|
1986 In Science
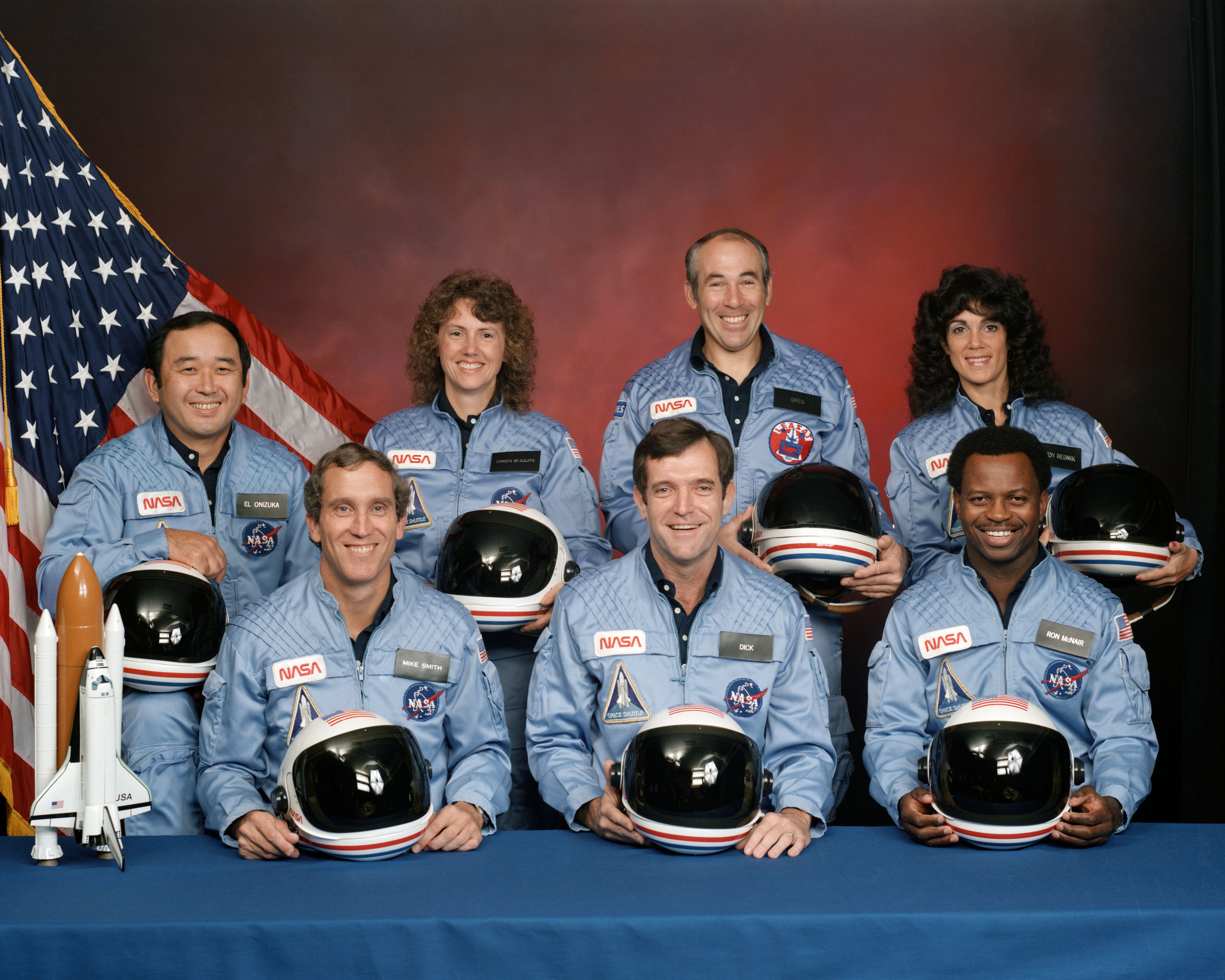
The year 1986 in science and technology involved many significant events, some not listed below. Astronomy and space exploration * January 24 – NASA ''Voyager 2'' space probe makes first encounter with Uranus. * January 28 – NASA Space Shuttle ''Challenger'' explodes on launch, killing all seven astronauts aboard. Their bodies are located by United States Navy divers on March 9. * February 19 – The Soviet Union launches the ''Mir'' space station. * March 8 – Japanese spacecraft ''Suisei'' flies by Halley's Comet, studying its UV hydrogen corona and solar wind. * October 10 – Aten asteroid 3753 Cruithne, in co-orbital configuration with Earth, is identified by Duncan Waldron. Biology * May – First reported methods for constructing a monoclonal antibody containing parts from mouse and human antibodies, a required first step toward the development of humanized antibodies used later as medical therapeutics (such as Infliximab). * English epidemiologist David Barker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, '' Voyager 1'', on a trajectory that took longer to reach gas giants Jupiter and Saturn but enabled further encounters with ice giants Uranus and Neptune. ''Voyager 2'' remains the only spacecraft to have visited either of the ice giant planets. ''Voyager 2'' was the fourth of five spacecraft to achieve Solar escape velocity, which allowed it to leave the Solar System. ''Voyager 2'' successfully fulfilled its primary mission of visiting the Jovian system in 1979, the Saturnian system in 1981, Uranian system in 1986, and the Neptunian system in 1989. The spacecraft is now in its extended mission of studying interstellar space. It has been operating for as of ; , it has reached a distance of from Earth. The probe entered interstellar space on Novemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Barker (epidemiologist)
David James Purslove Barker (29 June 1938 – 27 August 2013) was an English physician and epidemiologist and originator of the Barker Hypothesis that foetal and early infant conditions have a permanent conditioning effect on the body's metabolism and chronic conditions later in life.Cooper C (2013David Barker 1938–2013 Nature 502(7471), 304.Pincock S (2013David Barker The Lancet 382(9899), 1170. He was born in London the son of Hugh Barker, an engineer, and Joye, a concert cellist. At Oundle School, he developed an interest in Natural History and was given special access to the biology classrooms to study his finds. The Natural History Museum later asked him to mount an expedition to collect plant specimens from the Icelandic offshore island of Grimsey.Cooper C (2013David Barker Obituary The Guardian Wednesday 11 September 2013. He studied medicine at Guy's Hospital, London, but maintained his interest in Natural History, and had his first paper published in Nature in 196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Message Access Protocol
In computing, the Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) is an Internet standard protocol used by email clients to retrieve email messages from a mail server over a TCP/IP connection. IMAP is defined by . IMAP was designed with the goal of permitting complete management of an email box by multiple email clients, therefore clients generally leave messages on the server until the user explicitly deletes them. An IMAP server typically listens on port number 143. IMAP over SSL/TLS (IMAPS) is assigned the port number 993. Virtually all modern e-mail clients and servers support IMAP, which along with the earlier POP3 (Post Office Protocol) are the two most prevalent standard protocols for email retrieval. Many webmail service providers such as Gmail and Outlook.com also provide support for both IMAP and POP3. Email protocols The Internet Message Access Protocol is an application layer Internet protocol that allows an e-mail client to access email on a remote mail server. The curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LISTSERV
The term Listserv (styled by the registered trademark licensee, L-Soft International, Inc., as LISTSERV) has been used to refer to electronic mailing list software applications in general, but is more properly applied to a few early instances of such software, which allows a sender to send one email to a list, which then transparently sends it on to the addresses of the subscribers to the list. The original Listserv software, the Bitnic Listserv (also known as BITNIC LISTSERV) (1984–1986), allowed mailing lists to be implemented on IBM VM mainframes and was developed by Ira Fuchs, Daniel Oberst, and Ricky Hernandez in 1984. This mailing list service was known as Listserv@Bitnic (also known as LISTSERV@BITNIC) and quickly became a key service on the BITNET network. It provided functionality similar to a UNIX Sendmail alias and, as with Sendmail, subscriptions were managed manually. In 1986, Éric Thomas developed an independent application, originally named "Revised Listser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PC Convertible
The IBM PC Convertible (model 5140) is a laptop computer made by IBM, first sold in April 1986. The Convertible was IBM's first laptop-style computer, following the luggable IBM Portable, and introduced the 3½-inch floppy disk format to the IBM product line. Like modern laptops, it featured power management and the ability to run from batteries. It was replaced in 1991 by the IBM PS/2 L40 SX, and in Japan by the IBM Personal System/55note, the predecessor to the ThinkPad. Predecessors IBM had been working on a laptop for some time before the Convertible. In 1983, work was underway on a laptop similar to the Tandy Model 100, codenamed "Sweetpea," but it was rejected by Don Estridge for not being PC compatible. Another attempt in 1984 produced the "P-14" prototype machine, but it failed to pass IBM's human factors tests, especially after poor public reception of the display in the competing Data General-One. Description The PC Convertible came in three models: PC Convertibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Register
''The Register'' is a British technology news website co-founded in 1994 by Mike Magee, John Lettice and Ross Alderson. The online newspaper's masthead sublogo is "''Biting the hand that feeds IT''." Their primary focus is information technology news and opinions. Situation Publishing Ltd is listed as the site's publisher. Drew Cullen is an owner and Linus Birtles is the managing director. Andrew Orlowski was the executive editor before leaving the website in May 2019. History ''The Register'' was founded in London as an email newsletter called ''Chip Connection''. In 1998 ''The Register'' became a daily online news source. Magee left in 2001 to start competing publications '' The Inquirer'', and later the '' IT Examiner'' and '' TechEye''.Walsh, Bob (2007). ''Clear Blogging: How People Blogging Are Changing the World and How You Can Join Them.'' Apress, In 2002, ''The Register'' expanded to have a presence in London and San Francisco, creating ''The Register USA'' at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
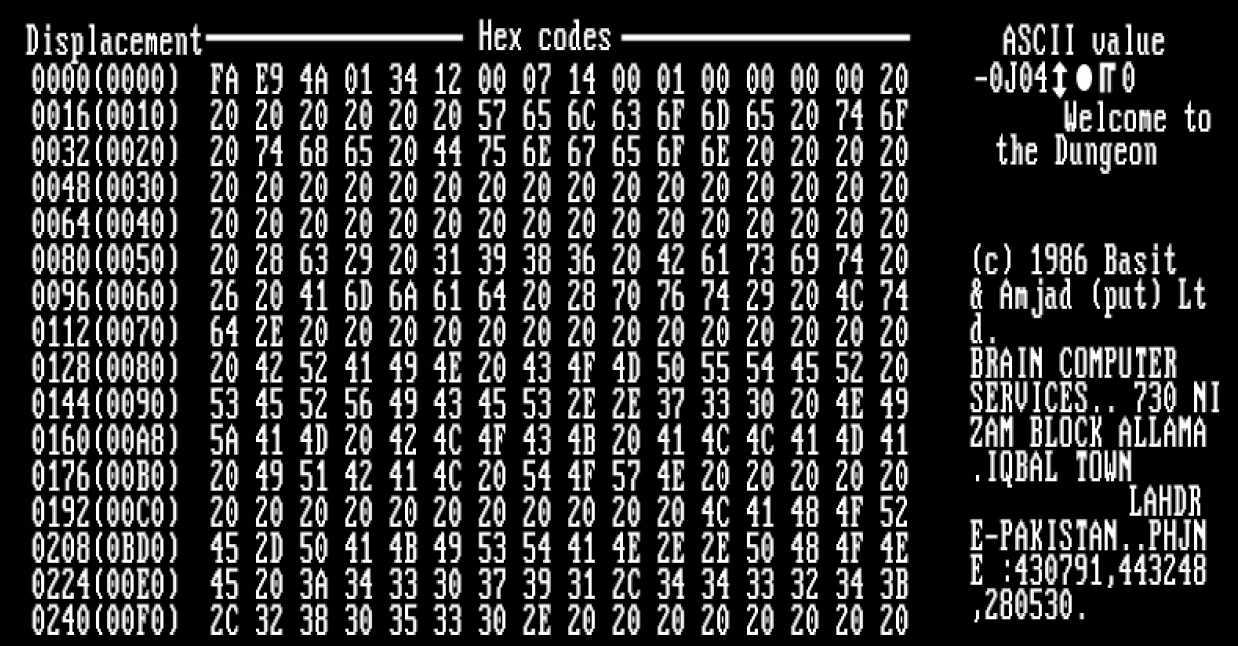
Brain (computer Virus)
Brain is the industry standard name for a computer virus that was released in its first form on 19 January 1986, and is considered to be the first computer virus for the IBM Personal Computer (IBM PC) and compatibles. Description Brain affects the PC by replacing the boot sector of a floppy disk with a copy of the virus. The real boot sector is moved to another sector and marked as bad. Infected disks usually have five kilobytes of bad sectors. The disk label is usually changed to ©Brain, and the following text can be seen in infected boot sectors: :Welcome to the Dungeon (c) 1986 Amjads (pvt) Ltd VIRUS_SHOE RECORD V9.0 Dedicated to the dynamic memories of millions of viruses who are no longer with us today - Thanks GOODNESS!!! BEWARE OF THE er..VIRUS : this program is catching program follows after these ....$#@%$@!! There are many minor and major variations to that version of the text. The virus slows down the floppy disk drive and makes seven kilobytes of memory unavailabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Virus
A computer virus is a type of computer program that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and inserting its own code. If this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected" with a computer virus, a metaphor derived from biological viruses. Computer viruses generally require a host program. The virus writes its own code into the host program. When the program runs, the written virus program is executed first, causing infection and damage. A computer worm does not need a host program, as it is an independent program or code chunk. Therefore, it is not restricted by the host program, but can run independently and actively carry out attacks. Virus writers use social engineering deceptions and exploit detailed knowledge of security vulnerabilities to initially infect systems and to spread the virus. Viruses use complex anti-detection/stealth strategies to evade antivirus software. Motives for creating viruses can inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS" (which is also the generic acronym for disk operating system). MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system. IBM licensed and re-released it in 1981 as PC DOS 1.0 for use in its PCs. Although MS-DOS and PC DOS were initially developed in parallel by Microsoft and IBM, the two products diverged after twelve years, in 1993, with recognizable differences in compatibility, syntax, and capabilities. Beginning in 1988 with DR-DO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Standards
In computer network engineering, an Internet Standard is a normative specification of a technology or methodology applicable to the Internet. Internet Standards are created and published by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). They allow interoperation of hardware and software from different sources which allows internets to function. As the Internet became global, Internet Standards became the lingua franca of worldwide communications. Engineering contributions to the IETF start as an Internet Draft, may be promoted to a Request for Comments, and may eventually become an Internet Standard. An Internet Standard is characterized by technical maturity and usefulness. The IETF also defines a Proposed Standard as a less mature but stable and well-reviewed specification. A Draft Standard was an intermediate level, discontinued in 2011. A Draft Standard was an intermediary step that occurred after a Proposed Standard but prior to an Internet Standard. As put in RFC 2026: In g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standards Organization
A standards organization, standards body, standards developing organization (SDO), or standards setting organization (SSO) is an organization whose primary function is developing, coordinating, promulgating, revising, amending, reissuing, interpreting, or otherwise contributing to the usefulness of technical standards to those who employ them. Such an organization works to create uniformity across producers, consumers, government agencies, and other relevant parties regarding terminology, product specifications (e.g. size, including units of measure), protocols, and more. Its goals could include ensuring that Company A's external hard drive works on Company B's computer, an individual's blood pressure measures the same with Company C's sphygmomanometer as it does with Company D's, or that all shirts that should not be ironed have the same icon (a clothes iron crossed out with an X) on the label. Most standards are voluntary in the sense that they are offered for adoption by peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |