|
1941 South Australian State Election
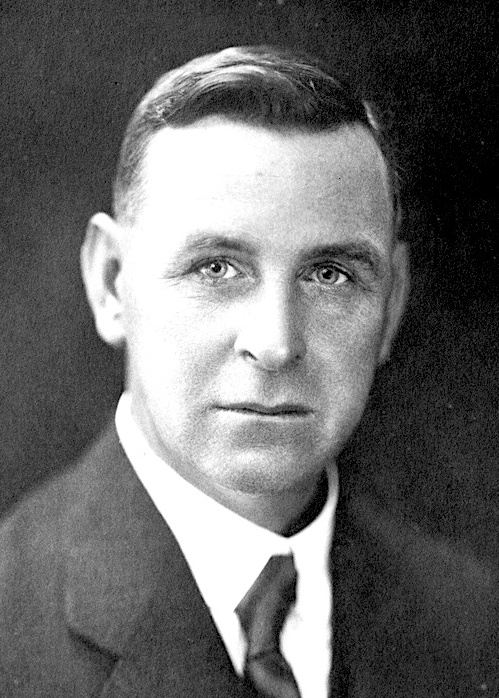
State elections were held in South Australia on 29 March 1941. All 39 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Liberal and Country League government led by Premier of South Australia Thomas Playford IV defeated the opposition Australian Labor Party led by Leader of the Opposition Robert Richards. Background Though the LCL was in minority government with 15 of 39 seats following the 1938 election, where 14 of 39 lower house MPs were elected as independents which as a grouping won more than either major party with 40 percent of the primary vote, the Playford LCL won a one-seat majority government following the 1941 election. Turnout crashed to a record-low 50 percent, triggering the government to institute compulsory voting from the 1944 election. Results See also * Results of the South Australian state election, 1941 (House of Assembly) * Members of the South Australian House of Assembly, 1941-1944 * Members of the South Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Australian House Of Assembly
The House of Assembly, or lower house, is one of the two chambers of the Parliament of South Australia. The other is the Legislative Council. It sits in Parliament House in the state capital, Adelaide. Overview The House of Assembly was created in 1857, when South Australia attained self-government. The development of an elected legislature — although only men could vote — marked a significant change from the prior system, where legislative power was in the hands of the Governor and the Legislative Council, which was appointed by the Governor. In 1895, the House of Assembly granted women the right to vote and stand for election to the legislature. South Australia was the second place in the world to do so after New Zealand in 1893, and the first to allow women to stand for election. (The first woman candidates for the South Australia Assembly ran in 1918 general election, in Adelaide and Sturt.) From 1857 to 1933, the House of Assembly was elected from multi-member dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1938 South Australian State Election
State elections were held in South Australia on 19 March 1938. All 39 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Liberal and Country League government led by Premier of South Australia Richard L. Butler defeated the opposition Australian Labor Party led by Leader of the Opposition Andrew Lacey. Background This election was the start of the electoral malapportionment which became known as the Playmander. It consisted of rural districts enjoying a 2-to-1 advantage in the state parliament, even though they contained less than half of the population, as well as a change from multi-member to single-member electorates, and the number of MPs in the lower house was reduced from 46 to 39. Labor remained out of power until the 1965 election. Tom Stott was one of 14 of 39 lower house MPs to be elected as an independent, which as a grouping won 40 percent of the primary vote, more than either of the major parties. Stott was the de facto leader of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1941 Elections In Australia
Events Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix. January * January–August – 10,072 men, women and children with mental and physical disabilities are asphyxiated with carbon monoxide in a gas chamber, at Hadamar Euthanasia Centre in Germany, in the first phase of mass killings under the Action T4 program here. * January 1 – Thailand's Prime Minister Plaek Phibunsongkhram decrees January 1 as the official start of the Thai solar calendar new year (thus the previous year that began April 1 had only 9 months). * January 3 – A decree (''Normalschrifterlass'') promulgated in Germany by Martin Bormann, on behalf of Adolf Hitler, requires replacement of blackletter typefaces by Antiqua. * January 4 – The short subject ''Elmer's Pet Rabbit'' is released, marking the second appearance of Bugs Bunny, and also the first to have his name on a title card. * January 5 – WWII: Battle of Bardia in Libya: Australian and British troops defeat I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elections In South Australia
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office. Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated since the 17th century. Elections may fill offices in the legislature, sometimes in the executive and judiciary, and for regional and local government. This process is also used in many other private and business organisations, from clubs to voluntary associations and corporations. The global use of elections as a tool for selecting representatives in modern representative democracies is in contrast with the practice in the democratic archetype, ancient Athens, where the elections were considered an oligarchic institution and most political offices were filled using sortition, also known as allotment, by which officeholders were chosen by lot. Electoral reform describes the process of introducing fair electoral systems where they are no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Playmander
The Playmander was a gerrymandering system, a pro-rural electoral malapportionment in the Australian state of South Australia, which was introduced by the incumbent Liberal and Country League (LCL) government in 1936, and remained in place for 32 years until 1968. This consisted of 26 low-population rural seats holding as much as a 10-to-1 advantage over the 13 high-population metropolitan seats in the state parliament, even though rural seats contained only a third of South Australia's population during this period. At the peak of the malapportionment in 1968, the rural seat of Frome had 4,500 formal votes, while the metropolitan seat of Enfield had 42,000 formal votes. Additionally, there was also a change from multi-member seats to single-member seats for the first time in South Australia's history, while the number of MPs in the lower house was reduced from 46 to 39. During the Playmander's existence, Labor managed to win enough parliamentary seats to form government onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Members Of The South Australian Legislative Council, 1941–1944
This is a list of members of the South Australian Legislative Council The Legislative Council, or upper house, is one of the two chambers of the Parliament of South Australia. Its central purpose is to act as a house of review for legislation passed through the lower house, the House of Assembly. It sits in Parli ... from 1941 to 1944 : Independent MLC Frank Halleday resigned on 14 July 1943 to contest the 1943 federal election in the House of Representatives seat of Barker. A by-election was not held due to the proximity of the 1944 state election. ReferencesParliament of South Australia — Statistical Record of the Legislature {{DEFAULTSORT:Members of the South Australian Legislative Council, 1941-1944 Members of South Australian parliaments by term 20th-century Australian politicians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Members Of The South Australian House Of Assembly, 1941-1944
Member may refer to: * Military jury, referred to as "Members" in military jargon * Element (mathematics), an object that belongs to a mathematical set * In object-oriented programming, a member of a class ** Field (computer science), entries in a database ** Member variable, a variable that is associated with a specific object * Limb (anatomy), an appendage of the human or animal body ** Euphemism for penis * Structural component of a truss, connected by nodes * User (computing), a person making use of a computing service, especially on the Internet * Member (geology), a component of a geological formation * Member of parliament * The Members, a British punk rock band * Meronymy, a semantic relationship in linguistics * Church membership, belonging to a local Christian congregation, a Christian denomination and the universal Church * Member, a participant in a club or learned society A learned society (; also learned academy, scholarly society, or academic association) is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Results Of The South Australian State Election, 1941 (House Of Assembly)
This is a list of House of Assembly results for the 1941 South Australian state election. Results by electoral district Adelaide * Preferences were not distributed. Albert * Preferences were not distributed. Alexandra Angas * Preferences were not distributed. Burnside * Preferences were not distributed. Burra Chaffey Eyre Flinders Frome Gawler Glenelg Goodwood Gouger Gumeracha Hindmarsh * Preferences were not distributed. Light * Preferences were not distributed. Mitcham * Preferences were not distributed. Mount Gambier Murray * Preferences were not distributed. Newcastle Norwood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent Politician
An independent or non-partisan politician is a politician not affiliated with any political party or bureaucratic association. There are numerous reasons why someone may stand for office as an independent. Some politicians have political views that do not align with the platforms of any political party, and therefore choose not to affiliate with them. Some independent politicians may be associated with a party, perhaps as former members of it, or else have views that align with it, but choose not to stand in its name, or are unable to do so because the party in question has selected another candidate. Others may belong to or support a political party at the national level but believe they should not formally represent it (and thus be subject to its policies) at another level. In running for public office, independents sometimes choose to form a party or alliance with other independents, and may formally register their party or alliance. Even where the word "independent" is used, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1944 South Australian State Election
State elections were held in South Australia on 29 April 1944. All 39 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Liberal and Country League government led by Premier of South Australia Thomas Playford IV defeated the opposition Australian Labor Party led by Leader of the Opposition Robert Richards. Background Labor won an additional five seats totaling 16 seats − the highest number of seats won by Labor from the 1933 election through to the 1959 election, an effort not even outdone at the 1953 election where Labor won 53 percent of the statewide two-party vote but the LCL retained government with the assistance of the Playmander − an electoral malapportionment that also saw a clear majority of the statewide two-party vote won by Labor while failing to form government in 1953, 1962 and 1968. The election was the first where the two-party vote had been retrospectively calculated. Unusually a wartime opposition won a clear majority o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compulsory Voting
Compulsory voting, also called mandatory voting, is the requirement in some countries that eligible citizens register and vote in elections. Penalties might be imposed on those who fail to do so without a valid reason. According to the CIA World Factbook, 21 countries, including 10 Latin American countries, officially had compulsory voting as of December 2021, with a number of those countries not enforcing it. Choosing a party to vote for is not obligatory, as blank votes can be cast, and are counted. During the first two decades of the 21st century, compulsory voting was introduced in Samoa and Bulgaria, while Chile, Cyprus, the Dominican Republic, Fiji and Paraguay repealed it. In 2022 Chile reintroduced it. Technically, compulsory voting is a practice that only requires citizens to attend a polling place to get their name crossed off the electoral roll. Because of the secret ballot, people can only be compelled to cast ballots, whether they choose to vote or not. History Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majority Government
A majority government is a government by one or more governing parties that hold an absolute majority of seats in a legislature. This is as opposed to a minority government, where the largest party in a legislature only has a plurality of seats. A government majority determines the balance of power. A majority government is usually assured of having its legislation passed and rarely if ever, has to fear being defeated in parliament, a state is also known as a working majority. In contrast, a minority government must constantly bargain for support from other parties in order to pass legislation and avoid being defeated on motions of no confidence. Single-party majority governments tend be formed in the aftermath of strong election performances. The term "majority government" may also be used for a stable coalition of two or more parties to form an absolute majority. One example of such an electoral coalition is in Australia, where the Liberal and National parties have run as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.gif)