|
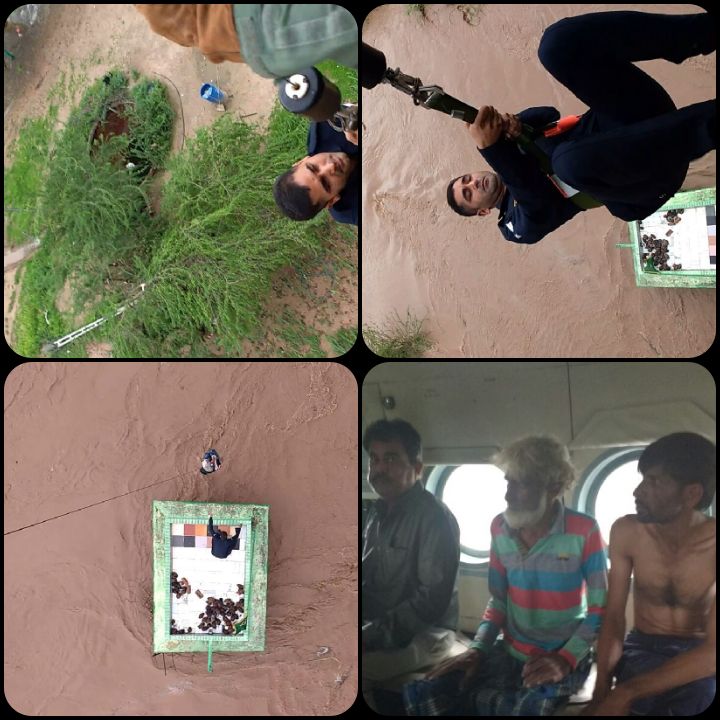
2006 Surat Flood
The 2006 Surat flood occurred over 7–10 August 2006, which affected Surat, India, and nearby villages. About 80–95% of Surat was flooded. The sudden release of a large amount of water into the Tapti River from the Ukai Dam caused the flood. The Government of Gujarat described the flood as a natural disaster, while reports from the ''People's Committee on Gujarat Floods of August 2006'' and the ''Surat Citizens' Council Trust's Committee'', described the flood as being the result of mismanagement. History of floods in Surat In the 20th century the city of Surat has suffered from some 20 floods. The 1968 flood was one of the major floods with peak water flow of about 15 ''lakh'' cubic foot per second (cfs or cusec), while the 1970 flood had a peak flow about 13.14 ''lakh'' cfs. The Ukai Dam was constructed in 1972, flood control was one of the objectives of the dam's construction. After the dam was constructed 90 km upstream from Surat, there were no major floods until 199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaurav Path
Gaurav Path is an expressway in Piplod, Surat, India. It was designed and constructed by the Surat Municipal Corporation as a part of a plan to connect Surat City with its airport, Magdalla Sea Port and Dumas Village. The expressway replaced the prior Surat-Dumas Road and is one of the best examples of Town and City Planning in India. This expressway has three travel lanes in each direction, two service lanes and a Bus Rapid Transit System (BRTS) lane in each direction. There are only two exits, the SVNIT Circle at Icchanath and Kargil Chowk at Piplod. It was designed to meet international standards and was integrated with BRTS. There is a study being carried out on IPTS (Integrated Public Transport System) by CES which is supported by the GIDB (Gujarat Industrial development Board). There are several illuminated bus stops either side of the expressway, which can be accessed through paved, broad footpaths. These footpaths divide the expressway with its service roads on either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surat
Surat is a city in the western Indian state of Gujarat. The word Surat literally means ''face'' in Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of the river Tapti near its confluence with the Arabian Sea, it used to be a large seaport. It is now the commercial and economic center in South Gujarat, and one of the largest urban areas of western India. It has well-established diamond and textile industry, and is a major supply centre for apparels and accessories. About 90% of the world's diamonds supply are cut and polished in the city. It is the second largest city in Gujarat after Ahmedabad and the eighth largest city by population and ninth largest urban agglomeration in India. It is the administrative capital of the Surat district. The city is located south of the state capital, Gandhinagar; south of Ahmedabad; and north of Mumbai. The city centre is located on the Tapti River, close to Arabian Sea. Surat will be the world's fastest growing city from 2019 to 2035, acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapti River
The Tapti River (or Tapi) is a river in central India located to the south of the Narmada river that flows westwards before draining into the Arabian Sea. The river has a length of around and flows through the states of Maharashtra, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh. It flows through Surat, and is crossed by the Magdalla, ONGC Bridge. On 7 August 1968, before the construction of the Ukai Dam to bring its waters under control and provide hydroelectric power, the Tapti River overflowed its banks during heavy rains during the monsoon season. More than 1,000 people drowned in the flood, and the city of Surat was submerged beneath 10 feet of water for several days. After the floodwaters receded, at least 1,000 more people died in Gujarat during a cholera epidemic from the contamination of the drinking water. Its basin covers the parts of Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat and Maharashtra. Course The Tapti River rises in Multai, in Madhya Pradesh, and has a total length of around . It is the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukai Dam
The Ukai Dam, constructed across the Tapi River, is the second largest reservoir in Gujarat after the Sardar Sarovar. It is also known as Vallabh Sagar. Constructed in 1972, the dam is meant for irrigation, power generation and flood control. Having a catchment area of about 62,255 km2 and a water spread of about 52,000 hectares, its capacity is almost same as that of the Bhakra Nangal Dam. The site is located 94 km from Surat. The dam is an earth-cum-masonry dam. Its embankment wall is 4,927 m long. Its earth dam is 105.156 meters high, whereas the masonry dam is 68.68 meters high. The dam's left bank canal feeds water to an area of 1,522 km2. and its right canal provides water to 2,275 km2 of land. A fort built by the Gaekwad dynasty of Baroda was submerged in the reservoir. It can be spotted when water levels in the reservoir goes down. Ukai Hydro Power Station There are four hydro turbine units, each of 75 MW with a total installed capacity of 300 MW. All ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Gujarat
The Government of Gujarat, also known as Gujarat Government, is the supreme governing authority of the Indian state of Gujarat and its 33 districts. It consists of an executive of the legislators appointed by the Governor of Gujarat, a judiciary and of a publicly elected legislative body. Like other states in India, the head of state of Gujarat is the Governor, appointed by the President of India on the advice of the Central (Union) government. The governor's role is largely ceremonial, but the governor considers the legislative composition and appoints the Chief Minister, who is the main head of government, as chair of the Council of Ministers of Gujarat and is vested, in some instances alone but as to most executive powers by Council consensus with virtually all of the executive powers. Gandhinagar, the capital of Gujarat, houses the relevant Vidhan Sabha (also known as the Gujarat Legislative Assembly) and the secretariat. The Gujarat High Court in Ahmedabad, has jurisdiction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Disaster
A natural disaster is "the negative impact following an actual occurrence of natural hazard in the event that it significantly harms a community". A natural disaster can cause loss of life or damage property, and typically leaves some economic damage in its wake. The severity of the damage depends on the affected population's resilience and on the infrastructure available. Examples of natural hazards include: avalanche, coastal flooding, cold wave, drought, earthquake, hail, heat wave, hurricane (tropical cyclone), ice storm, landslide, lightning, riverine flooding, strong wind, tornado, typhoon, tsunami, volcanic activity, wildfire, winter weather. In modern times, the divide between natural, man-made and man-accelerated disasters is quite difficult to draw. Human choices and activities like architecture, fire, resource management or even climate change potentially play a role in causing "natural disasters". In fact, the term "natural disaster" has been called a misnom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakh
A lakh (; abbreviated L; sometimes written lac) is a unit in the Indian numbering system equal to one hundred thousand (100,000; scientific notation: 105). In the Indian 2,2,3 convention of digit grouping, it is written as 1,00,000. For example, in India, 150,000 rupees becomes 1.5 ''lakh'' rupees, written as 1,50,000 or INR 1,50,000. It is widely used both in official and other contexts in Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. It is often used in Bangladeshi, Indian, Pakistani, and Sri Lankan English. Usage In Indian English, the word is used both as an attributive and non-attributive noun with either an unmarked or marked ("-s") plural, respectively. For example: "1 ''lakh'' people"; "''lakhs'' of people"; "20 ''lakh'' rupees"; "''lakhs'' of rupees". In the abbreviated form, usage such as "5L" or "5 lac" (for "5 ''lakh'' rupees") is common. In this system of numeration, 100 ''lakh'' is called one '' crore'' and is equa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Foot
Cubic may refer to: Science and mathematics * Cube (algebra), "cubic" measurement * Cube, a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex ** Cubic crystal system, a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube * Cubic function, a polynomial function of degree three * Cubic equation, a polynomial equation (reducible to ''ax''3 + ''bx''2 + ''cx'' + ''d'' = 0) * Cubic form, a homogeneous polynomial of degree 3 * Cubic graph (mathematics - graph theory), a graph where all vertices have degree 3 * Cubic plane curve (mathematics), a plane algebraic curve ''C'' defined by a cubic equation * Cubic reciprocity (mathematics - number theory), a theorem analogous to quadratic reciprocity * Cubic surface, an algebraic surface in three-dimensional space * Cubic zirconia, in geology, a mineral that is widely synthesized for use as a diamond simulacra * CUBIC, a histology method Computing * Cubic IDE, a modular de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2005 Gujarat Flood
The 2005 Gujarat floods, during the monsoon season, affected the state of Gujarat, India, that included 20 districts (out of 33), with 10 of them severely affected. 117 of the 225 Tehsils (Talukas or mandals), 11 cities were included, and more than 7,200 villages inundated, with up to 10,000 affected. The cumulative of rain left approximately 176,000 people homeless during the flooding that included the drowning of a rare Asiatic lion from the Gir wildlife sanctuary. At least 173 people were killed in the flooding. History Eleven cities were severely affected by the floods that were Vadodara, Nadiad, Ahmedabad, Navsari, Surat and Limbdi, Dakor, Anand, Kheda, Petlad, and Borsad. A brief time-line See also * Disaster Management Act, 2005 * Maharashtra floods of 2005 * 2005 Chennai floods * 2006 Surat flood * 2017 Gujarat flood * 2019 Vadodara flood References {{Reflist External links Rediff.com [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2017 Gujarat Flood
Following heavy rain in July 2017, the Indian state of Gujarat was affected by severe flooding. The floods were reported to have caused total 224 deaths between 1 June and 31 July 2017. 16 people had died in neighbouring Rajasthan state by 31 July. information The monsoon season in Gujarat typically starts in mid-June. In the 2017 season low pressure systems developed over the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal simultaneously, resulting in heavy rainfall. Moderate rain began across the state on 14 July, and heavy rains fell from 21 to 25 July. Flooding of Gujarat According to the Indian Meteorological Department data, between 1 and 28 July, Gujarat received 559.4 mm of rainfall, as against the average of 339.6 mm for the said period, representing an excess of 65%. The districts of Banaskantha, Patan, Gandhinagar, Morbi, Surendranagar, Mehsana and Sabarkantha received 267%, 208%, 189%, 174%, 172%, 130% and 115% respectively of their average rainfall for the same period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2019 Vadodara Flood
Due to heavy rain in July–August 2019, the city of Vadodara and its administrative district in the Indian state of Gujarat were affected by severe flooding. On 31 July 2019, nearly 50 cm of rain fell on Vadodara within 12 hours, with 424mm recorded in one 6 hour period. As a result, the nearby Vishwamitri River rose to 1 metre below the danger line and the Ajwa dam overflowed, flooding the city. Consequences The flood caused 8 deaths and the evacuation of more than 6000 people by the NDRF and SDRF. Train services were cancelled owing to water-logging, and the electricity supply was interrupted. On 1 August, Vadodara Airport was closed, GSRTC buses were cancelled and 69 trains passing through Vadodara Junction railway station were either cancelled or rerouted. As water in the Vadodara receded, Crocodile Crocodiles (family (biology), family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Disasters In India
Natural catastrophe in India, many of them related to the climate of India, cause massive losses of life and property. Droughts, flash floods, cyclones, avalanches, landslides brought by torrential rains, and snowstorms pose the greatest threats. A natural disaster might be caused by earthquakes, flooding, volcanic eruption, landslides, hurricanes etc. In order to be classified as a disaster, it will need to have a profound environmental effect and/or human loss and frequently incurs a financial loss. Other dangers include frequent summer dust storms, which usually track from north to south; they cause extensive property damage in North India. and deposit large amounts of dust and dirt from arid regions. Hail is also common in parts of India, causing severe damage to standing crops such as rice and wheat and many more ''crops.'' Landslides and avalanches Landslides are very common in the Lower Himalayas. The young age of the region's hills results in rock formations, which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |