|
1952 Mysore Legislative Assembly Election
Elections to the Vidhan Sabha, Legislative Assembly of the Indian state of Mysore State, Mysore were held on 26 March 1952. 394 candidates contested for 99 seats in 80 constituencies in the Assembly. There were 19 two-member constituencies and 61 single-member constituencies, accounting for 99 seats. Results !colspan=8, , - style="background-color:#E9E9E9; text-align:center;" ! class="unsortable" , ! Political party !! Flag !! Seats Contested !! Won !! % of Seats !! Votes !! Vote % , - style="background: #90EE90;" , , , 99 , , 74 , , 74.75 , , 12,76,318 , , 46.35 , - , , , 59 , , 8 , , 8.08 , , 3,91,653 , , 14.22 , - , , , 47 , , 3 , , 3.03 , , 240390 , , 8.73 , - , , , 7 , , 2 , , 2.02 , , 47,916 , , 1.74 , - , , , 5 , , 1 , , 1.01 , , 25,116 , , 0.91 , - , , , 154 , , 11 , , 11.11 , , 7,10,359 , , 25.79 , - class="unsortable" style="background-color:#E9E9E9" ! colspan = 3, Total seats ! 99 !! style="text-align:center;" , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karnataka Legislative Assembly
The Karnataka Legislative Assembly is the lower house of the bicameral legislature of the Indian state of Karnataka. Karnataka is one of the six states in India where the state legislature is bicameral, comprising two houses. The two houses are the ''Vidhan Sabha'' (lower house) and the ''Vidhan Parishad'' (upper house). The members of the Legislative Assembly are directly elected by people through adult franchise. There are 224 members of the ''Legislative Assembly'' of Karnataka. Karnataka is divided into 224 constituencies used to elect the Legislative assembly members. Each constituency elects one member of the assembly. Members are popularly known as MLAs. The assembly is elected using the simple plurality or "first past the post" electoral system. The elections are conducted by the Election Commission of India. The normal term of the members lasts for five years. In case of death, resignation, or disqualification of a member, a by-election is conducted for constitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kengal Hanumanthaiah
Kengal Hanumanthaiah (14 February 1908 – 1 December 1980), also spelt as Kengal Hanumanthaiya, was the second Chief Minister of Karnataka (then, Mysore State) from 30 March 1952 to 19 August 1956. He contributed to the construction of Vidhana Soudha, the seat of the state legislature. Early life Hanumanthaiah was born on 14 February 1908, in a Vokkaliga family in a Lakkappanahalli, a small village near Ramanagara, Ramanagara District. He graduated in Arts from the Maharaja College in Mysore in 1930 and later earned a degree in Law from Poona Law College in 1932. During his college days, he was elected as the Secretary of the Students Union and the Karnataka Sangha. After his graduation, he joined the bar council in the same year. Political career At that time, the independence movement was steadily growing and at the center stage of the movement was the Indian National Congress led by Mahatma Gandhi. Dr. P. Tandon, the then President of Indian National Congress, advised H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombay State
Bombay State was a large Indian state created at the time of India's Independence, with other regions being added to it in the succeeding years. Bombay Presidency (roughly equating to the present-day Indian state of Maharashtra, excluding South Maharashtra and Vidarbha) was merged with the princely states of Baroda, Western India and Gujarat (the present-day Indian state of Gujarat) and the Deccan States (which included parts of the present-day Indian states of Maharashtra and Karnataka). On 1 November 1956, Bombay State was re-organized under the States Reorganisation Act on linguistic lines, absorbing various territories including the Saurashtra and Kutch States, which ceased to exist. On 1 May 1960, Bombay State was dissolved and split on linguistic lines into the two states of Gujarat, with Gujarati speaking population and Maharashtra, with Marathi speaking population. History During the British Raj, portions of the western coast of India under direct British rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native speakers, and was additionally a second or third language for around 13 million non-native speakers in Karnataka. Kannada was the court language of some of the most powerful dynasties of south and central India, namely the Kadambas, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, Yadava Dynasty or Seunas, Western Ganga dynasty, Wodeyars of Mysore, Nayakas of Keladi Hoysalas and the Vijayanagara empire. The official and administrative language of the state of Karnataka, it also has scheduled status in India and has been included among the country's designated classical languages.Kuiper (2011), p. 74R Zydenbos in Cushman S, Cavanagh C, Ramazani J, Rouzer P, ''The Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics: Fourth Edition'', p. 767, Princeton Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and the Marathwada region of Maharashtra in India. The state was ruled from 1724 to 1857 by the Nizam, who was initially a viceroy of the Mughal empire in the Deccan. Hyderabad gradually became the first princely state to come under British paramountcy signing a subsidiary alliance agreement. During British rule in 1901 the state had an average revenue of Rs. 417,000,000, making it the wealthiest princely state in India. The native inhabitants of Hyderabad Deccan, regardless of ethnic origin, are called "Mulki" (countryman), a term still used today. The dynasty declared itself an independent monarchy during the final years of the British Raj. After the Partition of India, Hyderabad signed a standstill agreement with the new dominion of India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madras State
Madras State was a state of India during the mid-20th century. At the time of its formation in 1950, it included the whole of present-day Tamil Nadu (except Kanyakumari district), Coastal Andhra, Rayalaseema, the Malabar region of North and central Kerala, Bellary, South Canara and Kollegal. Coastal Andhra and Rayalaseema were separated to form Andhra State in 1953, while South Canara and Bellary districts along with the Kollegalam taluka of Coimbatore district were merged with Mysore State, and Malabar District with the State of Travancore-Cochin to form Kerala in 1956. Post State Reorganization in 1956, the remaining Madras State was renamed to Tamil Nadu on January 14, 1969. History After Indian Independence, the Madras Presidency became the Madras Province on 15 August 1947. On 26 January 1950, it was formed as Madras State by the Government of India. As a result of the 1956 States Reorganisation Act, the state's boundaries were re-organized following linguistic line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kasaragod
Kasaragod () is a municipal town and administrative headquarters of Kasaragod district in the state of Kerala, India. Established in 1966, Kasaragod was the first municipal town in the district. It is the northernmost district of Kerala and is also known as ''Saptha Bhasha Sangama Bhoomi'' ('The Land of seven Languages'). Situated in the rich biodiversity of Western Ghats, it is known for the Chandragiri and Bekal Fort, Chandragiri River, historic Kolathiri Rajas, natural environment of Ranipuram and Kottancheri Hills, historical and religious sites like the Madiyan Kulom temple, Madhur Temple, Ananthapuram Lake Temple and Malik Deenar Mosque. The historic hill of Ezhimala is located on the southern portion of Kavvayi Backwaters of Nileshwaram. Kasaragod is located 50 km south of the major port city and a commercial hub Mangalore and 364 km north of the major port city Kochi. Kasaragod district has the maximum number of rivers in Kerala - 12. The town is loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
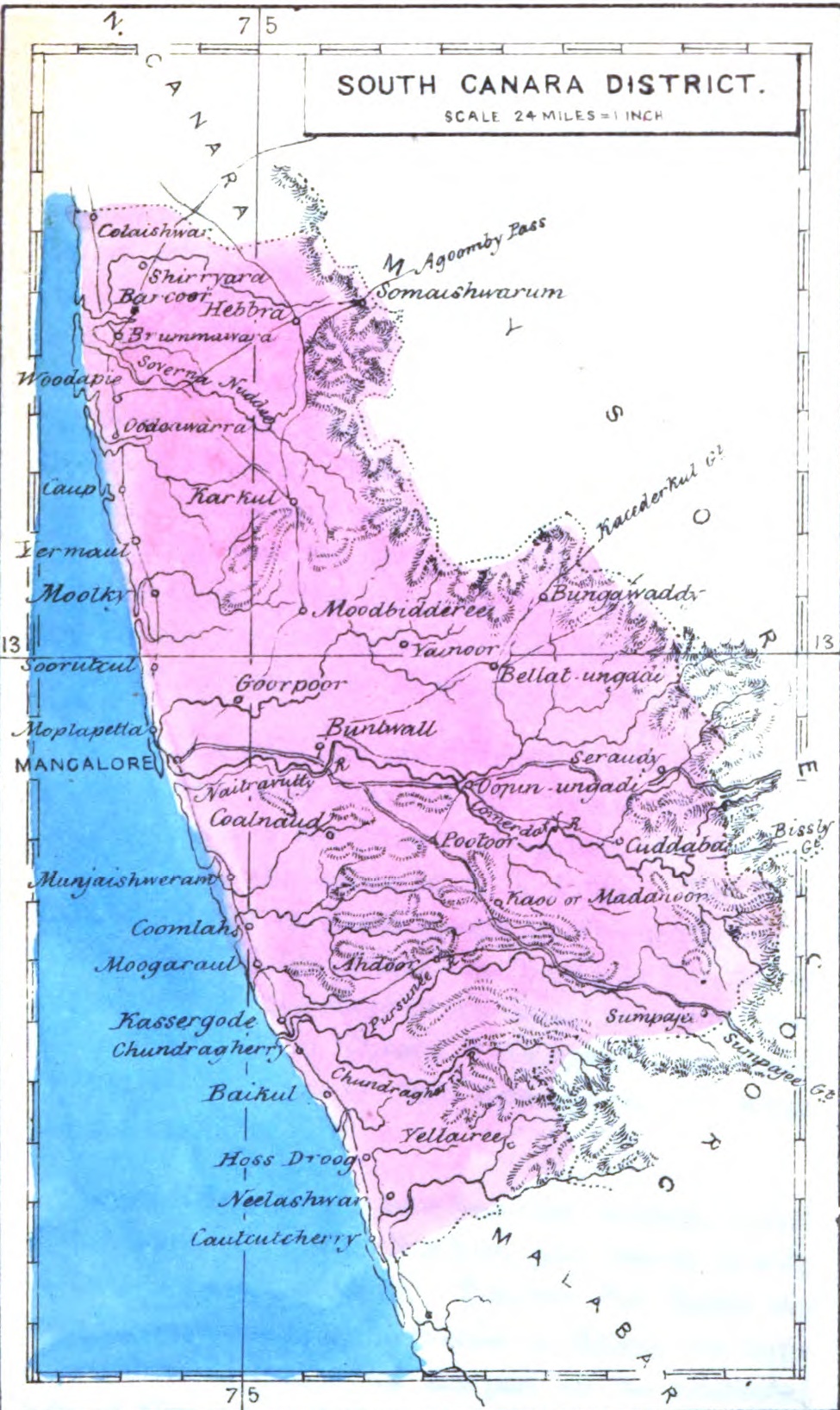
South Kanara
South Canara was a district of the Madras Presidency of British India, located at . It comprised the towns of Kassergode and Udipi and adjacent villages, with the capital in Mangalore city. South Canara was one of the most heterogeneous areas of Madras Presidency, with Tulu, Malayalam, Kannada, Konkani, Marathi, Urdu, and Beary languages being spoken side by side. It was succeeded by the Tulu-speaking areas of Dakshina Kannada district, the Malayalam-speaking area of Kasaragod district and the Amindivi islands sub-division of the Laccadives, in the year 1956. Geography Mangalore was the administrative headquarters of the district. The district covered an area of . South Canara District was bordered by North Canara to north, the princely state of Mysore to east, Coorg state to southeast, Malabar District to south, and Arabian Sea to west. South Canara was one of the two districts on the western coast (Malabar coast) of Madras Presidency along with Malabar District (otherwise kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kollegal
Kollegal is one of the major taluks in the Chamarajanagara District of Karnataka State in the south of India. It is also the largest taluk in Karnataka, Kollegal is well known for its silk industry which attracts traders from all over the state. History Until 1956, Kollegal was part of the Coimbatore district of the Madras Presidency. The States Reorganisation Act of 1956 moved Kollegal to Karnataka primarily organising it along linguistic lines. Kollegal is the name derived from the names of two hermits namely 'Kauhala' and 'Galava' who were believed to be instrumental in the development of Kollegal. Kollegal, also called "Silk City", is famous for its handloom silk saree industry. Kollegal is one of the larger taluks in Karnataka and was previously the largest. Plans are underway to divide Kollegal, making Hanur the capital of the new taluk in the Chamarajanagara District. This separation has been ongoing for years is not yet entirely in effect. Kollegal serves as a center ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coorg State
Coorg State was a Part-C state in India which existed from 1950 to 1956. When the Constitution of India came into force on 26 January 1950, most of the existing provinces were reconstituted into states. Thus, Coorg Province became Coorg State. Coorg State was ruled by a Chief Commissioner with Mercara as its capital. The head of the government was the Chief Minister. Coorg State was abolished on 1 November 1956 as per the States Reorganisation Act, 1956 and its territory were merged with Mysore State (later renamed as Karnataka in 1973). Presently, Coorg forms a district of Karnataka state. History The Coorg State came into being on 26 January 1950 as per the Constitution of India. Prior to the enactment of the Constitution, Coorg had been a province of the Dominion of India. The first legislative elections in Coorg were held in 1952. The main contenders were the Indian National Congress led in the state by C. M. Poonacha and the Takkadi party led by the Gandhian Pandyanda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)