|
1 Samuel 4
1 Samuel 4 is the fourth chapter of the First Book of Samuel in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible or the first part of the Books of Samuel in the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewish tradition the book was attributed to the prophet Samuel, with additions by the prophets Gad and Nathan, but modern scholars view it as a composition of a number of independent texts of various ages from c. 630–540 BCE. This chapter describes how the Ark of Covenant was taken by the Philistines, a part of the "Ark Narrative" (1 Samuel 4:1–7:1) within a section concerning the life of Samuel (1 Samuel 1:1–7:17). Text This chapter was originally written in the Hebrew language. It is divided into 22 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter in Hebrew are of the Masoretic Text tradition, which includes the Codex Cairensis (895), Aleppo Codex (10th century), and Codex Leningradensis (1008). Fragments containing parts of this chapter in Hebrew were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books Of Samuel
The Book of Samuel (, ''Sefer Shmuel'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Samuel) in the Old Testament. The book is part of the narrative history of Ancient Israel called the Deuteronomistic history, a series of books (Joshua, Judges, Samuel, and Kings) that constitute a theological history of the Israelites and that aim to explain God's law for Israel under the guidance of the prophets. According to Jewish tradition, the book was written by Samuel, with additions by the prophets Gad and Nathan, who together are three prophets who had appeared within 1 Chronicles during the account of David's reign. Modern scholarly thinking posits that the entire Deuteronomistic history was composed ''circa'' 630–540 BCE by combining a number of independent texts of various ages. The book begins with Samuel's birth and Yahweh's call to him as a boy. The story of the Ark of the Covenant follows. It tells of Israel's oppression by the Philistines, which brought about Sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond those contained in the Masoretic text of the Hebrew Bible as canonically used in the tradition of mainstream Rabbinical Judaism. The additional books were composed in Greek, Hebrew, or Aramaic, but in most cases, only the Greek version has survived to the present. It is the oldest and most important complete translation of the Hebrew Bible made by the Jews. Some targums translating or paraphrasing the Bible into Aramaic were also made around the same time. The first five books of the Hebrew Bible, known as the Torah or the Pentateuch, were translated in the mid-3rd century BCE. The remaining translations are presumably from the 2nd century BCE. The full title ( grc , Ἡ μετάφρασις τῶν Ἑβδομήκοντα, , The Translat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ark Of The Covenant
The Ark of the Covenant,; Ge'ez: also known as the Ark of the Testimony or the Ark of God, is an alleged artifact believed to be the most sacred relic of the Israelites, which is described as a wooden chest, covered in pure gold, with an elaborately designed lid called the mercy seat. According to the Book of Exodus, the Ark contained the two stone tablets of the Ten Commandments. According to the New Testament Book of Hebrews, it also contained Aaron's rod and a pot of manna. The biblical account relates that approximately one year after the Israelites' exodus from Egypt, the Ark was created according to the pattern given to Moses by God when the Israelites were encamped at the foot of Mount Sinai. Thereafter, the gold-plated acacia chest was carried by its staves by the Levites approximately 2,000 cubits (approximately ) in advance of the people when on the march. God spoke with Moses "from between the two cherubim" on the Ark's cover. Biblical account Construction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1100 BC
Eleven or 11 may refer to: *11 (number), the natural number following 10 and preceding 12 * one of the years 11 BC, AD 11, 1911, 2011, or any year ending in 11 Literature * ''Eleven'' (novel), a 2006 novel by British author David Llewellyn *''Eleven'', a 1970 collection of short stories by Patricia Highsmith *''Eleven'', a 2004 children's novel in The Winnie Years by Lauren Myracle *''Eleven'', a 2008 children's novel by Patricia Reilly Giff *''Eleven'', a short story by Sandra Cisneros Music *Eleven (band), an American rock band * Eleven: A Music Company, an Australian record label *Up to eleven, an idiom from popular culture, coined in the movie ''This Is Spinal Tap'' Albums * ''11'' (The Smithereens album), 1989 * ''11'' (Ua album), 1996 * ''11'' (Bryan Adams album), 2008 * ''11'' (Sault album), 2022 * ''Eleven'' (Harry Connick, Jr. album), 1992 * ''Eleven'' (22-Pistepirkko album), 1998 * ''Eleven'' (Sugarcult album), 1999 * ''Eleven'' (B'z album), 2000 * ''Eleven'' (Reamonn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Judges
The Book of Judges (, ') is the seventh book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. In the narrative of the Hebrew Bible, it covers the time between the conquest described in the Book of Joshua and the establishment of a kingdom in the Books of Samuel, during which biblical judges served as temporary leaders. The stories follow a consistent pattern: the people are unfaithful to Yahweh; he therefore delivers them into the hands of their enemies; the people repent and entreat Yahweh for mercy, which he sends in the form of a leader or champion (a "judge"; see ''shophet''); the judge delivers the Israelites from oppression and they prosper, but soon they fall again into unfaithfulness and the cycle is repeated. Scholars consider many of the stories in Judges to be the oldest in the Deuteronomistic history, with their major redaction dated to the 8th century BCE and with materials such as the Deborah#The Song of Deborah, Song of Deborah dating from much earlier. Conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphek (biblical)
The name Aphek or Aphec refers to one or several locations mentioned by the Hebrew Bible as the scenes of a number of battles between the Israelites and the Arameans or Philistines: *Most famously, a town near which one or more rulers of Damascus named Ben-hadad were defeated by the Israelites and in which the Damascene king and his surviving soldiers found a safe place of retreat (; ). Just before his death, the prophet Elisha predicted: :"The arrow of the Lord’s deliverance and the arrow of deliverance from Syria; for you must strike the Syrians at Aphek till you have destroyed them." *A place at which the Bible states that the Philistines had encamped, while the Israelites pitched in Eben-Ezer, before the Battle of Aphek in which the sons of Eli were killedI Samuel 4:1–ff. *A city of the Tribe of Issachar, near to Jezreel, in the north of the Sharon plain. The scene, according to the Bible; of another encampment of the Philistines, which led to the defeat and death of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
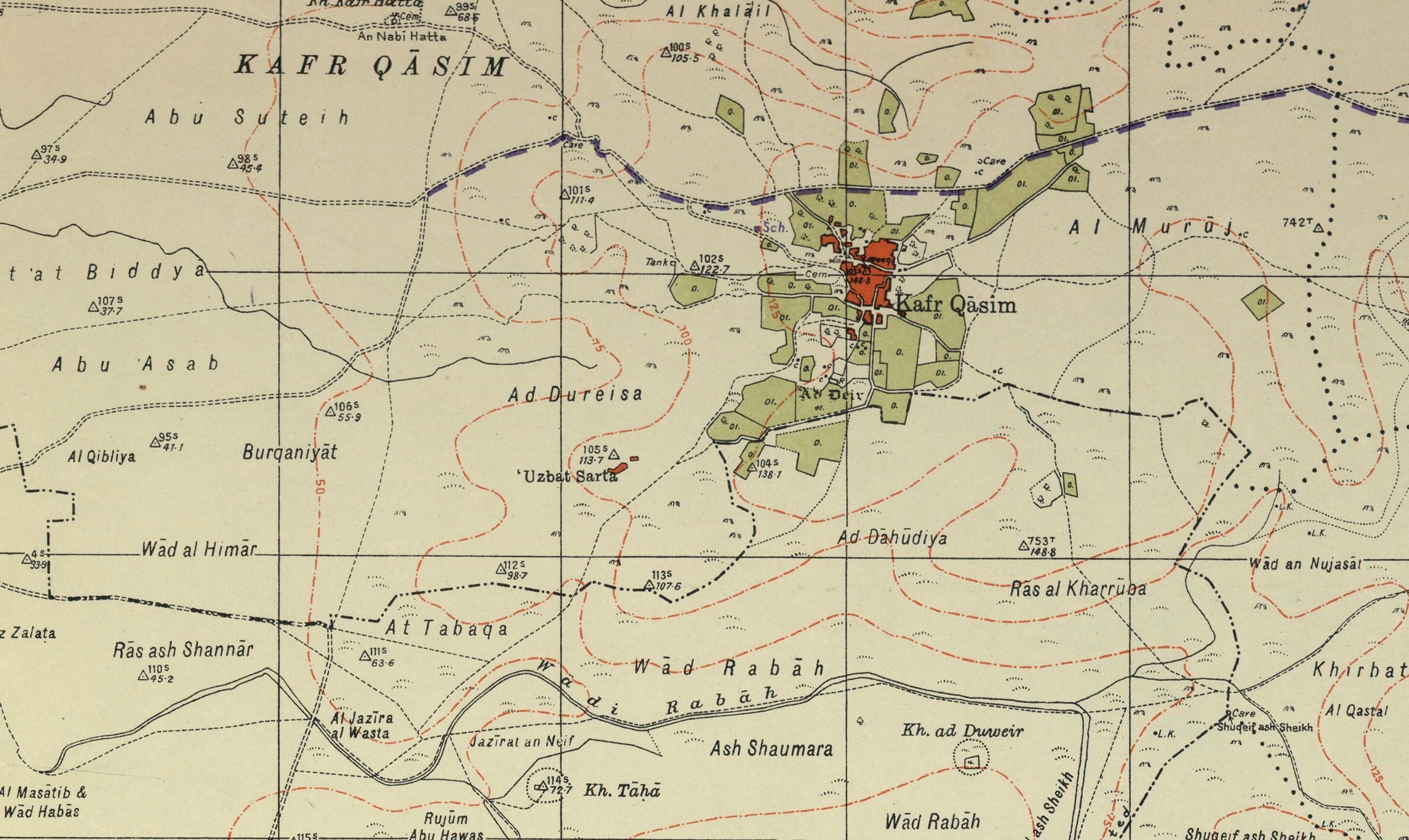
Kafr Qasim
Kafr Qasim ( ar, كفر قاسم, he, כַּפְר קָאסִם), also spelled as Kafr Qassem, Kufur Kassem, Kfar Kassem and Kafar Kassem, is a hill-top city in Israel with an Arab citizens of Israel, Arab population. It is located about east of Tel Aviv, on the Israeli side of the Green Line (Israel), Green Line separating Israel and the West Bank, in the southern portion of the "Triangle (Israel), Little Triangle" of Arab-Israeli towns and villages. In its population was . The town was the site of the Kafr Qasim massacre, in which the Israel Border Police killed 49 civilians on October 29, 1956. On February 12, 2008, Israeli Minister of the Interior Meir Sheetrit declared Kafr Qasim a city in a ceremony held at the town. History The town's area was populated in ancient times, based on remains from the Middle Paleolithic period found in the Qesem Cave. Cisterns, a winepress and terraced fields have also been documented, together with remains from the Byzantine Empire, Byzant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiloh (biblical City)
Shiloh (; he, שִׁלֹה, שִׁלוֹ ,שִׁילֹה, and שִׁילוֹ, variably, ''Šīlō'') was an ancient city and sanctuary in Samaria. According to the Hebrew Bible, Shiloh was the central sanctuary of the Israelites during the pre-monarchic period, before the First Temple in Jerusalem was built. After the Israelite conquest of Canaan, the Tabernacle was moved to Shiloh, and remained there during the period of the biblical judges. Shiloh has been positively identified with modern Khirbet Seilun, a tell known in Modern Hebrew as Tel Shiloh. It is located 31 km north of Jerusalem, in the West Bank, to the west of the modern Israeli settlement town of Shilo and to the north of the Palestinian town of Turmus Ayya. Relative to other archaeological sites, it is south of the biblical town of Lebonah and north of Bethel. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the Canaanites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)