke's Bay, Manawatu-Wanganui, Wellington, Tasman, Nelson and Marlborough region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquefied Petroleum Gas
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG or LP gas) is a fuel gas which contains a flammable mixture of hydrocarbon gases, specifically propane, propylene, butylene, isobutane and n-butane. LPG is used as a fuel gas in heating appliances, cooking equipment, and vehicles. It is increasingly used as an aerosol propellant and a refrigerant, replacing chlorofluorocarbons in an effort to reduce damage to the ozone layer. When specifically used as a vehicle fuel, it is often referred to as autogas or even just as gas. Varieties of LPG that are bought and sold include mixes that are mostly propane (), mostly butane (), and, most commonly, mixes including both propane and butane. In the northern hemisphere winter, the mixes contain more propane, while in summer, they contain more butane. In the United States, mainly two grades of LPG are sold: commercial propane and HD-5. These specifications are published by the Gas Processors Association (GPA) and the American Society of Testing and Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Circuit
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit. The opposite of a short circuit is an "open circuit", which is an infinite resistance between two nodes. Definition A short circuit is an abnormal connection between two nodes of an electric circuit intended to be at different voltages. This results in an electric current limited only by the Thévenin equivalent resistance of the rest of the network which can cause circuit damage, overheating, fire or explosion. Although usually the result of a fault, there are cases where short circuits are caused intentionally, for example, for the purpose of voltage-sensing crowbar circuit protectors. In circuit analysis, a ''short circuit'' is defined as a connection between two nodes that forces them to be at the same voltage. In an 'ideal' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Arcing
An electric arc, or arc discharge, is an electrical breakdown of a gas that produces a prolonged electrical discharge. The current through a normally nonconductive medium such as air produces a plasma; the plasma may produce visible light. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge and relies on thermionic emission of electrons from the electrodes supporting the arc. An archaic term is voltaic arc, as used in the phrase "voltaic arc lamp". Techniques for arc suppression can be used to reduce the duration or likelihood of arc formation. In the late 19th century, electric arc lighting was in wide use for public lighting. Some low-pressure electric arcs are used in many applications. For example, fluorescent tubes, mercury, sodium, and metal-halide lamps are used for lighting; xenon arc lamps have been used for movie projectors. Electric arcs can be utilized for manufacturing processes, such as electric arc welding, and electric arc furnaces for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transpower New Zealand Limited
Transpower New Zealand Limited (TPNZ) is the state-owned enterprise responsible for electric power transmission in New Zealand. It performs two major functions in the New Zealand electricity market. As the owner of the National Grid it provides the infrastructure of electric power transmission that allows consumers to have access to generation from a wide range of sources, and enables competition in the wholesale electricity market; as system operator it manages the real-time operation of the grid and the physical operation of the electricity market. Transpower was initially formed as an operating division of the Electricity Corporation of New Zealand (ECNZ) in 1987. In 1994 it was separated from ECNZ and corporatised to become a state-owned enterprise with its own board of directors and ministerial shareholders, the Minister of Finance and the Minister of State-Owned Enterprises. The New Zealand Treasury's Commercial Operations group (formerly the Crown Ownership Monitori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Substation
A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions. Between the generating station and consumer, electric power may flow through several substations at different voltage levels. A substation may include transformers to change voltage levels between high transmission voltages and lower distribution voltages, or at the interconnection of two different transmission voltages. They are a common component of the infrastructure, for instance there are 55,000 substations in the United States. Substations may be owned and operated by an electrical utility, or may be owned by a large industrial or commercial customer. Generally substations are unattended, relying on SCADA for remote supervision and control. The word ''substation'' comes from the days before the distribution system became a grid. As central generation stations became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand State Highway 2
State Highway 2 (SH 2) runs north–south through eastern parts of the North Island of New Zealand from the outskirts of Auckland to Wellington. It runs through Tauranga, Gisborne, Napier, Hastings and Masterton. It is the second-longest highway in the North Island, after State Highway 1, which runs the length of both of the country's main islands. For most of its length it consists of a two-lane single carriageway, with frequent passing lanes. There are sections of four-lane dual-carriageway expressway at Maramarua, Tauranga and Wellington. Route SH 2 leaves just north of Pōkeno, south of central Auckland. It heads east, crossing the Hauraki Plains before running the length of the Karangahake Gorge, a break in the hills between the Coromandel Peninsula and Kaimai Ranges. From the mining town of Waihi it runs southeast, skirting the edge of Tauranga Harbour, which it crosses on the Tauranga Harbour Bridge before connecting to the Tauranga Eastern Link, a four lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Air Ballooning
Hot air ballooning is the activity of flying hot air balloons. Attractive aspects of ballooning include the exceptional quiet (except when the propane burners are firing), the lack of a feeling of movement, and the bird's-eye view. Since the balloon moves with the direction of the winds, the passengers feel absolutely no wind, except for brief periods during the flight when the balloon climbs or descends into air currents of different direction or speed. Hot air ballooning has been recognized by Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI) as the safest air sport in aviation, and fatalities in hot air balloon accidents are rare, according to statistics from the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB). History First manned flight The first clearly recorded instance of a balloon carrying passengers used hot air to generate buoyancy and was built by the brothers Joseph-Michel and Jacques-Etienne Montgolfier in Annonay, France. After experimenting with unmanned bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2012 Carterton HAB Crash Map
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |