|
1947 World Ice Hockey Championships
The 14th Ice Hockey World Championships and 25th European Championship was the first after the Second World War. It was held from 15 to 23 February 1947 at Štvanice Stadium in Prague, Czechoslovakia. Eight teams participated, but the competition was notably missing the reigning world champion, Canada. The world champion was decided for the first time by round robin league play. Czechoslovakia won the world championship for the first time and the European championship for the seventh time. King Gustav V had sent a telegram of congratulations to the Swedish team after beating the Czechoslovaks, but they had barely finished celebrating when they were upset by the Austrians, costing them the gold medal. History The 1947 congress of the Ligue Internationale de Hockey sur Glace (LIHG) was the first meeting or the organization since World War II. During the war, the Canadian Amateur Hockey Association (CAHA) united with the Amateur Hockey Association of the United States (AHAUS) to form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimír Zábrodský
Vladimír Olegovic Zábrodský (7 March 1923 – 20 March 2020) was a Czechoslovak ice hockey and tennis player. Born in Prague, Czechoslovakia, he won a silver medal with the Czechoslovakian national team at the 1948 Winter Olympics, and won the world championships (1947 and 1949). Zábrodský was also a tennis player and member of the Czechoslovakian Davis Cup team. He was inducted into the International Ice Hockey Federation Hall of Fame in 1997. Ice hockey career He was one of the inaugural members of the International Ice Hockey Federation Hall of Fame, inducted in 1997. He played in the Czechoslovak First Ice Hockey League for LTC Prague from 1940 to 1950, Spartak ČKD Sokolovo from 1950 to 1960, and Bohemians ČKD Praha from 1963 to 1965, collecting 306 goals. Tennis career Zábrodský also represented Czechoslovakia in the Davis Cup during 1948, 1955, and 1956. He made his Davis Cup debut for Czechoslovakia in the 1948 Europe Zone second round tie against Brazil. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ice hockey league in the world, and is one of the four major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada. The Stanley Cup, the oldest professional sports trophy in North America, is awarded annually to the league playoff champion at the end of each season. The NHL is the fifth-wealthiest professional sport league in the world by revenue, after the National Football League (NFL), Major League Baseball (MLB), the National Basketball Association (NBA), and the English Premier League (EPL). The National Hockey League was organized at the Windsor Hotel in Montreal on November 26, 1917, after the suspension of operations of its predecessor organization, the National Hockey Association (NHA), which had been founded in 1909 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vilibald Šťovík
Vilibald Šťovík (9 October 1917 in Prague, Austria-Hungary – 8 November 1948 in La Manche) was an ice hockey player for the Czechoslovakian national team. He won a silver medal at the 1948 Winter Olympics The 1948 Winter Olympics, officially known as the V Olympic Winter Games (german: V. Olympische Winterspiele; french: Ves Jeux olympiques d'hiver; it, V Giochi olimpici invernali; rm, V Gieus olimpics d'enviern) and commonly known as St. Moritz .... He died when in the airplane disaster, when the airplane with Czechoslovakia ice hockey national team fell down to the English Channel on the flight from Paris to London. References External links * 1917 births 1948 deaths Ice hockey players at the 1948 Winter Olympics Medalists at the 1948 Winter Olympics Olympic ice hockey players for Czechoslovakia Olympic medalists in ice hockey Olympic silver medalists for Czechoslovakia Ice hockey people from Prague Victims of aviation accidents or incidents in Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josef Trousílek
Josef Trousílek (March 16, 1918 in Prague, Austria-Hungary – October 10, 1990 in Prague, Czechoslovakia) was an ice hockey player for the Czechoslovak national team. He won a silver medal at the 1948 Winter Olympics The 1948 Winter Olympics, officially known as the V Olympic Winter Games (german: V. Olympische Winterspiele; french: Ves Jeux olympiques d'hiver; it, V Giochi olimpici invernali; rm, V Gieus olimpics d'enviern) and commonly known as St. Moritz .... References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Trousilek, Josef 1918 births 1990 deaths HC Slavia Praha players HC Sparta Praha players Ice hockey players at the 1948 Winter Olympics Medalists at the 1948 Winter Olympics Olympic ice hockey players for Czechoslovakia Olympic medalists in ice hockey Olympic silver medalists for Czechoslovakia Ice hockey people from Prague Czech ice hockey defencemen Czech ice hockey coaches Czechoslovak ice hockey coaches Czechoslovak ice hockey defencemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zdeněk Jarkovský
Zdeněk Jarkovský (3 October 1918 in Nový Bydžov, Austria-Hungary – 8 November 1948 in English Channel, La Manche) was an ice hockey goaltender for the Czechoslovakia, Czechoslovak national team. He won a silver medal at the 1948 Winter Olympics. He died when in an airplane disaster when the airplane with Czechoslovakia ice hockey national team fell into the English Channel on the flight from Paris to London. References External links * 1918 births 1948 deaths Ice hockey players at the 1948 Winter Olympics Olympic ice hockey players for Czechoslovakia Olympic medalists in ice hockey Olympic silver medalists for Czechoslovakia People from Nový Bydžov Medalists at the 1948 Winter Olympics Victims of aviation accidents or incidents in Europe Victims of aviation accidents or incidents in international waters Ice hockey people from the Hradec Králové Region Czech ice hockey goaltenders Czechoslovak ice hockey goaltenders Victims of aviation accidents or incidents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohumil Modrý
Bohumil Modrý (24 September 1916 – 21 July 1963) was a goaltender for the Czechoslovakia men's national ice hockey team which won the silver medal at the 1948 Olympics and the 2 gold medals - at the 1947 World Championship and at the 1949 World Championship. Modrý played his club hockey with LTC Praha (LTC Prague), which suffered four defections at the 1948 Spengler Cup in Davos. He was still a player with LTC Praha, and travelling as a delegate with the 1950 Czechoslovakia national team in March, when he and his teammates were arrested by the communist authorities. Czech national team has been stopped (Saturday, Mar-11) at the Prague Airport while preparing to travel to London to defend their title at the 1950 World Championship tournament (reason: reporter's visas, but it was lie). On Monday Mar-13 they have been arrested after party on Mar-12. Party was provide in the "Gold Pub", U Herclíků, Pštrossova 192/24, 110 00 Praha 1 – Nové Město and personally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The United States
The national flag of the United States, United States of America, often referred to as the ''American flag'' or the ''U.S. flag'', consists of thirteen equal horizontal stripes of red (top and bottom) alternating with white, with a blue rectangle in the Glossary of vexillology#Flag elements, canton (referred to specifically as the "union") bearing fifty small, white, five-pointed stars arranged in nine offset horizontal rows, where rows of six stars (top and bottom) alternate with rows of five stars. The 50 stars on the flag represent the 50 U.S. states, and the 13 stripes represent the Thirteen Colonies, thirteen British colonies that declared independence from Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, and became the first states in the U.S. Nicknames for the flag include the ''Stars and Stripes'', ''Old Glory'', and the ''Star-Spangled Banner''. History The current design of the U.S. flag is its 27th; the design of the flag has been modified officially 26 times since 1777. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Belgium
The national flag of Belgium ( nl, vlag van België, french: drapeau de la Belgique, german: Flagge Belgiens) is a tricolour consisting of three equal vertical bands displaying the national colours of Belgium: black, yellow, and red. The colours were taken from the coat of arms of the Duchy of Brabant, and the vertical design may be based on the flag of France. When flown, the black band is nearest the pole (at the hoist side). It has the unusual proportions of 1315. In 1830, the flag, at that time non-officially, consisted of three horizontal bands, with the colors red, yellow and black. On 23 January 1831, the National Congress enshrined the tricolor in the Constitution, but did not determine the direction and order of the color bands. As a result, the "official" flag was given vertical stripes with the colors black, yellow and red. Previous flags After the death of Charlemagne, the present-day territory of Belgium (except the County of Flanders) became part of Lotharingia, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Switzerland
The national flag of Switzerland (german: Schweizerfahne; french: drapeau de la Suisse; it, bandiera svizzera; rm, bandiera da la Svizra) displays a white cross in the centre of a square red field. The white cross is known as the Swiss cross or the federal cross. Its arms are equilateral, and their ratio of length to width is 7:6. The size of the cross in relation to the field was set in 2017 as 5:8.Appendix 2 ''Wappenschutzgesetz'' (SR 232.21), 21 June 2013 (effective 1 January 2017) engt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
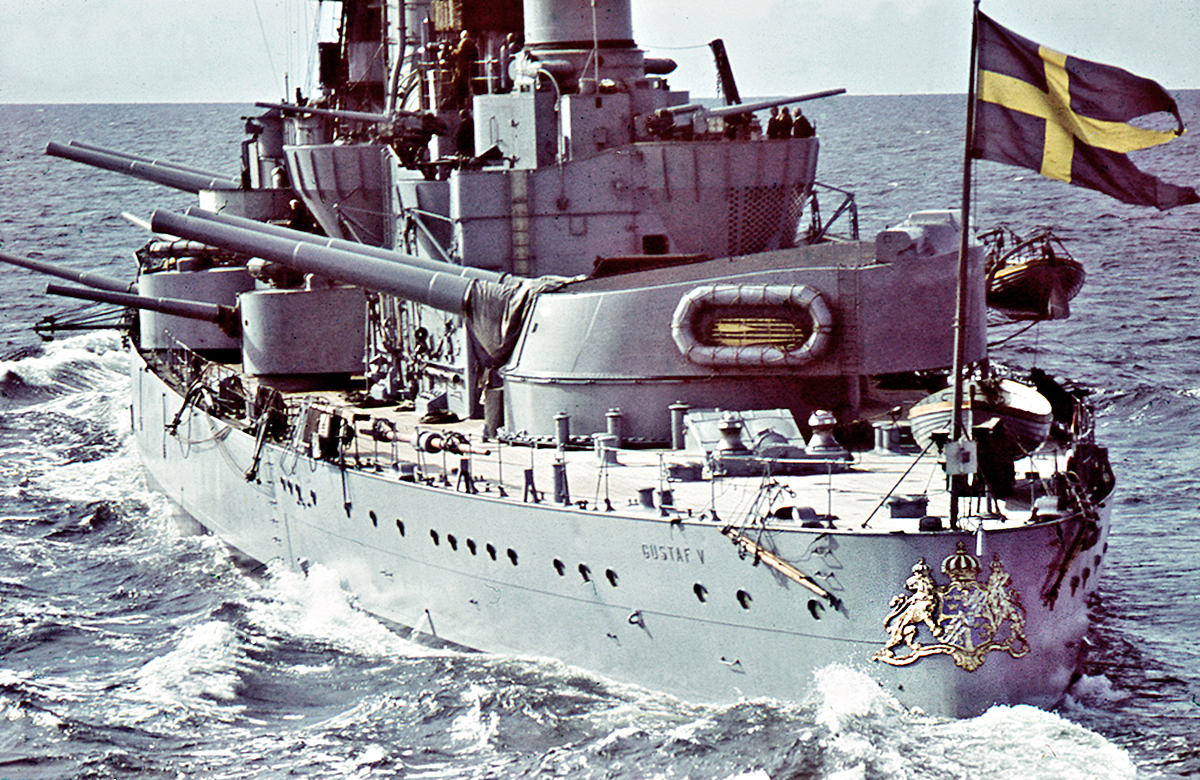
Flag Of Sweden
The national flag of Sweden ( sv, Sveriges flagga) consists of a yellow or gold Nordic cross (i.e. a horizontal cross extending to the edges, with the crossbar closer to the hoist than the fly) on a field of light blue. The Nordic cross design traditionally represents Christianity. The design and colours of the Swedish flag are believed to have been inspired by the present coat of arms of Sweden of 1442, which is blue divided quarterly by a cross pattée of gold, and modelled on the Danish flag. Blue and yellow have been used as Swedish colours at least since Magnus III's royal coat of arms of 1275. Specifics Ratio and colour scheme The Swedish flag is one of only five that use the ratio 5:8, the others being Argentina, Guatemala, Palau, and Poland. It is one of only four flags that currently use the colour scheme of blue and yellow, the others being Kazakhstan, Palau, and Ukraine. State flag and civil ensign The dimensions of the Swedish flag are 5:2:9 horizontally and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Romania
The national flag of Romania ( ro, drapelul României) is a tricolour. The Constitution of Romania states that "The flag of Romania is tricolour; the colours are arranged vertically in the following order from the flagpole: blue, yellow, red". The flag has a width-length ratio of 2:3; the proportions, shades of colour as well as the flag protocol were established by law in 1994, and extended in 2001. The civil flag of Andorra and the state flag of Chad are very similar to the Romanian national flag. The similarity with Chad's flag, which is identical apart from allowing a broader range of shades of blue, yellow and red, has caused international discussion. In 2004, Chad asked the United Nations to examine the issue. However, then-president of Romania Ion Iliescu announced that there would be no changes to the flag. The flag of Moldova is similar to the Romanian tricolour, except that it has a 1:2 ratio, a lighter shade of blue, a slightly different shade of yellow, and the Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The Czech Republic
The flag of the Czech Republic ( cs, státní vlajka České republiky) or flag of Czechia ( cs, vlajka Česka), or Czech Flag ( cs, česká vlajka) is the same as the flag of the former Czechoslovakia. Upon the dissolution of Czechoslovakia in 1993, the Czech Republic kept the Czechoslovak flag while Slovakia adopted its own flag. The first flag of Czechoslovakia was based on the flag of Bohemia and was white over red. This was almost identical to the flag of Poland (only the proportion was different), so a blue triangle was added at the hoist in 1920. The flag was banned by the Nazis in 1939 as they established a government nominally in control of Bohemia and Moravia, and a horizontal tricolour of white, red, and blue was used for the duration of the war. The 1920–1939 flag was restored in 1945. History The traditional colours of the Czech lands originated from an 1192 coat of arms (depicting a rampant lion with a double silver tail on a field of red). After the establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)