|
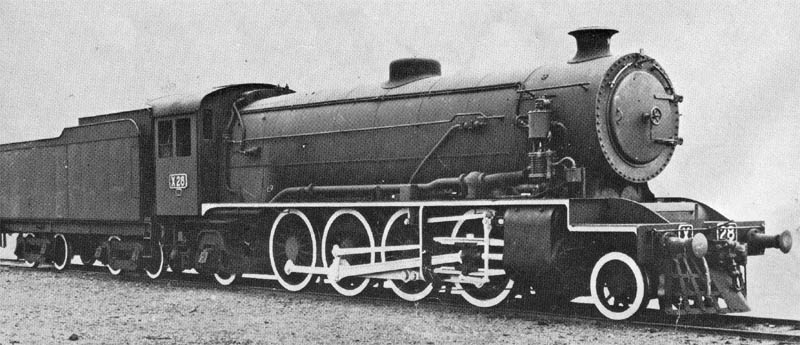
2-8-8-8-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a 2-8-8-8-4 has two leading wheels, three sets of eight driving wheels, and four trailing wheels. Other equivalent classifications are: UIC classification: 1DDD2 (also known as German classification and Italian classification) French classification: 140+040+042 Turkish classification: 45+44+46 Swiss classification: 4/5+4/4+4/6 The equivalent UIC classification is to be refined to (1'D)D(D2') for these engines. Only one 2-8-8-8-4 was ever built, a Mallet-type for the Virginian Railway in 1916. Built by Baldwin Locomotive Works, it became the only example of their class XA, so named due to the experimental nature of the locomotive. Like the same railroad's large articulated electrics and the Erie Railroad 2-8-8-8-2s, it was nicknamed "Triplex". An overview of Triplex engineering is given at Triplex (locomotive). The XA was unable to sustain a speed greater than five miles an hour, since the six cylinders could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triplex (locomotive)
A Triplex locomotive is a steam locomotive that divides the driving force on its wheels by using three pairs of cylinders rigidly mounted to a single locomotive frame. Inevitably any such locomotive will be articulated. All the examples that have been produced have been of the Mallet type but with one extra set of driving wheels under the tender. Triplex classes Baldwin Locomotive Works built three Triplex locomotives for the Erie Railroad between 1914 and 1916. The first was named ''Matt H. Shay'', after a beloved employee of that road. These Triplexes were given the classification of "P1" and they could reportedly pull 650 freight cars. The Triplexes were primarily used as pushers on grades requiring helper locomotives. Slow moving, the Triplexes were not considered highly successful, and no more were built for Erie. The Erie Railroad scrapped their Triplexes from 1929, 1931, and 1933.. Another very similar designed Triplex was built by Baldwin as a 2-8-8-8-4 for the Virgini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-8-8-8-2
A Triplex locomotive is a steam locomotive that Divided drive (locomotive), divides the driving force on its wheels by using three pairs of cylinders rigidly mounted to a single locomotive frame. Inevitably any such locomotive will be articulated locomotive, articulated. All the examples that have been produced have been of the Mallet locomotive, Mallet type but with one extra set of driving wheels under the tender. Triplex classes Baldwin Locomotive Works, Baldwin Locomotive Works built three Triplex locomotives for the Erie Railroad between 1914 and 1916. The first was named ''Matt H. Shay'', after a beloved employee of that road. These Triplexes were given the classification of "P1" and they could reportedly pull 650 freight cars. The Triplexes were primarily used as pushers on grades requiring helper locomotives. Slow moving, the Triplexes were not considered highly successful, and no more were built for Erie. The Erie Railroad scrapped their Triplexes from 1929, 1931, and 193 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whyte Notation
Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twentieth century following a December 1900 editorial in ''American Engineer and Railroad Journal''. The notation was adopted and remains in use in North America and the United Kingdom to describe the wheel arrangements of steam locomotives (in the latter case also for diesel and electric locomotives), but for modern locomotives, multiple units and trams it has been supplanted by the UIC system in Europe and by the AAR system (essentially a simplification of the UIC system) in North America. Structure of the system Basic form The notation in its basic form counts the number of leading wheels, then the number of driving wheels, and finally the number of trailing wheels, numbers being separated by dashes. For example, a locomotive with two leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driving Wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled together with side rods (also known as coupling rods); normally one pair is directly driven by the main rod (or connecting rod) which is connected to the end of the piston rod; power is transmitted to the others through the side rods. On diesel and electric locomotives, the driving wheels may be directly driven by the traction motors. Coupling rods are not usually used, and it is quite common for each axle to have its own motor. Jackshaft drive and coupling rods were used in the past (e.g. in the Swiss Crocodile locomotive) but their use is now confined to shunting locomotives. On an articulated locomotive or a duplex locomotive, driving wheels are grouped into sets which are linked together within the set. Diameter Driving wheels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railroad locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, in the early 20th century. The company was for decades the world's largest producer of steam locomotives, but struggled to compete as demand switched to diesel locomotives. Baldwin produced the last of its 70,000-plus locomotives in 1951, before merging with the Lima-Hamilton Corporation on September 11, 1951, to form the Baldwin-Lima-Hamilton Corporation. The company has no relation to the E.M. Baldwin and Sons of New South Wales, Australia, a builder of small diesel locomotives for sugar cane railroads. History: 19th century Beginning The Baldwin Locomotive Works had a humble beginning. Matthias W. Baldwin, the founder, was a jeweler and whitesmith, who, in 1825, formed a partnership with machinist David H. Mason, and engaged in the manufacture of bookbinders' tools and cylinders for cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotives Of The United States
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Steam that is saturated or superheated is invisible; however, "steam" often refers to wet steam, the visible mist or aerosol of water droplets formed as water vapor condenses. Water increases in volume by 1,700 times at standard temperature and pressure; this change in volume can be converted into mechanical work by steam engines such as reciprocating piston type engines and steam turbines, which are a sub-group of steam engines. Piston type steam engines played a central role in the Industrial Revolution and modern steam turbines are used to generate more than 80% of the world's electricity. If liquid water comes in contact with a very hot surface or depressurizes quickly below its vapor pressure, it can create a steam explosion. Types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baldwin Locomotives
Baldwin is a Germanic name, composed of the elements ''bald'' "bold" and ''win'' "friend". People * Baldwin (name) Places Canada * Baldwin, York Regional Municipality, Ontario * Baldwin, Ontario, in Sudbury District * Baldwin's Mills, Quebec United States * Baldwin County, Alabama * Baldwin, Florida * Baldwin, Georgia * Baldwin County, Georgia * Baldwin, Illinois * Baldwin, Iowa * Baldwin, Louisiana * Baldwin, Maine * Baldwin, Maryland * Baldwin, Michigan * Baldwyn, Mississippi * Baldwin, Chemung County, New York * Baldwin, Nassau County, New York ** Baldwin (LIRR station) * Baldwin, North Dakota * Baldwin, Pennsylvania * Baldwin, Wisconsin * Baldwin (town), Wisconsin Other places * Baldwin Street, in Dunedin, New Zealand, the world's steepest street * Baldwin Hills, neighborhood in Los Angeles, California * Montgomery, Powys, named in Welsh "Trefaldwyn", meaning "The Town of Baldwin" Companies * Baldwin Locomotive Works, one of the world's largest builders of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virginian Railway Locomotives
Virginian is a demonym used to describe something as being of, from, or related to the Commonwealth of Virginia of the United States of America; it can be used as both a noun and adjective. Virginian may also refer to: Railroads * Virginian (Amtrak train), a former Amtrak passenger train * Virginian Railway, a railroad located in Virginia and West Virginia in the United States that operated from 1909 to 1959 Ships * USS ''Virginian'', two United States Navy vessels * SS ''Virginian'', a passenger ship built in 1905 that became the Swedish transatlantic liner SS ''Drottningholm'' in 1920 Other uses * Virginian (automobile), an automobile produced briefly by the Richmond Iron Works of Richmond, Virginia * Virginian Golf Club, a golf course in Bristol, Virginia * Virginians, a barbershop chorus See also * * The Virginian (other) * Virginia (other) Virginia is a state in the United States of America. Virginia most often also refers to: *West Virginia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and two trailing wheels on one axle, usually in a trailing truck. This configuration of steam locomotive is most often referred to as a Mikado, frequently shortened to Mike. At times it was also referred to on some railroads in the United States of America as the McAdoo Mikado and, during World War II, the MacArthur. The notation 2-8-2T indicates a tank locomotive of this wheel arrangement, the "T" suffix indicating a locomotive on which the water is carried in tanks mounted on the engine rather than in an attached tender. Overview The 2-8-2 wheel arrangement allowed the locomotive's firebox to be placed behind instead of above the driving wheels, thereby allowing a larger firebox that could be both wide and deep. This supported a greater rate of combustion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-8-8-0
In the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, a 2-8-8-0 is a locomotive with a two-wheel leading truck, two sets of eight driving wheels, and no trailing truck. These were nicknamed "Bull Mooses". Equivalent classifications Other equivalent classifications are: *UIC classification: 1DD (also known as German classification and Italian classification) *French classification: 140+040 *Turkish classification: 45+44 *Swiss classification: 4/5+4/4 The UIC classification is refined to (1'D)D for Mallet locomotives. Examples The Great Northern Railway used the 2-8-8-0s as their N-1's which were built by Baldwin in 1912. They were rebuilt by GN in 1932 as a N-2, and later re-rebuilt in 1940 as an N-3, The locomotives, after their third rebuild into a N-3, had a larger boiler and bigger tender. The N-3's served on the GN for a collective 45 years (including previous service lives as N-1 and N-2 classes), in use until retired in 1957. The Union Pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erie Railroad
The Erie Railroad was a railroad that operated in the northeastern United States, originally connecting New York City — more specifically Jersey City, New Jersey, where Erie's Pavonia Terminal, long demolished, used to stand — with Lake Erie, at Dunkirk, New York. It expanded west to Chicago with its 1865 merger with the former Atlantic and Great Western Railroad, also known as the New York, Pennsylvania and Ohio Railroad (NYPANO RR). Its mainline route proved influential in the development and economic growth of the Southern Tier of New York State, including cities such as Binghamton, Elmira, and Hornell. The Erie Railroad repair shops were located in Hornell and was Hornell's largest employer. Hornell was also where Erie's mainline split into two routes, one northwest to Buffalo and the other west to Chicago. On October 17, 1960, the Erie merged with former rival Delaware, Lackawanna & Western Railroad to form the Erie Lackawanna Railroad. The Hornell repair shops were c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |