|
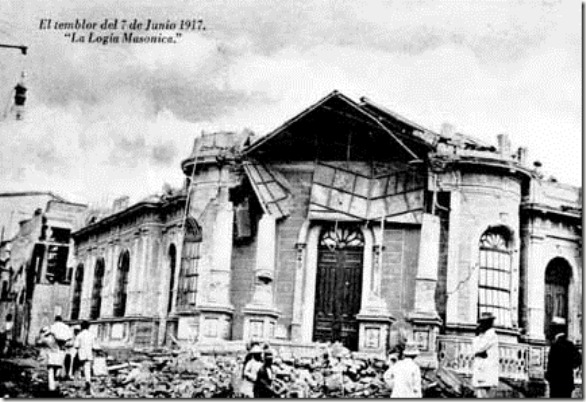
1917 San Salvador Earthquake
The 1917 San Salvador earthquake occurred on June 7 at 18:55 local time near the Salvadoran capital. The hypocenter of the 6.7 was at a shallow depth of , and occurred along a shallow crustal fault near San Salvador. The earthquake caused significant destruction of the city and left approximately 1,050 dead. It was followed by an eruption on San Salvador that killed another 1,100. Only behind the earthquake of 1986, it is the second deadliest in El Salvador's history. Earthquake El Salvador lies atop the Chortis Block, near its western margin. It is bounded by the Motagua– Polochic Fault between the North American–Caribbean transform boundary. Along the western margin, at the Middle America Trench, the Cocos Plate subducts beneath it at /year. Subduction produces volcanism along the Central America Volcanic Arc (CAVA) which stretches from Costa Rica to Guatemala. Within the shallow crust of El Salvador, seismicity is associated with the El Salvador Fault Zone (ESFZ), a shea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Time Zone
The North American Central Time Zone (CT) is a time zone in parts of Canada, the United States, Mexico, Central America, some Caribbean Islands, and part of the Eastern Pacific Ocean. Central Standard Time (CST) is six hours behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). During summer, most of the zone uses daylight saving time (DST), and changes to Central Daylight Time (CDT) which is five hours behind UTC. The largest city in the Central Time Zone is Mexico City; the Mexico City metropolitan area is the largest metropolitan area in the zone and in North America. Regions using (North American) Central Time Canada The province of Manitoba is the only province or territory in Canada that observes Central Time in all areas. The following Canadian provinces and territories observe Central Time in the areas noted, while their other areas observe Eastern Time: * Nunavut (territory): western areas (most of Kivalliq Region and part of Qikiqtaaluk Region) * Ontario (province): a port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
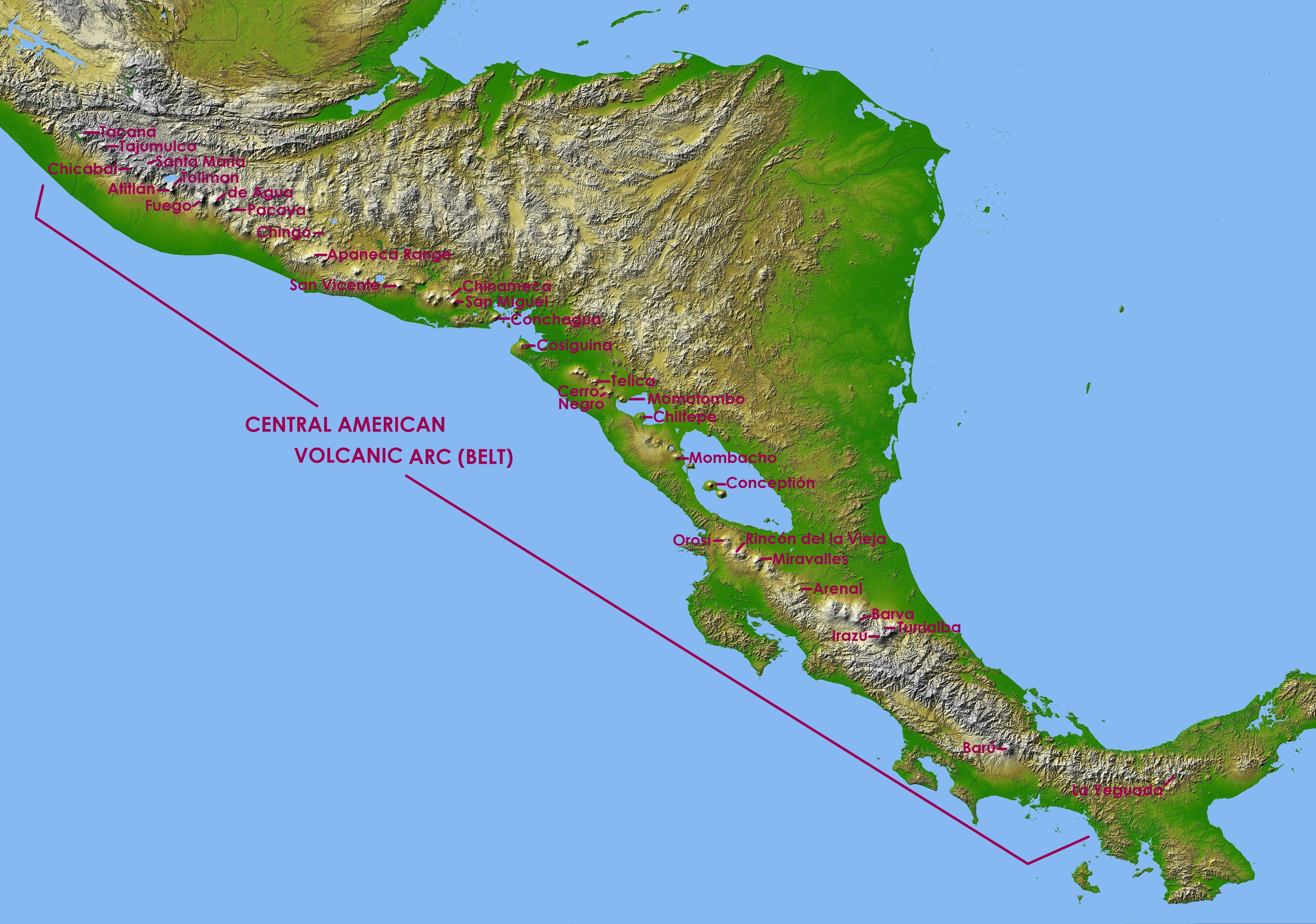
Central America Volcanic Arc
The Central American Volcanic Arc (often abbreviated to CAVA) is a chain of volcanoes which extends parallel to the Pacific coastline of the Central American Isthmus, from Mexico to Panama. This volcanic arc, which has a length of 1,100 kilometers (680 mi)Rose, W., Conway, F., Pullinger, C., Deino, A. and McIntosh, W., 1999. An improved age framework for late Quaternary silicic eruptions in northern Central America. ''Bulletin of Volcanology'', 61(1-2), pp.106-120. is formed by an active subduction zone, with the Cocos Plate subducting underneath the Caribbean Plate.Álvarez-Gómez, J., Meijer, P., Martínez-Díaz, J. and Capote, R., 2008. Constraints from finite element modeling on the active tectonics of northern Central America and the Middle America Trench. ''Tectonics'', 27(1) The region has been volcanically and geologically active for at least the past several million years. Numerous volcanoes are spread throughout various Central American countries; many have been active i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coffee Plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. The crops that are grown include cotton, coffee, tea, cocoa, sugar cane, opium, sisal, oil seeds, oil palms, fruits, rubber trees and forest trees. Protectionist policies and natural comparative advantage have sometimes contributed to determining where plantations are located. In modern use the term is usually taken to refer only to large-scale estates, but in earlier periods, before about 1800, it was the usual term for a farm of any size in the southern parts of British North America, with, as Noah Webster noted, "farm" becoming the usual term from about Maryland northwards. It was used in most British colonies, but very rarely in the United Kingdom itself in this sense. There, as also in America, it was used mainly for tree plantations, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Tecla, El Salvador
Santa Tecla () is a municipality in the La Libertad department of El Salvador. It is the capital of the department of La Libertad. The city was named after Saint Thecla who was a saint of the early Christian Church, and a reported follower of Paul of Tarsus in the 1st century AD. She is not mentioned in the New Testament, but the earliest record of her comes from the apocryphal ''Acts of Paul and Thecla'', probably composed in the early 2nd century. Santa Tecla is situated at the southern foot of the San Salvador Volcano, and very close to San Salvador (14.5 km, the capital city. The municipality of Antiguo Cuscatlán sits on its eastern border. History Santa Tecla was founded as "Nueva San Salvador" on August 8, 1854, by President José María San Martín after the capital city was destroyed by an earthquake. It served as capital of the republic from 1855 to 1859 and became departmental capital in 1865. The continued development of the city was spurred by the success of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quezaltepeque, La Libertad
Quezaltepeque is a municipality in the La Libertad department of El Salvador. It is located about 15 km from San Salvador. The word Quezaltepeque is a Nahuat word meaning "hills of quetzal." A quetzal is a bird that used to live around the area of Quezaltepeque. High levels of deforestation forced the bird to migrate to other areas. People * Darwin Cerén (born 1989), Salvadoran footballer who plays for Houston Dynamo FC and the El Salvador national football team * Manuel Flores Cornejo (born 1965), Farabundo Martí National Liberation Front (FMLN) 2024 presidential candidate * Alfonso Quijada Urías (born 1940), poet * Salvador Sánchez Cerén (born 1944), 42nd president of El Salvador The president of El Salvador ( es, Presidente de El Salvador), officially known as the President of the Republic of El Salvador ( es, Presidente de la República de El Salvador), is the Head of State, head of state and Head of Government, head ... (2014–2019) Sports The local f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenia, Sonsonate
Armenia is a Municipalities of El Salvador, municipality in the Sonsonate Department, Sonsonate department of El Salvador. The municipality has a population of around 14,997. History The name of this town was originally "Guaymoco" in ancient Pipil dialect of Nahuat and means "the oratory of the frogs". The current mayor is Carlos Rivera Molina (ARENA). Molina was first elected in 2002, taking the place of Moises Alvarado of the FMLN, and was re-elected to a second term in March 2006. Sports The local professional football clubs are named C.D. Salvadoreño and Rácing Junior and they both currently play in the Tercera Division de Fútbol Salvadoreño, Salvadoran Third Division. References External linksFinding the Armenians of Central America Municipalities of the Sonsonate Department {{ElSalvador-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porfirio Barba-Jacob
Miguel Ángel Osorio Benítez (July 29, 1883 – January 14, 1942), better known by his pseudonym, Porfirio Barba-Jacob, was a Colombian poet and writer. Born in Santa Rosa de Osos, Antioquia, to parents Antonio María Osorio and Pastora Benítez, he was raised by his grandparents in Angostura. In 1895 he started his travels, first through Colombia, and from 1907 to Central America and the United States, before finally settling down in 1930 in Mexico City. Around 1902 in Bogotá, he founded the literary magazine "El cancionero antioqueño" (''The Antioquian songbook''), which he managed under the pseudonym Marín Jiménez. Short after, he wrote the novel "Virginia", which was never published because the original manuscript was confiscated by the mayor of Santa Rosa for alleged immorality. In 1906 he moved to Barranquilla where he adopted the pseudonym Ricardo Arenales. He continued to use this pseudonym until 1922 when in Guatemala he adopted a new pseudonym which he would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface-wave Magnitude
The surface wave magnitude (M_s) scale is one of the magnitude scales used in seismology to describe the size of an earthquake. It is based on measurements of Rayleigh surface waves that travel along the uppermost layers of the Earth. This magnitude scale is related to the local magnitude scale proposed by Charles Francis Richter in 1935, with modifications from both Richter and Beno Gutenberg throughout the 1940s and 1950s. It is currently used in People's Republic of China as a national standard (GB 17740-1999) for categorising earthquakes. Recorded magnitudes of earthquakes through the mid 20th century, commonly attributed to Richter, could be either M_s or M_L. Definition The formula to calculate surface wave magnitude is: :M_s = \log_\left(\frac\right)_ + \sigma(\Delta)\,, where A is the maximum particle displacement in surface waves (vector sum of the two horizontal displacements) in μm, T is the corresponding period in s (usually 20 2 seconds), Δ is the epi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment Magnitude Scale
The moment magnitude scale (MMS; denoted explicitly with or Mw, and generally implied with use of a single M for magnitude) is a measure of an earthquake's magnitude ("size" or strength) based on its seismic moment. It was defined in a 1979 paper by Thomas C. Hanks and Hiroo Kanamori. Similar to the local magnitude scale, local magnitude/Richter scale () defined by Charles Francis Richter in 1935, it uses a logarithmic scale; small earthquakes have approximately the same magnitudes on both scales. Despite the difference, news media often says "Richter scale" when referring to the moment magnitude scale. Moment magnitude () is considered the authoritative magnitude scale for ranking earthquakes by size. It is more directly related to the energy of an earthquake than other scales, and does not saturate—that is, it does not underestimate magnitudes as other scales do in certain conditions. It has become the standard scale used by seismological authorities like the U.S. Geological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
February 2001 El Salvador Earthquake
The February 2001 El Salvador earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 6.6 on 13 February at 14:22:05 UTC. The epicentre was 15 miles (30 km) E of San Salvador, El Salvador. At least 315 people were killed, 3,399 were injured, and extensive damage affected the area. Another 16,752 homes were damaged and 44,759 destroyed. The most severe damage occurred in the San Juan Tepezontes- San Vicente-Cojutepeque area, though it was felt throughout the country and in neighboring Guatemala and Honduras. Landslides occurred in many areas of El Salvador. Tectonic setting El Salvador lies above the convergent boundary where oceanic crust of the Cocos Plate is being subducted beneath the Caribbean Plate at rate of about 72 mm per year along the Middle America Trench. This boundary is associated with earthquakes resulting from movement on the plate interface itself, such as the 7.7 1992 Nicaragua earthquake, and from faulting within both the overriding Caribbean Plate associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1965 San Salvador Earthquake
The 1965 San Salvador earthquake occurred at 04:01 in the morning on May 3, 1965. It had a moment magnitude of 5.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (''Severe''). The shock caused severe damage to El Salvador's capital city, San Salvador. The town of Ilopango, Soyapango, and Delgado was also hard hit. The earthquake was the most destructive to affect the city prior to the 1986 earthquake. Tectonic setting El Salvador lies above the convergent boundary where oceanic crust of the Cocos Plate is being subducted beneath the Caribbean Plate at rate of about 72 mm per year along the Middle America Trench. This boundary is associated with earthquakes resulting from movement on the plate interface itself, such as the 7.7 1992 Nicaragua earthquake, and from faulting within both the overriding Caribbean Plate and the subducting Cocos Plate, such as the 1982 El Salvador earthquake. Damage and casualties The earthquake left 125 people dead across the San Salvador metropolitan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |