|
1936 Democratic National Convention
The 1936 Democratic National Convention was held in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania from June 23 to 27, 1936. The convention resulted in the nomination of President Franklin D. Roosevelt and Vice President John N. Garner for reelection. Changes to rules At the 1936 Democratic Convention, the rule requiring candidates for President and Vice President to have a majority of two-thirds of the delegates votes to win nomination, which had existed since 1832, was abolished. Roosevelt had long pushed for the rule's abolition, in part due to past deadlocks: for example, the 1924 convention had required 103 ballots over roughly two weeks to nominate John W. Davis. The conventioneers provided that a simple majority of delegates would be required to win nomination, allowing for candidates to more easily be nominated and thus produce less balloting. In this regard, only one Democratic Convention after 1932 has required multiple ballots (that of 1952, which required three). This also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelphia Convention Hall And Civic Center
The Philadelphia Convention Hall and Civic Center – more commonly known simply as the Philadelphia Civic Center – was a convention center complex located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It developed out of a series of buildings dedicated to expanding trade which began with the National Export Exhibition in 1899. The two most significant buildings in the complex were the original main exhibition hall built in 1899, which later housed the Philadelphia Commercial Museum, and the Municipal Auditorium, later called the Convention Hall, which was built in 1931 to the designers of architect Philip H. Johnson. The site was host to national political conventions in 1900, 1936, 1940 and 1948. Location The Convention Hall arena was located at 3400 Civic Center Boulevard, on the edge of the campus of the University of Pennsylvania, and just to the southwest of Franklin Field. It was built in 1930 and its highest capacity was approximately 12,000. The building was an Art Deco landmark, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
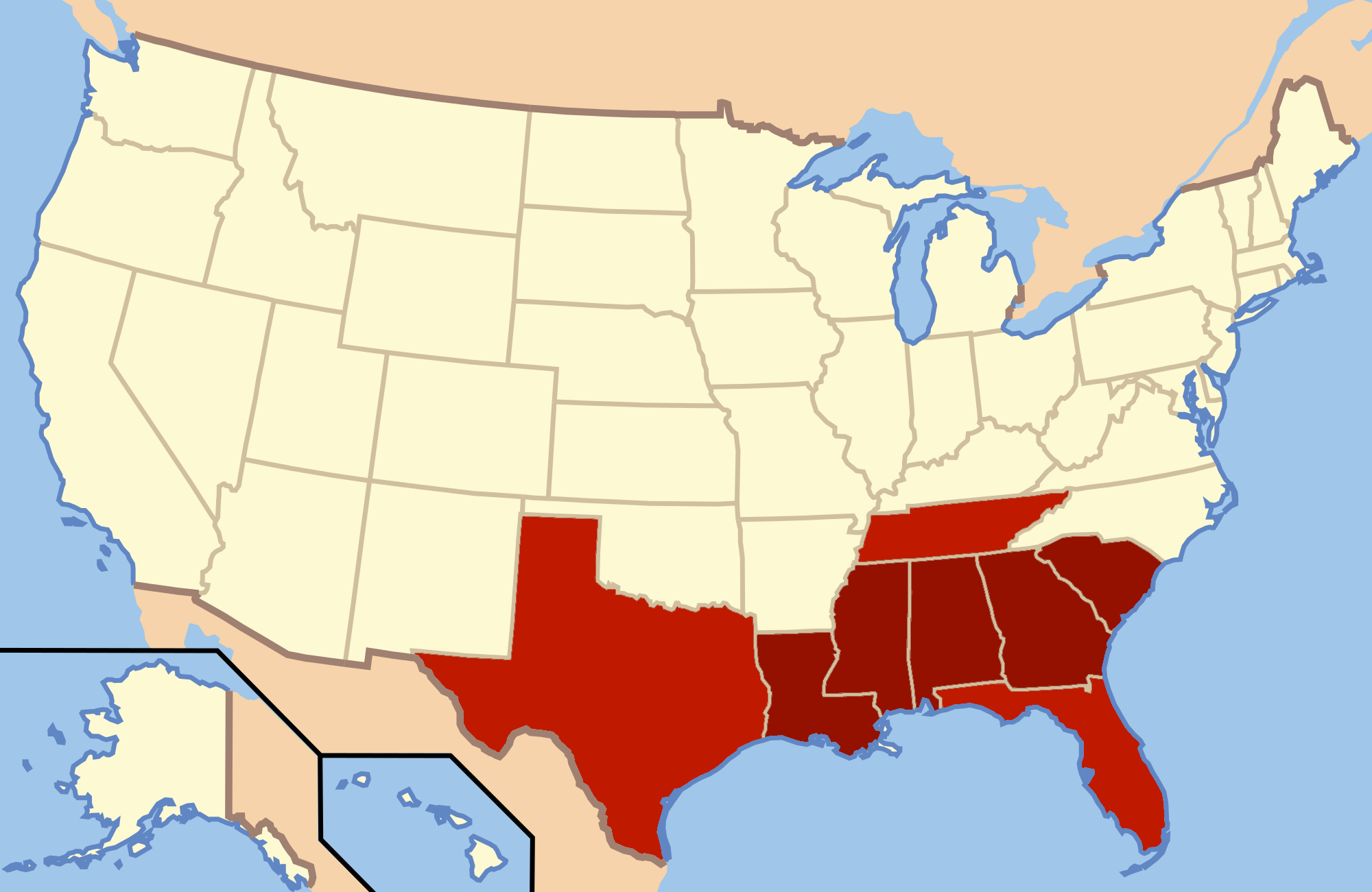
Dixiecrat
The States' Rights Democratic Party (whose members are often called the Dixiecrats) was a short-lived segregationist political party in the United States, active primarily in the South. It arose due to a Southern regional split in opposition to the Democratic Party. After President Harry S. Truman, a member of the Democratic Party, ordered integration of the military in 1948 and other actions to address civil rights of African Americans, many Southern conservative white politicians who objected to this course organized themselves as a breakaway faction. The Dixiecrats wished to protect Southern states' rights to maintain racial segregation. Supporters assumed control of the state Democratic parties in part or in full in several Southern states. The Party opposed racial integration and wanted to retain Jim Crow laws and white supremacy in the face of possible federal intervention. Its members were referred to as "Dixiecrats", a portmanteau of "Dixie", referring to the Southe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago, Illinois
(''City in a Garden''); I Will , image_map = , map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Country , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_type1 = U.S. state, State , subdivision_type2 = List of counties in Illinois, Counties , subdivision_name1 = Illinois , subdivision_name2 = Cook County, Illinois, Cook and DuPage County, Illinois, DuPage , established_title = Settled , established_date = , established_title2 = Municipal corporation, Incorporated (city) , established_date2 = , founder = Jean Baptiste Point du Sable , government_type = Mayor–council government, Mayor–council , governing_body = Chicago City Council , leader_title = Mayor of Chicago, Mayor , leader_name = Lori Lightfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1932 Democratic National Convention
The 1932 Democratic National Convention was held in Chicago, Illinois June 27 – July 2, 1932. The convention resulted in the nomination of Governor Franklin D. Roosevelt of New York for president and Speaker of the House John N. Garner from Texas for vice president. Beulah Rebecca Hooks Hannah Tingley was a member of the Democratic National Committee and Chair of the Democratic Party of Florida. She seconded the nomination of Franklin Delano Roosevelt, becoming the second woman to address a Democratic National Convention. The candidates The three major candidates: Convention The three major contenders for the presidential nomination were Roosevelt, Garner and former Governor of New York and 1928 presidential candidate, Al Smith, who roughly represented three competing factions of the Democratic Party: Smith was supported by the Tammany Hall machine in New York City, and had many supporters in the Democratic National Committee, as well as in Chicago, where Chicago mayor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1936 United States Presidential Election
The 1936 United States presidential election was the 38th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1936. In the midst of the Great Depression, incumbent Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt defeated Republican Governor Alf Landon of Kansas. Roosevelt won the highest share of the popular and electoral vote since the largely uncontested 1820 election. The sweeping victory consolidated the New Deal Coalition in control of the Fifth Party System. Roosevelt and Vice President John Nance Garner were re-nominated without opposition. With the backing of party leaders, Landon defeated progressive Senator William Borah at the 1936 Republican National Convention to win his party's presidential nomination. The populist Union Party nominated Congressman William Lemke for president. The election took place as the Great Depression entered its eighth year. Roosevelt was still working to push the provisions of his New Deal economic policy through Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1936 Republican National Convention
The 1936 Republican National Convention was held June 9–12 at the Public Auditorium in Cleveland, Ohio. It nominated Governor Alfred Landon of Kansas for president and Frank Knox of Illinois for vice president. The convention supported many New Deal programs, including Social Security. The keynote address was given on June 9 by Frederick Steiwer, U.S. Senator from Oregon. Image:LandonPortr.jpg, Image:William Edgar Borah cph.3b19589.jpg, Image:FrankKnox c1943 g399009.jpg, Image:Fredericksteiwer.jpg, Image:President_Hoover_portrait.jpg, Although many candidates sought the Republican nomination, only two, Governor Landon and Senator Borah, were considered to be serious candidates. Although favorite sons County Attorney Earl Warren of California, Governor Warren E. Green of South Dakota, and Stephen A. Day of Ohio won their respective primaries, the 70-year-old Borah, a well-known progressive and "insurgent," carried the Wisconsin, Nebraska, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Presidential Nominating Convention
A United States presidential nominating convention is a political convention held every four years in the United States by most of the political parties who will be fielding nominees in the upcoming U.S. presidential election. The formal purpose of such a convention is to select the party's nominee for popular election as President, as well as to adopt a statement of party principles and goals known as the '' party platform'' and adopt the rules for the party's activities, including the presidential nominating process for the next election cycle. Since 1972, the delegates have been mostly selected in presidential primaries state by state. This allows the nominees to be decided before the convention opens. In the 1976 GOP race, Ronald Reagan did well in the primaries but had clearly lost to incumbent Gerald Ford when the convention opened. Other delegates to these conventions include political party members who are seated automatically, and are called "unpledged delegates" bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Democratic National Conventions
This is a list of Democratic National Conventions. These conventions are the presidential nominating conventions of the Democratic Party of the United States. List of Democratic National Conventions * Conventions whose nominees won the subsequent presidential election are tinted in light blue. * Four other conventions — in 1876, 1888, 2000, and 2016 — which nominated candidates who won the popular vote, but not the Electoral College, are tinted in pale yellow. Footnotes 1832A resolution endorsing "the repeated nominations which he acksonhas received in various parts of the Union" was passed by the convention. 2840A resolution stating "that the convention deem it expedient at the present time not to choose between the individuals in nomination, but to leave the decision to their Republican fellow-citizens in the several states" was passed by the convention. Most Van Buren electors voted for Richard Mentor Johnson of Kentucky for the vice presidency; others voted for Lit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1936 Democratic Party Presidential Primaries
From March 10 to May 19, 1936, voters of the Democratic Party chose its nominee for president in the 1936 United States presidential election. Incumbent President Franklin D. Roosevelt was selected as the nominee through a series of primary elections and caucuses culminating in the 1936 Democratic National Convention held from June 23 to June 27, 1936, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Candidates Before his assassination, there was a challenge from Louisiana Senator Huey Long. But, due to his untimely assassination, President Roosevelt faced only one primary opponent other than various favorite sons. Primaries See also * Republican Party presidential primaries, 1936 *White primary White primaries were primary elections held in the Southern United States in which only white voters were permitted to participate. Statewide white primaries were established by the state Democratic Party units or by state legislatures in South C ... References {{United States presiden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The United States Democratic Party
The Democratic Party is one of the two major political parties of the United States political system and the oldest existing political party in that country founded in the 1830s and 1840s. It is also the oldest voter-based political party in the world. The party has changed significantly during its nearly two centuries of existence. Known as the party of the "common man," the early Democratic Party stood for individual rights and state sovereignty, and opposed banks and high tariffs. In the first decades of its existence, from 1832 to the mid-1850s (known as the Second Party System), under Presidents Andrew Jackson, Martin Van Buren and James K. Polk, the Democrats usually bested the opposition Whig Party by narrow margins. Before the American Civil War the party supported or tolerated slavery; and after the war until the Great Depression the party opposed civil rights reforms in order to retain the support of Southern voters. During this second period (1865-1932), th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshall L
Marshall may refer to: Places Australia * Marshall, Victoria, a suburb of Geelong, Victoria Canada * Marshall, Saskatchewan * The Marshall, a mountain in British Columbia Liberia * Marshall, Liberia Marshall Islands * Marshall Islands, an island nation in the Pacific Ocean United States of America * Marshall, Alaska * Marshall, Arkansas * Marshall, California * Lotus, California, former name Marshall * Marshall Pass, a mountain pass in Colorado * Marshall, Illinois * Marshall, Indiana * Marshall, Michigan * Marshall, Minnesota * Marshall, Missouri * Marshall, New York * Marshall, North Carolina * Marshall, North Dakota * Marshall, Oklahoma * Marshall, Texas, the largest U.S. city named Marshall * Marshall, Virginia * Marshall, Wisconsin (other) ** Marshall, Dane County, Wisconsin ** Marshall, Richland County, Wisconsin ** Marshall, Rusk County, Wisconsin Businesses * Marshall of Cambridge, a British holding company encompassing aerospace, fleet management, property ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)
