|
2D Adaptive Filters
A two-dimensional (2D) adaptive filter is very much like a one-dimensional adaptive filter in that it is a linear system whose parameters are adaptively updated throughout the process, according to some optimization approach. The main difference between 1D and 2D adaptive filters is that the former usually take as inputs signals with respect to time, what implies in causality constraints, while the latter handles signals with 2 dimensions, like x-y coordinates in the space domain, which are usually non-causal. Moreover, just like 1D filters, most 2D adaptive filters are digital filters, because of the complex and iterative nature of the algorithms. Motivation The topic of 2D adaptive filters is very important in electrical engineering and signal processing since these filters have the ability to take into account the nonstationary statistical properties of 2D signals. Adaptive filters find applications in areas such as Noise cancellation, Signal prediction, Equalization and Echo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
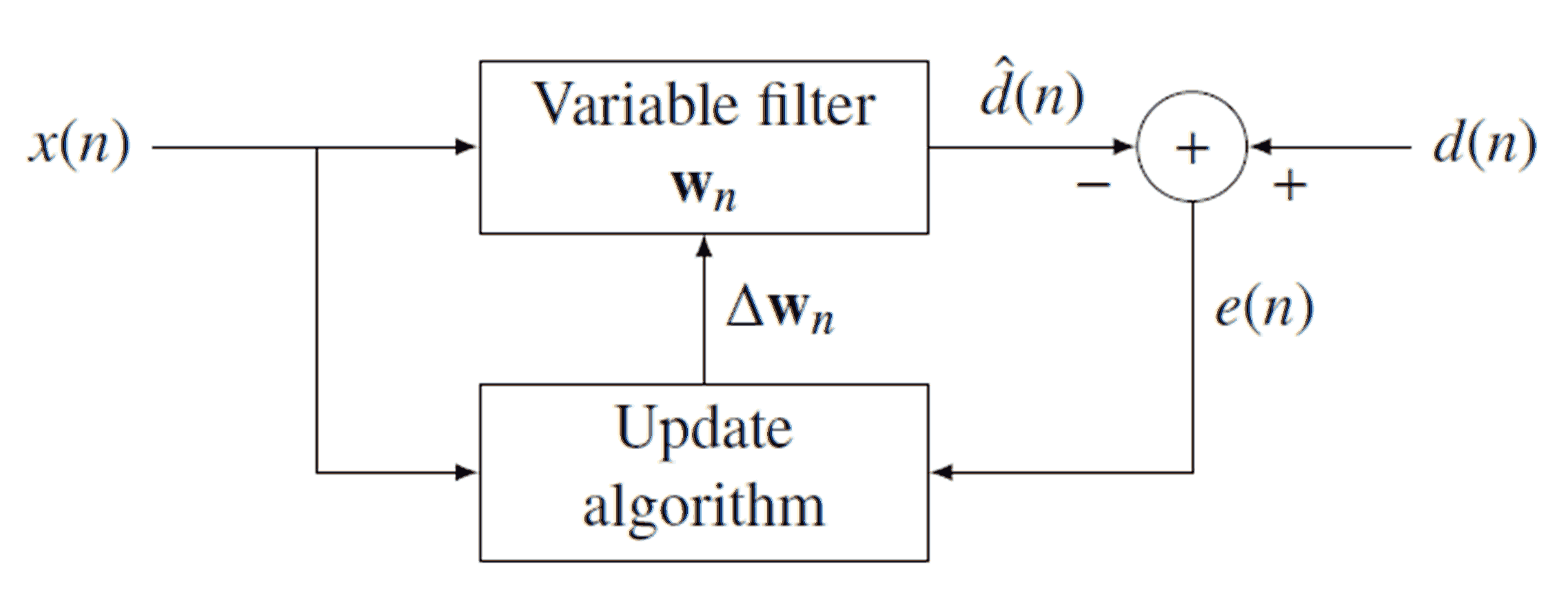
Adaptive Filter
An adaptive filter is a system with a linear filter that has a transfer function controlled by variable parameters and a means to adjust those parameters according to an optimization algorithm. Because of the complexity of the optimization algorithms, almost all adaptive filters are digital filters. Adaptive filters are required for some applications because some parameters of the desired processing operation (for instance, the locations of reflective surfaces in a reverberant space) are not known in advance or are changing. The closed loop adaptive filter uses feedback in the form of an error signal to refine its transfer function. Generally speaking, the closed loop adaptive process involves the use of a cost function, which is a criterion for optimum performance of the filter, to feed an algorithm, which determines how to modify filter transfer function to minimize the cost on the next iteration. The most common cost function is the mean square of the error signal. As the pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recursive Least Squares Filter
Recursive least squares (RLS) is an adaptive filter algorithm that recursively finds the coefficients that minimize a weighted linear least squares cost function relating to the input signals. This approach is in contrast to other algorithms such as the least mean squares (LMS) that aim to reduce the mean square error. In the derivation of the RLS, the input signals are considered deterministic, while for the LMS and similar algorithms they are considered stochastic. Compared to most of its competitors, the RLS exhibits extremely fast convergence. However, this benefit comes at the cost of high computational complexity. Motivation RLS was discovered by Gauss but lay unused or ignored until 1950 when Plackett rediscovered the original work of Gauss from 1821. In general, the RLS can be used to solve any problem that can be solved by adaptive filters. For example, suppose that a signal d(n) is transmitted over an echoey, noisy channel that causes it to be received as :x(n)=\sum_^q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infinite Impulse Response
Infinite impulse response (IIR) is a property applying to many linear time-invariant systems that are distinguished by having an impulse response h(t) which does not become exactly zero past a certain point, but continues indefinitely. This is in contrast to a finite impulse response (FIR) system in which the impulse response ''does'' become exactly zero at times t>T for some finite T, thus being of finite duration. Common examples of linear time-invariant systems are most electronic and digital filters. Systems with this property are known as ''IIR systems'' or ''IIR filters''. In practice, the impulse response, even of IIR systems, usually approaches zero and can be neglected past a certain point. However the physical systems which give rise to IIR or FIR responses are dissimilar, and therein lies the importance of the distinction. For instance, analog electronic filters composed of resistors, capacitors, and/or inductors (and perhaps linear amplifiers) are generally IIR filter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least Mean Squares Filter
Least mean squares (LMS) algorithms are a class of adaptive filter used to mimic a desired filter by finding the filter coefficients that relate to producing the least mean square of the error signal (difference between the desired and the actual signal). It is a stochastic gradient descent method in that the filter is only adapted based on the error at the current time. It was invented in 1960 by Stanford University professor Bernard Widrow and his first Ph.D. student, Ted Hoff. Problem formulation Relationship to the Wiener filter The realization of the causal Wiener filter looks a lot like the solution to the least squares estimate, except in the signal processing domain. The least squares solution, for input matrix \mathbf and output vector \boldsymbol y is : \boldsymbol = (\mathbf ^\mathbf\mathbf)^\mathbf^\boldsymbol y . The FIR least mean squares filter is related to the Wiener filter, but minimizing the error criterion of the former does not rely on cross-corr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impulse Response
In signal processing and control theory, the impulse response, or impulse response function (IRF), of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an Dirac delta function, impulse (). More generally, an impulse response is the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change. In both cases, the impulse response describes the reaction of the system as a Function (mathematics), function of time (or possibly as a function of some other independent variable that parameterizes the dynamic behavior of the system). In all these cases, the dynamic system and its impulse response may be actual physical objects, or may be mathematical systems of equations describing such objects. Since the impulse function contains all frequencies (see Dirac delta function#Fourier transform, the Fourier transform of the Dirac delta function, showing infinite frequency bandwidth that the Dirac delta function has), the impulse response defines the response ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions ( and ) that produces a third function (f*g) that expresses how the shape of one is modified by the other. The term ''convolution'' refers to both the result function and to the process of computing it. It is defined as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result (see #Properties, commutativity). The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function. Some features of convolution are similar to cross-correlation: for real-valued functions, of a continuous or discrete variable, convolution (f*g) differs from cross-correlation (f \star g) only in that either or is reflected about the y-axis in convolution; thus it is a cross-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LTI System Theory
LTI can refer to: * ''LTI – Lingua Tertii Imperii'', a book by Victor Klemperer * Language Technologies Institute, a division of Carnegie Mellon University * Linear time-invariant system, an engineering theory that investigates the response of a linear, time-invariant system to an arbitrary input signal * ''Licensed to Ill'', the 1986 debut album by the Beastie Boys * Lost Time Incident or industrial injury or Occupational injury * Learning Tools Interoperability * Louisiana Training Institute-East Baton Rouge, later known as the Jetson Center for Youth (JCY), a juvenile prison in Louisiana Companies * London Taxis International * Larsen & Toubro Infotech Biology and medicine * Lymphoid tissue-inducer cell, see innate lymphoid cell Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are the most recently discovered family of innate immune cells, derived from common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs). In response to pathogenic tissue damage, ILCs contribute to immunity via the secretion of signalling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
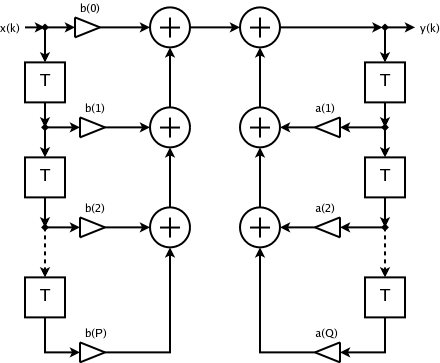
Block Diagram Of 2d Adaptive Filters
Block or blocked may refer to: Arts, entertainment and media Broadcasting * Block programming, the result of a programming strategy in broadcasting * W242BX, a radio station licensed to Greenville, South Carolina, United States known as ''96.3 the Block '' * WFNZ-FM, a radio station licensed to Harrisburg, North Carolina, United States, branded as ''92.7 The Block'' * Blocked (''The Flash''), an episode of the television series ''The Flash'' Music * Block Entertainment, a record label * Blocks Recording Club, a record label * Woodblock (instrument), a small piece of slit drum made from one piece of wood and used as a percussion instrument * "Blocks", by C418 from '' Minecraft - Volume Beta'', 2013 Toys * Toy block, one of a set of wooden or plastic pieces, of various shapes * Unit block, a type of standardized wooden toy block for children Video game * Blocked (video game), a puzzle game for the iPhone and iPod Touch Building and construction * Breeze block, cinder block or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causal System
In control theory, a causal system (also known as a physical or nonanticipative system) is a system where the output depends on past and current inputs but not future inputs—i.e., the output y(t_) depends only on the input x(t) for values of t \le t_. The idea that the output of a function at any time depends only on past and present values of input is defined by the property commonly referred to as causality. A system that has ''some'' dependence on input values from the future (in addition to possible dependence on past or current input values) is termed a non-causal or acausal system, and a system that depends ''solely'' on future input values is an anticausal system. Note that some authors have defined an anticausal system as one that depends solely on future ''and present'' input values or, more simply, as a system that does not depend on past input values. Classically, nature or physical reality has been considered to be a causal system. Physics involving special relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echo Suppression And Cancellation
Echo suppression and echo cancellation are methods used in telephony to improve voice quality by preventing echo from being created or removing it after it is already present. In addition to improving subjective audio quality, echo suppression increases the capacity achieved through silence suppression by preventing echo from traveling across a telecommunications network. Echo suppressors were developed in the 1950s in response to the first use of satellites for telecommunications. Echo suppression and cancellation methods are commonly called acoustic echo suppression (AES) and acoustic echo cancellation (AEC), and more rarely line echo cancellation (LEC). In some cases, these terms are more precise, as there are various types and causes of echo with unique characteristics, including acoustic echo (sounds from a loudspeaker being reflected and recorded by a microphone, which can vary substantially over time) and line echo (electrical impulses caused by, e.g., coupling between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equalization (audio)
Equalization, or simply EQ, in sound recording and reproduction is the process of adjusting the volume of different frequency bands within an audio signal. The circuit or equipment used to achieve this is called an equalizer. Most hi-fi equipment uses relatively simple filters to make bass and treble adjustments. Graphic and parametric equalizers have much more flexibility in tailoring the frequency content of an audio signal. Broadcast and recording studios use sophisticated equalizers capable of much more detailed adjustments, such as eliminating unwanted sounds or making certain instruments or voices more prominent. Since equalizers "adjust the amplitude of audio signals at particular frequencies" they are, "in other words, frequency-specific volume knobs." Equalizers are used in recording studios, radio studios and production control rooms, and live sound reinforcement and in instrument amplifiers, such as guitar amplifiers, to correct or adjust the response of mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |