|
2011 Shizuoka Earthquake
The 2011 Shizuoka earthquake () was an earthquake that occurred approximately 42 km (26 mi) north-northeast of Shizuoka City at 22:31 (Japan Time), 15 March 2011. The magnitude was 6.0 or 6.4,「平成23 年(2011 年)東北地方太平洋沖地震」について(第28 報) Press Release), 25 March 2011. Published by Japan Meteorological Agency. and the depth was 9 km (5.6 mi). The of this earthquake is thought to have been near the presumed location of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Crack In The Road By The East Shizuoka Earthquake
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Tohoku Earthquake
Eleven or 11 may refer to: *11 (number), the natural number following 10 and preceding 12 * one of the years 11 BC, AD 11, 1911, 2011, or any year ending in 11 Literature * ''Eleven'' (novel), a 2006 novel by British author David Llewellyn *''Eleven'', a 1970 collection of short stories by Patricia Highsmith *''Eleven'', a 2004 children's novel in The Winnie Years by Lauren Myracle *''Eleven'', a 2008 children's novel by Patricia Reilly Giff *''Eleven'', a short story by Sandra Cisneros Music *Eleven (band), an American rock band * Eleven: A Music Company, an Australian record label *Up to eleven, an idiom from popular culture, coined in the movie ''This Is Spinal Tap'' Albums * ''11'' (The Smithereens album), 1989 * ''11'' (Ua album), 1996 * ''11'' (Bryan Adams album), 2008 * ''11'' (Sault album), 2022 * ''Eleven'' (Harry Connick, Jr. album), 1992 * ''Eleven'' (22-Pistepirkko album), 1998 * ''Eleven'' (Sugarcult album), 1999 * ''Eleven'' (B'z album), 2000 * ''Eleven'' (Reamonn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Earthquakes
This is a list of earthquakes in 2011. Only earthquakes of magnitude 6 or above are included, unless they result in damage and/or casualties, or are notable for some other reason. All dates are listed according to UTC time. The 9.1 Tōhoku earthquake was the fourth most powerful ever recorded and triggered a massive tsunami (around 20,000 deaths). In a very busy year, many earthquakes caused damage in Turkey, New Zealand, Myanmar, India and United States. Compared to other years Overall By death toll * Note: At least 10 dead By magnitude * Note: At least 7.0 magnitude * Note: Aftershocks of the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami are included as they are still over magnitude 7. By month January February Note: The 2010 Maule Earthquake's aftershocks have not been included due to cluttering. March Note: Aftershocks of the Japan earthquake have not been included unless they are above magnitude 7 or lead to casualties. April May June July * A ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March 2011 Events In Japan
March is the third month of the year in both the Julian and Gregorian calendars. It is the second of seven months to have a length of 31 days. In the Northern Hemisphere, the meteorological beginning of spring occurs on the first day of March. The March equinox on the 20 or 21 marks the astronomical beginning of spring in the Northern Hemisphere and the beginning of autumn in the Southern Hemisphere, where September is the seasonal equivalent of the Northern Hemisphere's March. Origin The name of March comes from '' Martius'', the first month of the earliest Roman calendar. It was named after Mars, the Roman god of war, and an ancestor of the Roman people through his sons Romulus and Remus. His month ''Martius'' was the beginning of the season for warfare, and the festivals held in his honor during the month were mirrored by others in October, when the season for these activities came to a close. ''Martius'' remained the first month of the Roman calendar year perhaps as la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
静岡県
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshu. Shizuoka Prefecture has a population of 3,637,998 and has a geographic area of . Shizuoka Prefecture borders Kanagawa Prefecture to the east, Yamanashi Prefecture to the northeast, Nagano Prefecture to the north, and Aichi Prefecture to the west. Shizuoka is the capital and Hamamatsu is the largest city in Shizuoka Prefecture, with other major cities including Fuji, Numazu, and Iwata. Shizuoka Prefecture is located on Japan's Pacific Ocean coast and features Suruga Bay formed by the Izu Peninsula, and Lake Hamana which is considered to be one of Japan's largest lakes. Mount Fuji, the tallest volcano in Japan and cultural icon of the country, is partially located in Shizuoka Prefecture on the border with Yamanashi Prefecture. Shizuoka Prefecture has a significant motoring heritage as the founding location of Honda, Suzuki, and Yamaha, and is home to the Fuji International Speedway. History Shizuoka Prefecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Outage
A power outage (also called a powercut, a power out, a power failure, a power blackout, a power loss, or a blackout) is the loss of the electrical power network supply to an end user. There are many causes of power failures in an electricity network. Examples of these causes include faults at power stations, damage to electric transmission lines, substations or other parts of the distribution system, a short circuit, cascading failure, fuse or circuit breaker operation. Power failures are particularly critical at sites where the environment and public safety are at risk. Institutions such as hospitals, sewage treatment plants, and mines will usually have backup power sources such as standby generators, which will automatically start up when electrical power is lost. Other critical systems, such as telecommunication, are also required to have emergency power. The battery room of a telephone exchange usually has arrays of lead–acid batteries for backup and also a socket ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercalli Intensity Scale
The Modified Mercalli intensity scale (MM, MMI, or MCS), developed from Giuseppe Mercalli's Mercalli intensity scale of 1902, is a seismic intensity scale used for measuring the intensity of shaking produced by an earthquake. It measures the effects of an earthquake at a given location, distinguished from the earthquake's inherent force or strength as measured by seismic magnitude scales (such as the "" magnitude usually reported for an earthquake). While shaking is caused by the seismic energy released by an earthquake, earthquakes differ in how much of their energy is radiated as seismic waves. Deeper earthquakes also have less interaction with the surface, and their energy is spread out across a larger volume. Shaking intensity is localized, generally diminishing with distance from the earthquake's epicenter, but can be amplified in sedimentary basins and certain kinds of unconsolidated soils. Intensity scales empirically categorize the intensity of shaking based on the effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fujinomiya
is a city located in central Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 132,507 in 56,655 households, and a population density of 340 persons per km². The total area of the city is . History The city name comes from the former shrine name of Fujisan Hongū Sengen Taisha, "Fujinomiya". It is an ancient settlement that developed as a properous ''toriimae-machi'' (town in front of torii) of Fujisan Hongū Sengen Taisha, where the Fuji clan served as the high priest of the shrine. Nearby is the sanctuary of Taiseki-ji temple, founded in 1290 by Nikkō Shōnin as the headquarters of Nichiren Shōshū Buddhism. Fujinomiya is closely related to Mount Fuji, and was located in the crossroad of Ōmiya and Murayamaguchi mountain pilgrimage trails. During the Kamakura period, the hunting event Fuji no Makigari arranged by shogun Minamoto no Yoritomo was held in the ancient region of Fujino, where the Revenge of the Soga Brothers incident also took place. These e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Meteorological Agency Seismic Intensity Scale
The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) Seismic Intensity Scale (known in Japan as the Shindo seismic scale) is a seismic intensity scale used in Japan to categorize the intensity of local ground shaking caused by earthquakes. The JMA intensity scale should not be confused or conflated with magnitude measurements like the moment magnitude (Mw) and the earlier Richter scales, which represent how much energy an earthquake releases. Much like the Mercalli scale, the JMA scheme quantifies how much ground-surface shaking takes place ''at measurement sites distributed throughout an affected area''. Intensities are expressed as numerical values called ; the higher the value, the more intense the shaking. Values are derived from peak ground acceleration and duration of the shaking, which are themselves influenced by factors such as distance to and depth of the hypocenter (focus), local soil conditions, and nature of the geology in between, as well as the event's magnitude; every qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triggered Earthquake
Remotely triggered earthquakes are a result of the effects of large earthquakes at considerable distance, outside of the immediate aftershock zone. The farther one gets from the initiating earthquake in both space and time, the more difficult it is to establish an association. The physics of triggering an earthquake are complex. Most earthquake-generating zones are in a state of being close to failure. If such a zone were to be left completely alone, it would generate significant earthquakes spontaneously. Remote earthquakes, however, are in a position to disturb this critical state, either by shifting the stresses statically, or by dynamic change caused by passing seismic waves. The first type of triggering may be due to static changes in the critical state. For example, after the magnitude 7.3 Landers earthquake struck California in 1992, it is said that "the earthquake map of California lit up like a Christmas tree". This event reinforced the idea of remotely triggered earthqua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Ground Acceleration
Peak ground acceleration (PGA) is equal to the maximum ground acceleration that occurred during earthquake shaking at a location. PGA is equal to the amplitude of the largest absolute acceleration recorded on an wikt:accelerogram, accelerogram at a site during a particular earthquake. Earthquake shaking generally occurs in all three directions. Therefore, PGA is often split into the horizontal and vertical components. Horizontal PGAs are generally larger than those in the vertical direction but this is not always true, especially close to large earthquakes. PGA is an important parameter (also known as an intensity measure) for earthquake engineering, The design basis earthquake ground motion (DBEGM) is often defined in terms of PGA. Unlike the Richter magnitude scale, Richter and Moment magnitude scale, moment magnitude scales, it is not a measure of the total seismic scales#Magnitude and intensity, energy (magnitude, or size) of an earthquake, but rather of how hard the earth shake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
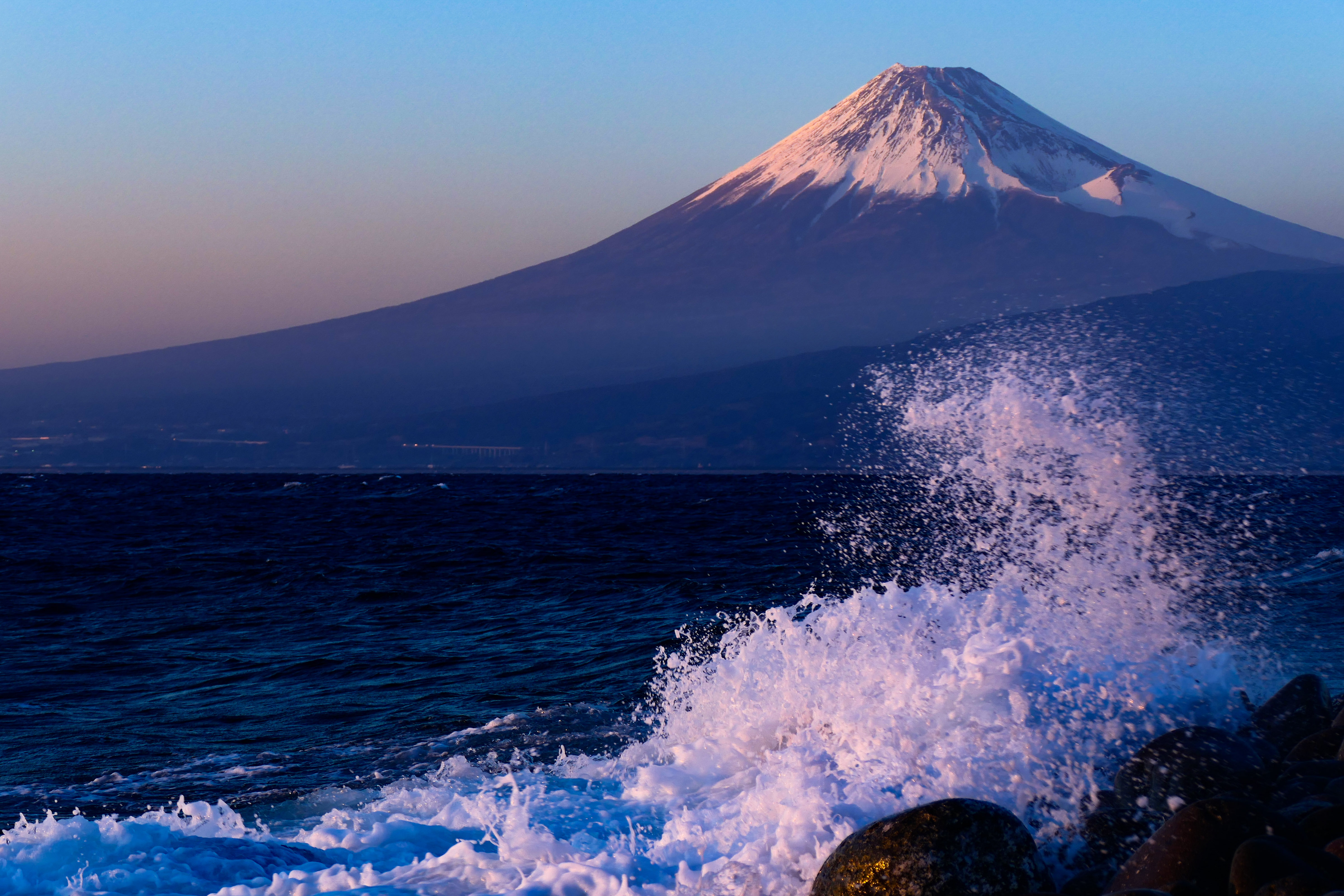
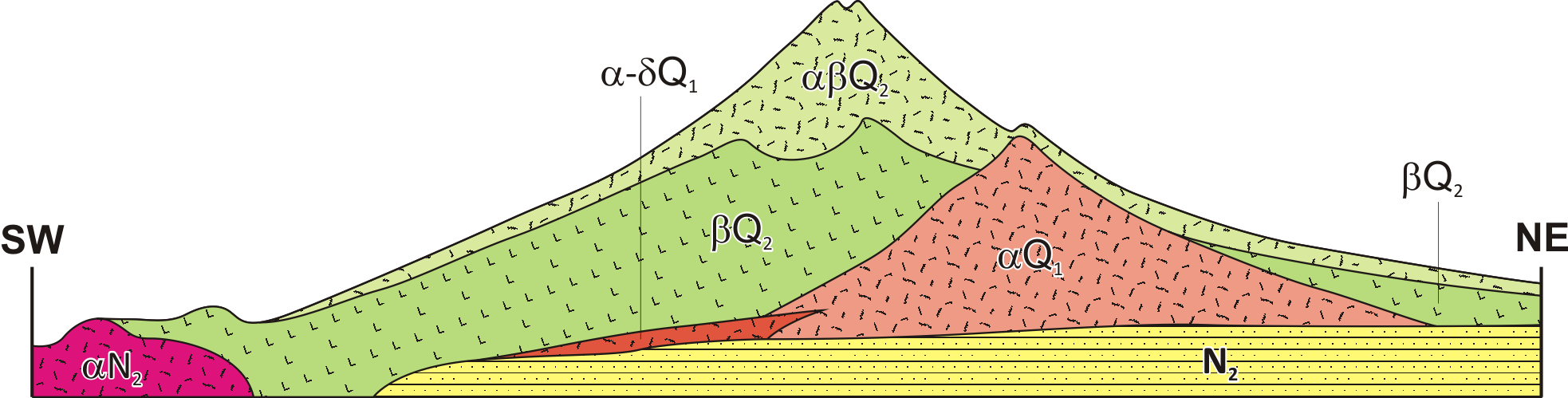
Mount Fuji
, or Fugaku, located on the island of Honshū, is the highest mountain in Japan, with a summit elevation of . It is the second-highest volcano located on an island in Asia (after Mount Kerinci on the island of Sumatra), and seventh-highest peak of an island on Earth. Mount Fuji is an active stratovolcano that last erupted from 1707 to 1708. The mountain is located about southwest of Tokyo and is visible from there on clear days. Mount Fuji's exceptionally symmetrical cone, which is covered in snow for about five months of the year, is commonly used as a cultural icon of Japan and it is frequently depicted in art and photography, as well as visited by sightseers and climbers. Mount Fuji is one of Japan's along with Mount Tate and Mount Haku. It is a Special Place of Scenic Beauty and one of Japan's Historic Sites. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)