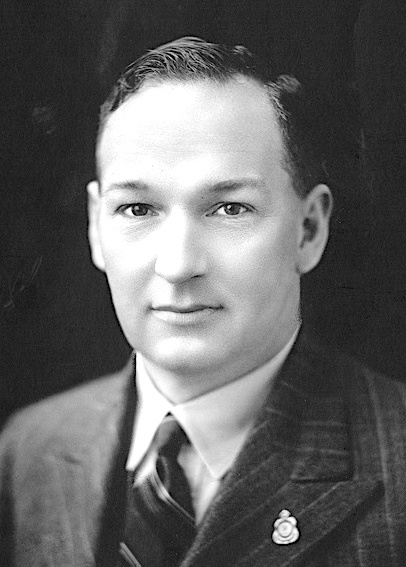|
1953 South Australian State Election
State elections were held in South Australia on 7 March 1953. All 39 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Liberal and Country League led by Premier of South Australia Thomas Playford IV defeated the Australian Labor Party led by Leader of the Opposition Mick O'Halloran. Background Labor won three seats, metropolitan Norwood and Prospect and rural Victoria from the LCL. The LCL won one seat, rural Murray from Labor. Neither major party contested the independent-held seat of Ridley. The Labor opposition won 53 percent of the statewide two-party vote, but the LCL retained government with the assistance of the Playmander − an electoral malapportionment that also saw a clear majority of the statewide two-party vote won by Labor while failing to form government in 1944, 1962 and 1968. Results * The primary vote figures were from contested seats, while the state-wide two-party-preferred vote figures were estimated from all se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Australian House Of Assembly
The House of Assembly, or lower house, is one of the two chambers of the Parliament of South Australia. The other is the Legislative Council. It sits in Parliament House in the state capital, Adelaide. Overview The House of Assembly was created in 1857, when South Australia attained self-government. The development of an elected legislature — although only men could vote — marked a significant change from the prior system, where legislative power was in the hands of the Governor and the Legislative Council, which was appointed by the Governor. In 1895, the House of Assembly granted women the right to vote and stand for election to the legislature. South Australia was the second place in the world to do so after New Zealand in 1893, and the first to allow women to stand for election. (The first woman candidates for the South Australia Assembly ran in 1918 general election, in Adelaide and Sturt.) From 1857 to 1933, the House of Assembly was elected from multi-member di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunday Mail (Adelaide)
The ''Sunday Mail'' (originally titled ''The Mail'') is an Adelaide newspaper first published on 4 May 1912 by Clarence Moody. Through much of the 20th century, '' The Advertiser'' was Adelaide's morning broadsheet, '' The News'' the afternoon tabloid, ''The Sunday Mail'' a vehicle for covering weekend sport, and ''Messenger Newspapers'' covering community news. "Sunday Mail" is a business name of Advertiser Newspapers Pty Ltd, a private company that is part of News Corp Australia, which since 2004 has been a component of the U.S. multinational mass media company, News Corp. History ''Mail'' In 1912, Clarence Moody initially set up three newspapers – the ''Sporting Mail'' (1912-1914), ''Saturday Mail'' (1912-1917), and the ''Mail''. The first two titles lasted only a few years, and the ''Mail'' itself went into liquidation in late 1914. Ownership passed briefly to George Annells and Frank Stone, and then to Herbert Syme. In May 1923 News Limited purchased the ''Mail'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hector White
Hector Burnard White (18 June 1900 – 9 June 1969) was an Australian politician who represented the South Australian House of Assembly seat of Murray from 1953 to 1956 for the Liberal and Country League Liberal or liberalism may refer to: Politics * a supporter of liberalism ** Liberalism by country * an adherent of a Liberal Party * Liberalism (international relations) * Sexually liberal feminism * Social liberalism Arts, entertainment and .... In local politics, he was mayor of the Corporate Town of Murray Bridge from 1951 to 1956. References 1900 births 1969 deaths Members of the South Australian House of Assembly Liberal and Country League politicians 20th-century Australian politicians Mayors of places in South Australia {{Australia-Liberal-politician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colin Dunnage
Colin Rosslyn Dunnage (10 October 1896 – 7 November 1969) was an Australian politician who represented the South Australian House of Assembly seat of Unley from 1941 to 1962 for the Liberal and Country League Liberal or liberalism may refer to: Politics * a supporter of liberalism ** Liberalism by country * an adherent of a Liberal Party * Liberalism (international relations) * Sexually liberal feminism * Social liberalism Arts, entertainment and .... References Members of the South Australian House of Assembly 1896 births 1969 deaths Liberal and Country League politicians 20th-century Australian politicians {{Australia-politician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral District Of Unley
Unley is a single-member electoral district for the South Australian House of Assembly. Named after the suburb of the same name, it is the state's smallest electorate by area at just . It is a suburban electorate in Adelaide's inner south, taking in the suburbs of Eastwood, Frewville, Fullarton, Glenside, Glenunga, Goodwood, Highgate, Hyde Park, Kings Park, Malvern, Myrtle Bank, Parkside, Unley, Unley Park and Wayville, as well as parts of Glen Osmond and Millswood. Unley was created as a conservative seat. It was first contested at the 1938 election, where it was held by conservatives until the 1962 election, when Gil Langley captured the seat for Labor. Unley was one of the seats that put Labor in government at the 1965 election after decades of the Playmander in opposition, with Labor managing to retain Unley in the close 1968 and 1975 elections and the 1979 election loss. Langley was succeeded by Labor's Kym Mayes at the 1982 election, a state government minist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1968 South Australian State Election
The 1968 South Australian State election was held in South Australia on 2 March 1968. All 39 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election; 38 of the 39 contests were won by candidates from Australia's two major political parties. The incumbent Australian Labor Party (South Australian Branch), Australian Labor Party (led by Premiers of South Australia, Premier of South Australia Don Dunstan) and the Liberal and Country League (led by Leader of the Opposition (South Australia), Leader of the Opposition Steele Hall) both won 19 seats. The sole independent candidate to win a race, Tom Stott of the Ridley electorate, joined with the LCL's 19 seats to form a coalition government that held a 20 to 19 majority, thus defeating the Dunstan Labor government. Key dates Outcome The election saw the Liberal and Country League opposition form a minority government, winning the same number of seats in the House of Assembly as the incumbent Australian Labor Party (South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1962 South Australian State Election
State elections were held in South Australia on 3 March 1962. All 39 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Liberal and Country League led by Premier of South Australia Thomas Playford IV defeated the Australian Labor Party led by Leader of the Opposition Frank Walsh. This was the first and only time that a South Australian Government won a tenth consecutive term in office. Background The Playford government, in power since 1938, went into the 1962 elections in a precarious position. At the time the writs were issued, South Australia was dogged by a massive recession. This led observers to think that Labor would finally have a chance at power; longtime opposition leader Mick O'Halloran had died suddenly in 1960, and Labor was led into the election by former deputy leader Frank Walsh. The Labor opposition won in excess of 54 percent of the statewide two-party vote, however the LCL retained government with the assistance of the Pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1944 South Australian State Election
State elections were held in South Australia on 29 April 1944. All 39 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Liberal and Country League government led by Premier of South Australia Thomas Playford IV defeated the opposition Australian Labor Party led by Leader of the Opposition Robert Richards. Background Labor won an additional five seats totaling 16 seats − the highest number of seats won by Labor from the 1933 election through to the 1959 election, an effort not even outdone at the 1953 election where Labor won 53 percent of the statewide two-party vote but the LCL retained government with the assistance of the Playmander − an electoral malapportionment that also saw a clear majority of the statewide two-party vote won by Labor while failing to form government in 1953, 1962 and 1968. The election was the first where the two-party vote had been retrospectively calculated. Unusually a wartime opposition won a clear majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apportionment (politics)
Apportionment is the process by which seats in a legislative body are distributed among administrative divisions, such as states or parties, entitled to representation. This page presents the general principles and issues related to apportionment. The page Apportionment by country describes specific practices used around the world. The page Mathematics of apportionment describes mathematical formulations and properties of apportionment rules. The simplest and most universal principle is that elections should give each voter's intentions equal weight. This is both intuitive and stated in laws such as the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution (the Equal Protection Clause). However, there are a variety of historical and technical reasons why this principle is not followed absolutely or, in some cases, as a first priority. Common problems Fundamentally, the representation of a population in the thousands or millions by a reasonable size, thus accountable governi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Playmander
The Playmander was a gerrymandering system, a pro-rural electoral malapportionment in the Australian state of South Australia, which was introduced by the incumbent Liberal and Country League (LCL) government in 1936, and remained in place for 32 years until 1968. This consisted of 26 low-population rural seats holding as much as a 10-to-1 advantage over the 13 high-population metropolitan seats in the state parliament, even though rural seats contained only a third of South Australia's population during this period. At the peak of the malapportionment in 1968, the rural seat of Frome had 4,500 formal votes, while the metropolitan seat of Enfield had 42,000 formal votes. Additionally, there was also a change from multi-member seats to single-member seats for the first time in South Australia's history, while the number of MPs in the lower house was reduced from 46 to 39. During the Playmander's existence, Labor managed to win enough parliamentary seats to form government on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-party-preferred Vote
In Australian politics, the two-party-preferred vote (TPP or 2PP) is the result of an election or opinion poll after preferences have been distributed to the highest two candidates, who in some cases can be independents. For the purposes of TPP, the Liberal/National Coalition is usually considered a single party, with Labor being the other major party. Typically the TPP is expressed as the percentages of votes attracted by each of the two major parties, e.g. "Coalition 50%, Labor 50%", where the values include both primary votes and preferences. The TPP is an indicator of how much swing has been attained/is required to change the result, taking into consideration preferences, which may have a significant effect on the result. The TPP assumes a two-party system, i.e. that after distribution of votes from less successful candidates, the two remaining candidates will be from the two major parties. However, in some electorates this is not the case. The two-candidate-preferred vote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral District Of Ridley
The Electoral district of Ridley was an electoral district of the South Australian House of Assembly, existing between 1938 and 1970 and between 1993 and 1997. Named after John Ridley, the inventor of a successful threshing machine, Ridley was a rural electorate located in the riverland area of South Australia, stretching along the southern bank of the Murray River from Morgan to the New South Wales border. Ridley also contained the towns of Waikerie, Lyrup and Loxton. Created for the 1938 South Australian election, following the change from multi-member to single-member electorates, Ridley was held by Tom Stott for its entire existence. Stott was the longest serving independent in Australian political history. Ridley was abolished at the 1970 election.Jaensch, D. (1977) ''The Government of South Australia'', University of Queensland Press, St Lucia, . Ridley was recreated as an electoral district in a 1991 redistribution for the 1993 election. In this incarnation, Ridle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |