|
2023–24 South-West Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 2023–24 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season is the current event of the annual cycle of tropical and subtropical cyclogenesis. It began on 15 November 2023, and will end on 30 April 2024, with the exception for Mauritius and the Seychelles, for which it will end on 15 May 2024. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical and subtropical cyclones form in the basin, which is west of 90°E and south of the Equator. However, tropical cyclones can form year-round, and all tropical cyclones that will form between 1 July 2023 and 30 June 2024 will be part of the season. Tropical and subtropical cyclones in this basin are monitored by the Regional Specialised Meteorological Centre in Réunion and unofficially by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. __TOC__ Seasonal forecasts In October 2023, Météo-France issued its seasonal forecast of cyclone activity for the basin, predicting a below-average season with 5–8 moderate tropical storms due to an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021–22 South-West Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 2021–22 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season featured the record latest start for the first system to develop. Despite the late start, it was an above-average season that produced 12 named storms, with 5 becoming tropical cyclones. The season began on 15 November 2021, and ended on 30 April 2022, with the exception for Mauritius and the Seychelles, for which it ended on 15 May 2022. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical and subtropical cyclones form in the basin, which is west of 90°E and south of the Equator. However, tropical cyclones that form at any time between 1 July 2021 and 30 June 2022 will count towards the season total. Tropical and subtropical cyclones in this basin are monitored by the Regional Specialised Meteorological Centre in Réunion and unofficially by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. __TOC__ Seasonal summary ImageSize = width:1070 height:225 PlotArea = top:10 bottom:80 right:20 left:20 Legend = columns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Météo-France
Météo-France is the French national meteorological service. Organisation The organisation was established by decree in June 1993 and is a department of the Ministry of Transportation. It is headquartered in Paris but many domestic operations have been decentralised to Toulouse. Its budget of around €300 million is funded by state grants, aeronautic royalties and sale of commercial services. Météo-France has a particularly strong international presence, and is the French representative at the World Meteorological Organization. The organisation is a leading member of EUMETSAT, responsible for the procurement of Meteosat weather satellites. It is also member of the Institut au service du spatial, de ses applications et technologies. It also a critical national weather service member of the ECMWF and hosts one of two major centres of the IFS numerical weather prediction model widely used worldwide. Worldwide In addition to its operations in metropolitan France, the agen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergence Zone
A convergence zone in meteorology is a region in the atmosphere where two prevailing flows meet and interact, usually resulting in distinctive weather conditions. This causes a mass accumulation that eventually leads to a vertical movement and to the formation of clouds and precipitation. Large-scale convergence, called synoptic-scale convergence, is associated with weather systems such as baroclinic troughs, low-pressure areas, and cyclones. The large-scale convergence zone formed over the equator, the Intertropical Convergence Zone, has condensed and intensified as a result of the global increase in temperature. Small-scale convergence will give phenomena from isolated cumulus clouds to large areas of thunderstorms. The inverse of convergence is divergence. Large scale An example of a convergence zone is the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a low pressure area which girdles the Earth at the Equator.Waliser, D.E.; Jiang, X. (2015). "Tropical Meteorology and Climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beira, Mozambique
Beira is the capital and largest city of Sofala Province, where the Pungwe River meets the Indian Ocean, in the central region of Mozambique. It is the fourth-largest city by population in Mozambique, after Maputo, Matola and Nampula. Beira had a population of 397,368 in 1997, which grew to 530,604 in 2019. A coastal city, it holds the regionally significant Port of Beira, which acts as a gateway for both the central interior portion of the country as well as the land-locked nations of Zimbabwe, Zambia and Malawi. Originally called Chiveve after a local river, it was renamed Beira to honour the Portuguese Crown prince Dom Luís Filipe (titled Prince of Beira, itself referring to the traditional Portuguese province of Beira), who had visited Mozambique in the early 1900s. It was first developed by the Portuguese Mozambique Company in the 19th century, supplanting Sofala as the country's main port. It was then directly developed by the Portuguese colonial government from 1947 until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Convection
Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air masses lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes. Overview There are a few general archetypes of atmospheric instability that are used to explain convection (or lack thereof). A necessary (but not sufficient) condition for convection is that the environmental lapse rate (the rate of decrease of temperature with height) is steeper than the lapse rate experienced by a rising parcel of air. When this condition is met, upward-displaced air parcels can become buoyant and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon Trough
The monsoon trough is a portion of the Intertropical Convergence Zone in the Western Pacific,Bin WangThe Asian Monsoon.Retrieved 2008-05-03. as depicted by a line on a weather map showing the locations of minimum sea level pressure, and as such, is a convergence zone between the wind patterns of the southern and northern hemispheres. Westerly monsoon winds lie in its equatorward portion while easterly trade winds exist poleward of the trough. Right along its axis, heavy rains can be found which usher in the peak of a location's respective rainy season. As it passes poleward of a location, hot and dry conditions develop. The monsoon trough plays a role in creating many of the world's rainforests. The term ''monsoon trough'' is most commonly used in monsoonal regions of the Western Pacific such as Asia and Australia. The migration of the ITCZ/monsoon trough into a landmass heralds the beginning of the annual rainy season during summer months. Depressions and tropical cyclones ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
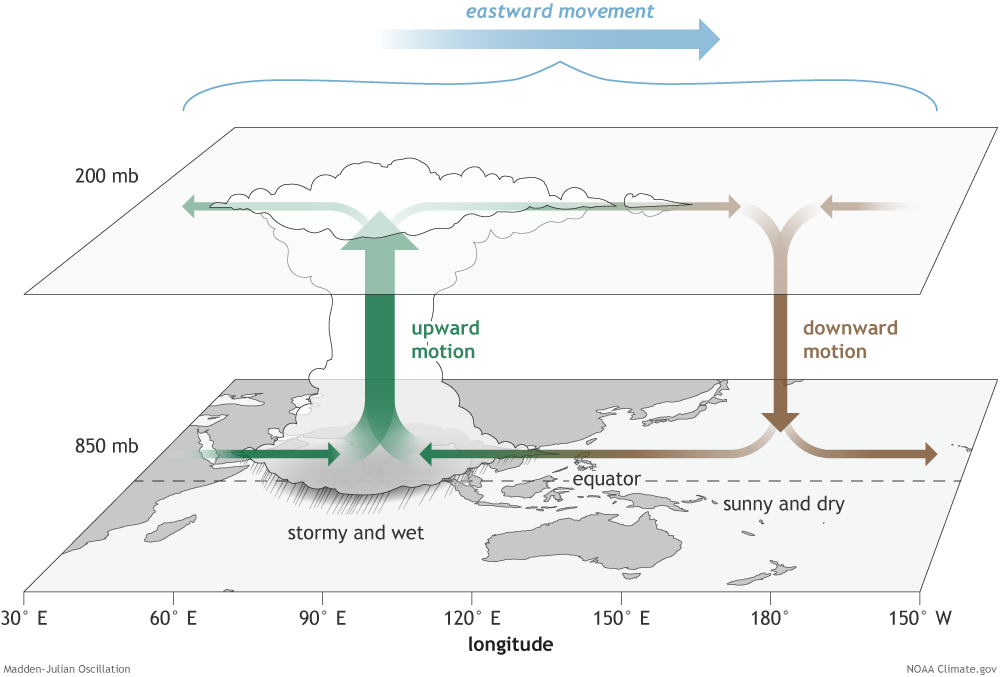
Madden–Julian Oscillation
The Madden–Julian oscillation (MJO) is the largest element of the intraseasonal (30- to 90-day) variability in the tropical atmosphere. It was discovered in 1971 by Roland Madden and Paul Julian of the American National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). It is a large-scale coupling between atmospheric circulation and tropical deep atmospheric convection. Unlike a standing pattern like the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), the Madden–Julian oscillation is a traveling pattern that propagates eastward, at approximately , through the atmosphere above the warm parts of the Indian and Pacific oceans. This overall circulation pattern manifests itself most clearly as anomalous rainfall. The Madden–Julian oscillation is characterized by an eastward progression of large regions of both enhanced and suppressed tropical rainfall, observed mainly over the Indian and Pacific Ocean. The anomalous rainfall is usually first evident over the western Indian Ocean, and remains evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rossby Wave
Rossby waves, also known as planetary waves, are a type of inertial wave naturally occurring in rotating fluids. They were first identified by Sweden-born American meteorologist Carl-Gustaf Arvid Rossby. They are observed in the atmospheres and oceans of planets owing to the rotation of the planet. Atmospheric Rossby waves on Earth are giant meanders in high-altitude winds that have a major influence on weather. These waves are associated with pressure systems and the jet stream (especially around the polar vortices). Oceanic Rossby waves move along the thermocline: the boundary between the warm upper layer and the cold deeper part of the ocean. Rossby wave types Atmospheric waves Atmospheric Rossby waves result from the conservation of potential vorticity and are influenced by the Coriolis force and pressure gradient. The rotation causes fluids to turn to the right as they move in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere. For example, a fluid that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin Wave
A Kelvin wave is a wave in the ocean or atmosphere that balances the Earth's Coriolis force against a topographic boundary such as a coastline, or a waveguide such as the equator. A feature of a Kelvin wave is that it is non-dispersive, i.e., the phase speed of the wave crests is equal to the group speed of the wave energy for all frequencies. This means that it retains its shape as it moves in the alongshore direction over time. A Kelvin wave (fluid dynamics) is also a long scale perturbation mode of a vortex in superfluid dynamics; in terms of the meteorological or oceanographical derivation, one may assume that the meridional velocity component vanishes (i.e. there is no flow in the north–south direction, thus making the momentum and continuity equations much simpler). This wave is named after the discoverer, Lord Kelvin (1879). Coastal Kelvin wave In a stratified ocean of mean depth ''H'', perturbed by some amount ''η'', free waves propagate along coastal boundaries (and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
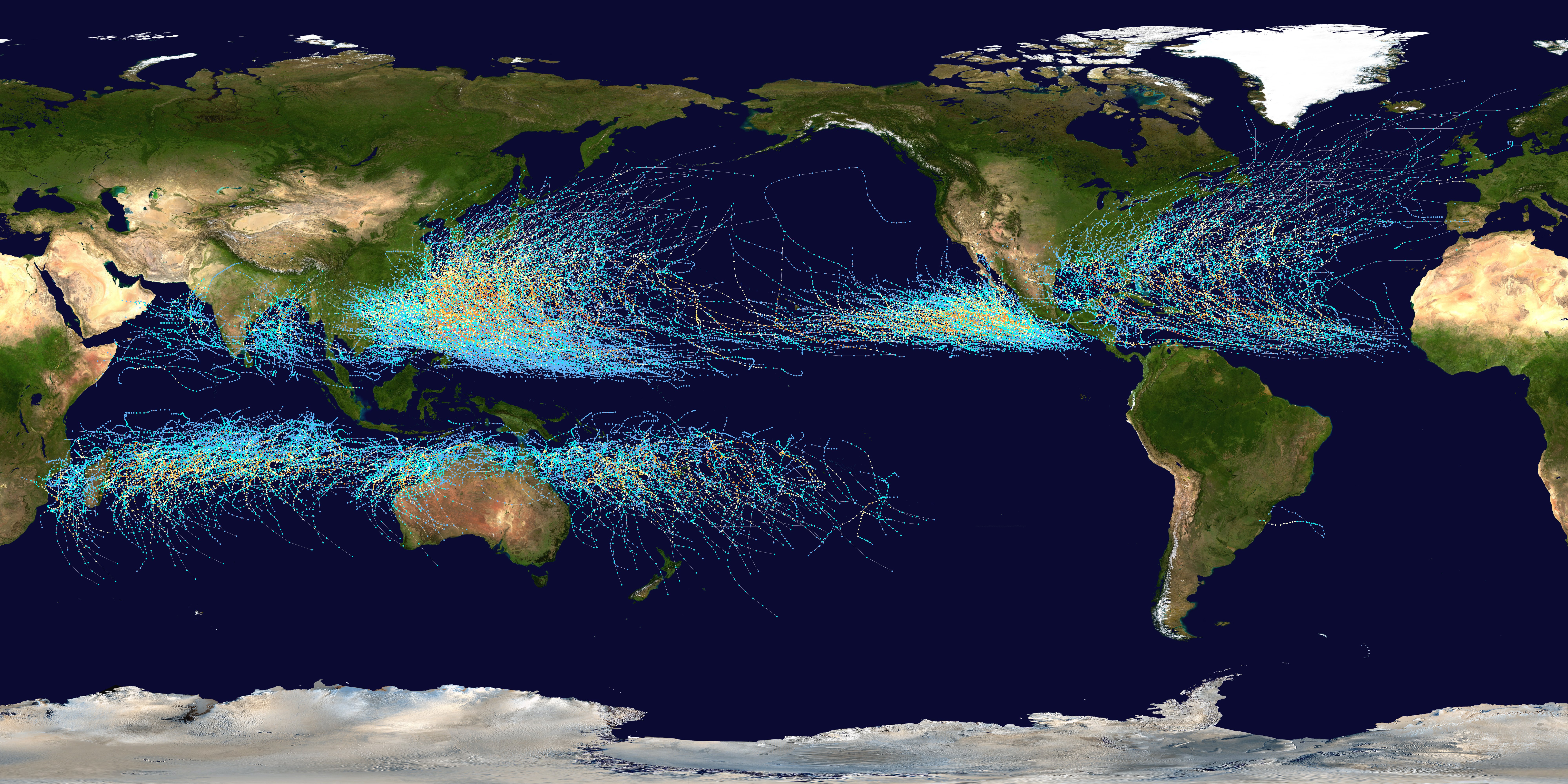
Tropical Cyclogenesis
Tropical cyclogenesis is the development and strengthening of a tropical cyclone in the atmosphere. The mechanisms through which tropical cyclogenesis occurs are distinctly different from those through which temperate cyclogenesis occurs. Tropical cyclogenesis involves the development of a warm-core cyclone, due to significant convection in a favorable atmospheric environment. Tropical cyclogenesis requires six main factors: sufficiently warm sea surface temperatures (at least ), atmospheric instability, high humidity in the lower to middle levels of the troposphere, enough Coriolis force to develop a low-pressure center, a pre-existing low-level focus or disturbance, and low vertical wind shear. Tropical cyclones tend to develop during the summer, but have been noted in nearly every month in most basins. Climate cycles such as ENSO and the Madden–Julian oscillation modulate the timing and frequency of tropical cyclone development. There is a limit on tropical cyclone i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa across the Mozambique Channel. At Madagascar is the world's List of island countries, second-largest island country, after Indonesia. The nation is home to around 30 million inhabitants and consists of the island of Geography of Madagascar, Madagascar (the List of islands by area, fourth-largest island in the world), along with numerous smaller peripheral islands. Following the prehistoric breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana, Madagascar split from the Indian subcontinent around 90 million years ago, allowing native plants and animals to evolve in relative isolation. Consequently, Madagascar is a biodiversity hotspot; over 90% of wildlife of Madagascar, its wildlife is endemic. Human settlement of Madagascar occurred during or befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morombe (district)
Morombe is a district of Atsimo-Andrefana in Madagascar. Communes The district is further divided into eight communes: * Ambahikily * Antanimeva * Antongo Vaovao * Basibasy * Befandefa * Befandriana Sud * Morombe Morombe is an urban municipality (commune urbaine) on the south-west coast in Atsimo-Andrefana, Madagascar. It can be reached by the National road 55 or pirogue from Morondava. It is situated at 283 km from Tulear. An airport serves the town. ... * Nosy Ambositra References Districts of Atsimo-Andrefana {{Madagascar-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |