|
1957 Andreanof Islands Earthquake
The 1957 Andreanof Islands earthquake took place on March 9 with a moment magnitude of 8.6 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (''Severe''). It occurred south of the Andreanof Islands group, which is part of the Aleutian Islands arc. The event occurred along the Aleutian Trench, the convergent plate boundary that separates the Pacific Plate and the North American Plates near Alaska. A basin wide tsunami followed, with effects felt in Alaska and Hawaii. Total losses were around $5 million. Tectonic setting The Aleutian Subduction Zone is the convergent boundary of the Pacific and North American Plates. This oceanic trench runs from the Kuril Subduction Zone in the west to the Yakutat Collision Zone in the east. At each end of the subduction zone are right-lateral transform faults, including the Queen Charlotte Fault in the east, and a similar structure at the far west end of the arc near Attu Island. Earthquake Because the shock occurred before the World Wide Standardised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller islands. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, but some belong to the Russian Federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying a land area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and act as a border between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing 180th meridian, longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude (Amatignak Island) and the easternmost by longitude ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for Episodic tremor and slip, non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Seismological Centre
The International Seismological Centre (ISC) is a non-governmental, nonprofit organisation charged with the final collection, definitive analysis and publication of global seismicity. The ISC was formed in 1964 as an international organisation independent of national governments that would carry on the work of the International Seismological Summary in collecting and analyzing seismic data from around the world, and particularly to handle increased flow of data from the World-Wide Standard Seismograph Network (WWSSN), also established that year. The ISC considers its prime task to be the collection and re-analysis of all available earthquake seismic date in order to produce definitive data on earthquakes. The ISC's catalog is considered "the most complete and authoritative final depository of global earthquake parameter data." Purpose The main scientific goal of the Centre is the definitive compilation of earthquake information and the readings on which they are based. Collecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Vsevidof
Mount Vsevidof ( or ; russian: Вулкан Всевидова) is a stratovolcano in the U.S. state of Alaska. Its summit is the highest point on Umnak Island, one of the eastern Aleutian Islands. Its symmetrical cone rises abruptly from its surroundings. The base of the volcano is around wide, steepening from about 15 degrees at altitude to around 30 degrees near the summit. Some glacial tongues have cut through narrow canyons up to deep, due to ice filling the crater and extending down the north and east flanks of the cone. Vsevidof's most recent eruption was caused by an earthquake on March 9, 1957. The mountain erupted on March 11, 1957, and the eruption ended the next day.This is recorded as a "questionable eruption" by the Alaska Volcano Observator(Vsevidof History Page) Other possible eruptions or activity occurred in 1784, 1790, 1830, 1878, and 1880. Its name comes from Russian words for “all” and “sight”, suggesting that it was implied to mean “seen from e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Earthquakes In The United States
The following is a list of notable earthquakes and tsunamis which had their epicenter in areas that are now part of the United States with the latter affecting areas of the United States. Those in ''italics'' were not part of the United States when the event occurred. List of earthquakes Earthquake swarms which affected the United States: * 1962–71 Denver earthquake swarm * Enola earthquake swarm * 2008 Reno earthquakes * Guy-Greenbrier earthquake swarm * Oklahoma earthquake swarms (2009–present) Earthquakes which affected the United States but whose epicenters were outside the United States borders: * 1925 Charlevoix–Kamouraska earthquake – magnitude 6.2 earthquake, no injuries or fatalities anywhere * 1979 Imperial Valley earthquake – magnitude 6.4 earthquake with an epicenter less than 1 km inside Mexico – significant damage and injuries on both sides of the border (60 in the US) * 2010 Baja California earthquake (Mexico near S California) – magnitude 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Earthquakes In Alaska ...
This is an incomplete list of earthquakes in Alaska. See also *Geology of Alaska References {{Authority control Earthquakes Alaska Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Earthquakes In 1957
This is a list of earthquakes in 1957. Only magnitude 6.0 or greater earthquakes appear on the list. Lower magnitude events are included if they have caused death, injury or damage. Events which occurred in remote areas will be excluded from the list as they wouldn't have generated significant media interest. All dates are listed according to UTC time. An extremely active year in a large way helped by a magnitude 8.6 earthquake in Alaska in March. This event was one of the largest on record in the United States and was followed by an energetic aftershock sequence which resulted in 6 aftershocks measuring greater than magnitude 7.0. Other parts of the world such as Mongolia, Bolivia and Turkey to name a few saw large events. Turkey and Iran had several earthquakes with high death tolls. Overall By death toll * Note: At least 10 casualties By magnitude * Note: At least 7.0 magnitude Notable events January February March April May ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haleiwa, Hawaii
Haleiwa () is a North Shore community and census-designated place (CDP) in the Waialua District of the island of Oahu, City and County of Honolulu. Haleiwa is located on Waialua Bay, the mouth of Anahulu Stream (also known as Anahulu River). A small boat harbor is located here, and the shore of the bay is surrounded by Haleiwa Beach Park (north side) and Haleiwa Alii Beach Park (south side). Further west from the center of town is Kaiaka State Recreation Area on Kiaka Point beside Kaiaka Bay. As of the 2020 census, the CDP had a population of 4,941. The 2018 estimate was 4,040. It is the largest commercial center on the North Shore of the island. Its old plantation town character is preserved in many of the buildings, making this a popular destination for tourists and residents alike, visiting surfing and diving sites along the north shore. The U.S. postal code for Haleiwa, including Kawailoa, is 96712. Geography Haleiwa is located at 21°35'24" North, 158°6'50" West (21 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waialua, Hawaii
Waialua () is a census-designated place and North Shore community in the Waialua District on the island of Oahu, City & County of Honolulu, Hawaii, United States. As of the 2020 census, the CDP had a population of 4,062. Waialua was one of the six original districts of ancient Hawaii on the island, known as ''moku''. Waialua is a former (sugar) mill town and residential area, quite different in its quiet ambiance from nearby Haleiwa, which is more commercial and tourist oriented. The Waialua Sugar Mill is the center of this town and the historical base of its plantation history. The U.S. postal code for Waialua is 96791. Geography Waialua is located at 21°34'31" North, 158°7'46" West (21.575300, -158.129457), southwest of Haleiwa, reached on Waialua Beach Road (State Rte. 82) or Kaukonahua Road (State Rte. 830). Kaukonahua Road turns eastward and, as State Rte. 803 then 801 runs up into the central plateau of Oahu to Wahiawā or (as 803) to Schofield Barracks. Farringt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
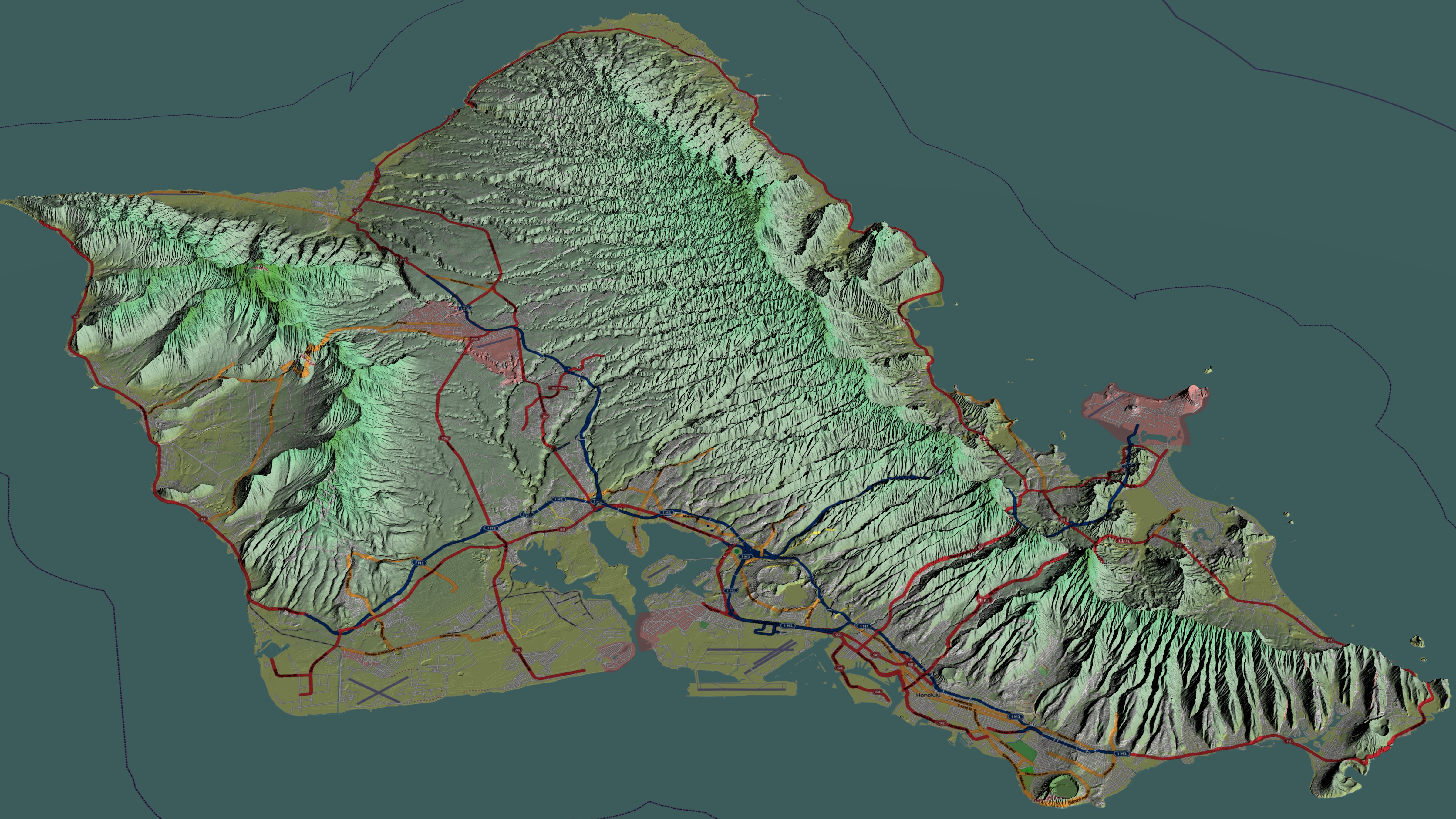
Oahu
Oahu () (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Oʻahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering place#Island of Oʻahu as The Gathering Place, Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million people—over two-thirds of the population of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The island of O’ahu and the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands constitute the City and County of Honolulu, Hawaii, City and County of Honolulu. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oʻahu's southeast coast. Oʻahu had a population of 1,016,508 according to the 2020 U.S. Census, up from 953,207 people in 2010 (approximately 70% of the total 1,455,271 population of the State of Hawaii, with approximately 81% of those living in or near the Honolulu urban area). Name The Island of O{{okinaahu in Hawaii is often nicknamed (or translated as) ''"The Gathering Place"''. It appears that O{{okinaahu grew into this nickname; it is currently the most populated Hawaiian islands, Hawaiian Island, how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1946 Aleutian Islands Earthquake
The 1946 Aleutian Islands earthquake occurred near the Aleutian Islands, Alaska on April 1, 1946. The shock had a moment magnitude () of 8.6, a tsunami magnitude of 9.3, and a surface-wave magnitude () of only 7.4, and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (''Strong''). It resulted in 165–173 casualties and over $26 million in damage. The seafloor along the fault was elevated, triggering a Pacific-wide tsunami with multiple destructive waves at heights ranging from . The tsunami obliterated the Scotch Cap Lighthouse on Unimak Island, Alaska among others, and killed all five lighthouse keepers. Despite the destruction to the Aleutian Island Unimak, the tsunami had almost an imperceptible effect on the Alaskan mainland. Tectonic setting The Aleutian Islands are a group of 14 large and 55 smaller volcanic islands situated between mainland Alaska and Kamchatka. They are situated along the Aleutian Trench as they were formed by the active subduction of the oceanic Pacific plate unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kauai
Kauai, () anglicized as Kauai ( ), is geologically the second-oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands (after Niʻihau). With an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), it is the fourth-largest of these islands and the 21st largest island in the United States. Nicknamed the Garden Isle, Kauai lies 73 miles (117 km) across the Kauai Channel, northwest of Oahu. This island is the site of Waimea Canyon State Park and the Na Pali Coast State Park. The United States Census Bureau defines Kauai as census tracts 401 through 409 of Kauai County, Hawaii, which comprises all of the county except the islands of Kaʻula, Lehua and Niihau. The 2020 United States census population of the island was 73,298. The most populous town is Kapaa. Etymology and language Hawaiian narrative locates the name's origin in the legend of Hawaiiloa, the Polynesian navigator credited with discovery of the Hawaiian Islands. The story relates how he named the island of Kauai after a favorite son; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |