|
2003 Pacific Typhoon Season
The 2003 Pacific typhoon season was a slightly below average yearlong period of tropical cyclogenesis exhibiting the development of 45 tropical depressions, of which 21 became named storms; of those, 14 became typhoons. Though every month with the exception of February and March featured tropical activity, most storms developed from May through October. During the season, tropical cyclones affected the Philippines, Japan, China, the Korean Peninsula, Indochina, and various islands in the western Pacific. The season ran year-round, with the first storm, Yanyan, developing west of the Marshall Islands on January 15. In April, Typhoon Kujira became one of the longest-lasting Pacific typhoons in history and attained climatological records for its unusually early impacts. Typhoon Imbudo in July caused several deaths and extensive damage across the Philippines and China. In September, Typhoon Maemi became one of the costliest typhoons in recorded history after striking South K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoon Maemi
Typhoon Maemi () or (), known in the Philippines as Typhoon Pogi, was the most powerful typhoon to strike South Korea since record-keeping began in the country in 1904. Maemi formed on September 4, 2003 from a disturbance in a monsoon trough in the western Pacific Ocean. It slowly intensified into Tropical Storm Maemi while moving northwestward, becoming a typhoon on September 8. That day, favorable conditions facilitated more rapid strengthening; the storm developed a well-defined eye and reached peak maximum sustained winds of 195 km/h (120 mph). While near peak intensity, Maemi decelerated and began turning to the north-northeast. Soon after, the eyewall passed over the Japanese island of Miyako-jima on September 10 and produced an air pressure reading of , the fourth-lowest recorded in the nation. Due to warm waters, Maemi was able to maintain much of its intensity before it made landfall just west of Busan, South Korea, on September 12. The typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barometric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 760 mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696 psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitudes—the Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Surface Temperature
Sea surface temperature (SST), or ocean surface temperature, is the ocean temperature close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air masses in the Earth's atmosphere are highly modified by sea surface temperatures within a short distance of the shore. Localized areas of heavy snow can form in bands downwind of warm water bodies within an otherwise cold air mass. Warm sea surface temperatures are known to be a cause of tropical cyclogenesis over the Earth's oceans. Tropical cyclones can also cause a cool wake, due to turbulent mixing of the upper of the ocean. SST changes diurnally, like the air above it, but to a lesser degree. There is less SST variation on breezy days than on calm days. In addition, ocean currents such as the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO), can affect SST's on multi-decadal time scales, a major impact results from the global thermohaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different names, including hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean, and a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean, South Pacific, or (rarely) South Atlantic, comparable storms are referred to simply as "tropical cyclones", and such storms in the Indian Ocean can also be called "severe cyclonic storms". "Tropical" refers to the geographical origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively over tropical seas. "Cyclone" refers to their winds moving in a circle, whirling ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University College London
, mottoeng = Let all come who by merit deserve the most reward , established = , type = Public research university , endowment = £143 million (2020) , budget = £1.544 billion (2019/20) , chancellor = Anne, Princess Royal(as Chancellor of the University of London) , provost = Michael Spence , head_label = Chair of the council , head = Victor L. L. Chu , free_label = Visitor , free = Sir Geoffrey Vos , academic_staff = 9,100 (2020/21) , administrative_staff = 5,855 (2020/21) , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , coordinates = , campus = Urban , city = London, England , affiliations = , colours = Purple and blue celeste , nickname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical And Astronomical Services Administration
Pagasa may refer to: * ''Pagasa'' (genus), an insect genus in the family Nabidae * PAGASA, an acronym for the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration *"May Pagasa", a pen-name of José Rizal José Protasio Rizal Mercado y Alonso Realonda (, ; June 19, 1861 – December 30, 1896) was a Filipino nationalist, writer and polymath active at the end of the Spanish colonial period of the Philippines. He is considered the national h ... *Pagasa, alternate spelling of Pagasae, a city of ancient Thessaly See also * Pag-asa (other) {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Typhoon Warning Center
The Joint typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) is a joint United States Navy – United States Air Force command in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The JTWC is responsible for the issuing of tropical cyclone warnings in the North-West Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean, and Indian Ocean for all branches of the U.S. Department of Defense and other U.S. government agencies. Their warnings are intended for the protection of primarily military ships and aircraft as well as military installations jointly operated with other countries around the world. Its U.S. Navy components are aligned with the Naval Meteorology and Oceanography Command. History The origins of the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) can be traced back to June 1945, when the Fleet Weather Center/Typhoon Tracking Center was established on the island of Guam, after multiple typhoons, including Typhoon Cobra of December 1944 and Typhoon Connie in June 1945, had caused a significant loss of men and ships. At this time the center ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2003 Pacific Hurricane Season
The 2003 Pacific hurricane season was the first season to feature no major hurricanes – storms of Category 3 intensity or higher on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS) – since 1977. The dates conventionally delimiting the period when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific Ocean are May 15 in the Eastern Pacific Ocean and June 1 in the Central Pacific, with both seasons ending on November 30. The 2003 season featured 16 tropical storms between May 19 and October 26; 7 of these became hurricanes, which was then considered an average season. Damage across the basin reached US$129 million, and 23 people were killed by the storms. Despite the overall lack of activity, the season produced an unusually large number of tropical cyclones that affected Mexico, with eight tropical cyclones making landfall on either side of Mexico, which was the second highest on record. Tropical Storm Carlos struck Oaxaca in late June, resultin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Date Line
The International Date Line (IDL) is an internationally accepted demarcation on the surface of Earth, running between the South and North Poles and serving as the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific Ocean, roughly following the 180° line of longitude and deviating to pass around some territories and island groups. Crossing the date line eastbound decreases the date by one day, while crossing the date line westbound increases the date. Geography Circumnavigating the globe People traveling westward around the world must set their clocks: *Back by one hour for every 15° of longitude crossed, and *Forward by 24 hours upon crossing the International Date Line. People traveling eastward must set their clocks: *Forward by one hour for every 15° of longitude crossed, and *Back by 24 hours upon crossing the International Date Line. Failing to do this would make their time inaccurate to the local time. The Arab geographer Abul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federated States Of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise around 607 islands (a combined land area of approximately ) that cover a longitudinal distance of almost just north of the equator. They lie northeast of Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, south of Guam and the Marianas, west of Nauru and the Marshall Islands, east of Palau and the Philippines, about north of eastern Australia, 3,400 km (2,133 mi) southeast of Japan, and some southwest of the main islands of the Hawaiian Islands. While the FSM's total land area is quite small, the country's waters occupy more than of the Pacific Ocean, giving the country the 14th-largest exclusive economic zone in the world. The sovereign island nation's capital is Palikir, located on Pohnpei Island, while the largest city is Weno, loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
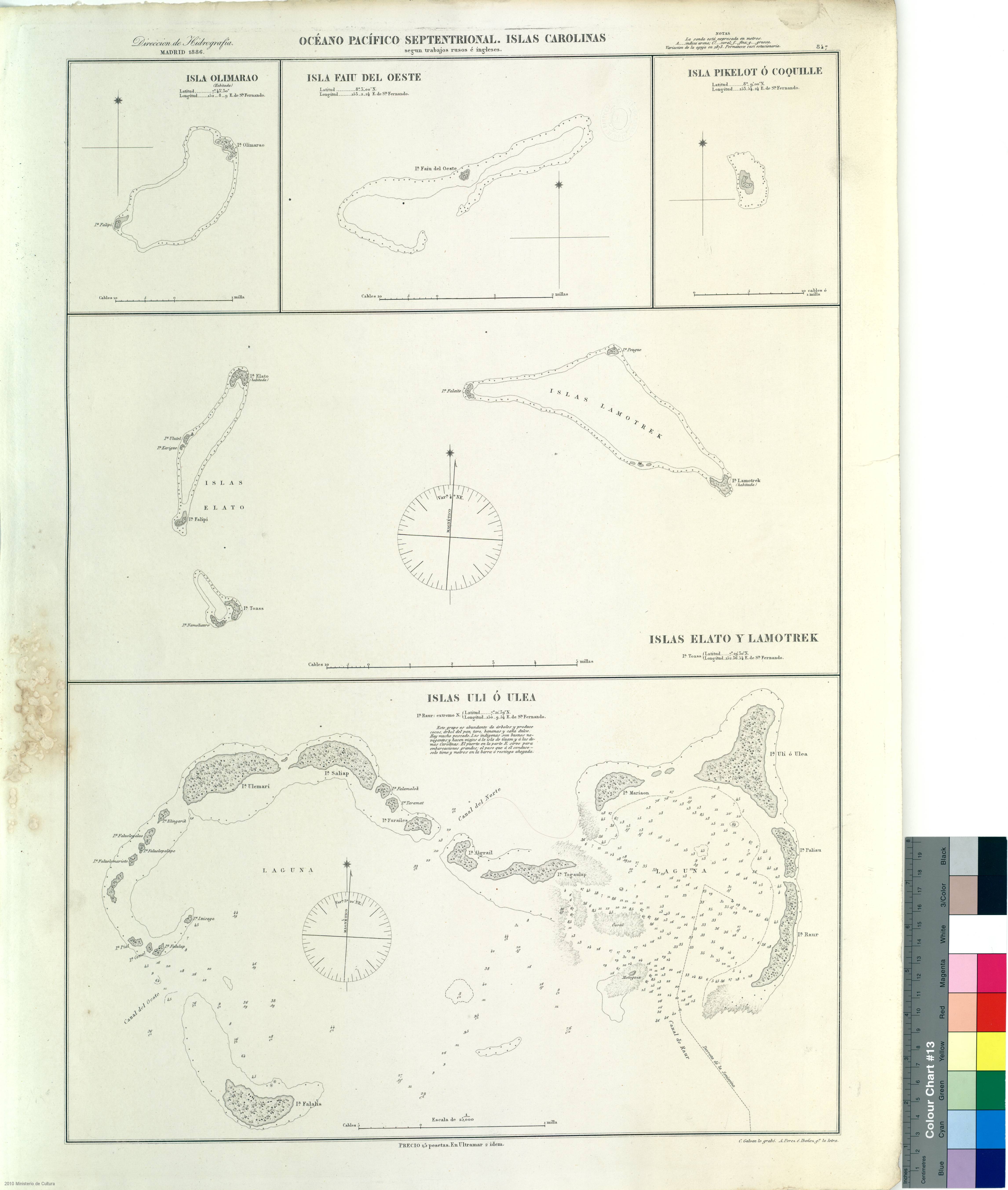
Yap State
Yap State, also known in the Yapese language as Nam nu Wa'ab (lit. "Island of Yap") or simply as Wa'ab, is one of the four states of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM). The other states are Kosrae State, Pohnpei State, and Chuuk State. Colonia is the capital of Yap State, which administers both the Yap Main Islands and the island of Satawal, as well as fourteen atolls reaching to the east and south for some . Historically, a tributary system existed between the Neighboring Islands and the Yap Main Islands. This probably related to the need for goods from the high islands, including food, as well as wood for construction of seagoing vessels. According to the FSM Statistics Office, the population of Colonia and the municipalities of the State of Yap was 11,577 in 2020. The state has a total land area of . History The islands are thought to have been populated from the Malay Archipelago. In approximately 950 AD it was the seat of the Yapese Empire contemporary to the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoon Lupit (2003)
Typhoon Lupit (''lu-PIT'', ʊˈpit Filipino word meaning "cruelty" or "viciousness"), known in the Philippines as Typhoon Yoyoy, destroyed the food supply in several small islands in Yap State in the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM). It formed on November 18, 2003, from the monsoon trough to the west of the Marshall Islands. Early in its duration, it moved generally to the west or west-southwest. On November 21, the depression intensified into Tropical Storm Lupit, the 21st storm named by the Japan Meteorological Agency of the 2003 Pacific typhoon season. Two days later, it strengthened into a typhoon and developed an eye. Lupit later began a prolonged movement to the northwest, during which it passed near several islands in Yap State. The typhoon reached peak intensity on November 26, with peak 10-minute sustained winds of . It later weakened due to increasing wind shear and drier air, and after recurving to the northeast, Lupit became extratropical south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |