|
1888 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1888 Atlantic hurricane season ran through the summer and the first half of fall in 1888. In the 1888 Atlantic season there were two tropical storms, four hurricanes, and two major hurricanes. However, in the absence of modern satellite and other remote-sensing technologies, only storms that affected populated land areas or encountered ships at sea are known, so the actual total could be higher. An undercount bias of zero to six tropical cyclones per year between 1851 and 1885 and zero to four per year between 1886 and 1910 has been estimated. __TOC__ Seasonal Summary ImageSize = width:800 height:200 PlotArea = top:10 bottom:80 right:20 left:20 Legend = columns:3 left:30 top:58 columnwidth:270 AlignBars = early DateFormat = dd/mm/yyyy Period = from:01/06/1888 till:31/12/1888 TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal ScaleMinor = grid:black unit:month increment:1 start:01/06/1888 Colors = id:canvas value:gray(0.88) id:GP value:red id:TD value:rgb(0.43,0.76,0.92) le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1886 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1886 Atlantic hurricane season ran through the early summer and the first half of fall in 1886. This is the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. It was a very active year, with ten hurricanes, six of which struck the United States, an event that would not occur again until 1985 and 2020. Four hurricanes became major hurricanes (Category 3+). However, in the absence of modern satellite and other remote-sensing technologies, only storms that affected populated land areas or encountered ships at sea are known, so the actual total could be higher. An undercount bias of zero to six tropical cyclones per year between 1851 and 1885 and zero to four per year between 1886 and 1910 has been estimated. Of the known 1886 cyclones, Hurricane Seven and Tropical Storm Eleven were first documented in 1996 by Jose Fernandez-Partagas and Henry Diaz. They also proposed large alterations to the known tracks of several other 1886 storms.Partagas, J.F. and H.F. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
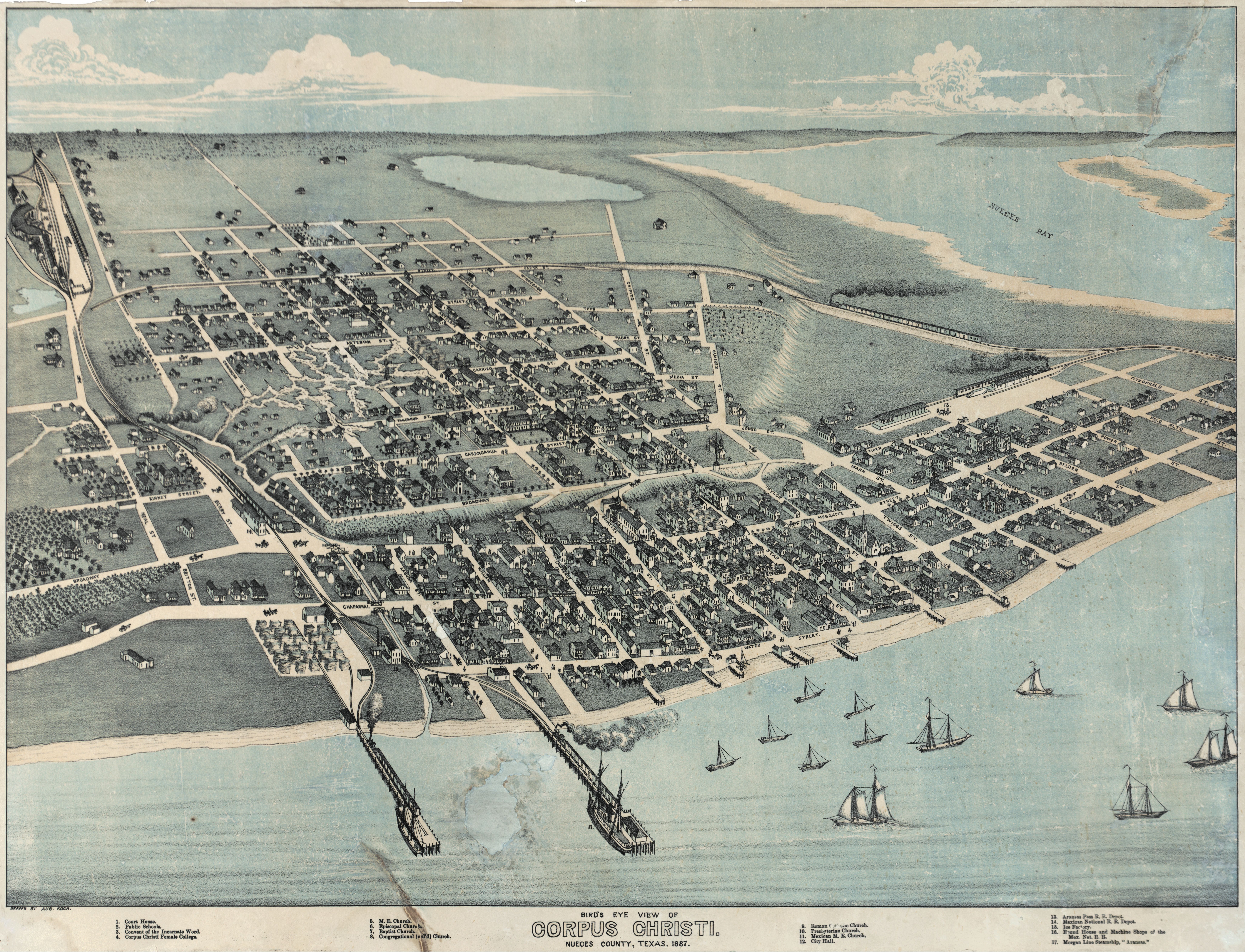
Corpus Christi, Texas
Corpus Christi (; Ecclesiastical Latin: "'' Body of Christ"'') is a coastal city in the South Texas region of the U.S. state of Texas and the county seat and largest city of Nueces County, it also extends into Aransas, Kleberg, and San Patricio Counties. It is southeast of San Antonio. Its political boundaries encompass Nueces Bay and Corpus Christi Bay. Its zoned boundaries include small land parcels or water inlets of three neighboring counties. The city's population was 317,863 in 2020, making it the eighth-most populous city in Texas. The Corpus Christi metropolitan area had an estimated population of 442,600. It is also the hub of the six-county Corpus Christi-Kingsville Combined Statistical Area, with a 2013 estimated population of 516,793. The Port of Corpus Christi is the fifth-largest in the United States. The region is served by the Corpus Christi International Airport. The city's name means body of Christ in Ecclesiastical Latin, in reference to the Christian sac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extratropical Cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of producing anything from cloudiness and mild showers to severe gales, thunderstorms, blizzards, and tornadoes. These types of cyclones are defined as large scale (synoptic) low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth. In contrast with tropical cyclones, extratropical cyclones produce rapid changes in temperature and dew point along broad lines, called weather fronts, about the center of the cyclone. Terminology The term " cyclone" applies to numerous types of low pressure areas, one of which is the extratropical cyclone. The descriptor ''extratropical'' signifies that this type of cyclone generally occurs outside the tropics and in the middle latitudes of Earth between 30° and 60° latitude. They are term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
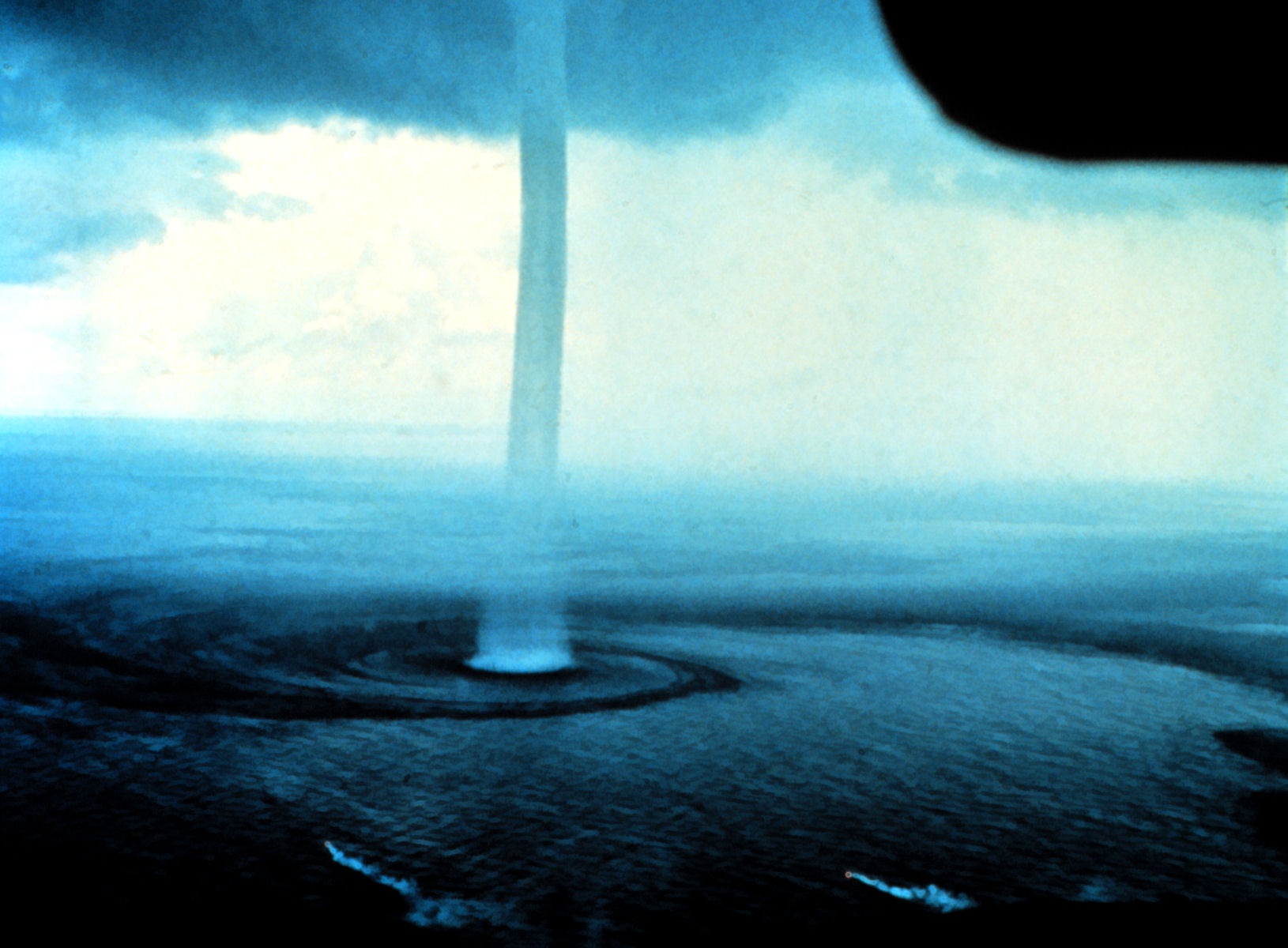
Waterspout
A waterspout is an intense columnar vortex (usually appearing as a funnel cloud, funnel-shaped cloud) that occurs over a body of water. Some are connected to a cumulus congestus cloud, some to a cumuliform cloud and some to a cumulonimbus cloud. In the common form, it is a non-supercell tornado over water having a five-part life cycle: formation of a dark spot on the water surface, spiral pattern on the water surface, formation of a spray ring, development of the visible condensation funnel, and ultimately, decay. Most waterspouts do not suck up water; they are small and weak rotating columns of air over water. Although they are most often weaker than their land counterparts, stronger versions spawned by mesocyclones do occur. While waterspouts form mostly in tropical and subtropical areas, other areas also report waterspouts, including Europe, Western Asia (the Middle East), Australia, New Zealand, the Great Lakes, Antarctica, and on rare occasions, the Great Salt Lake, amon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
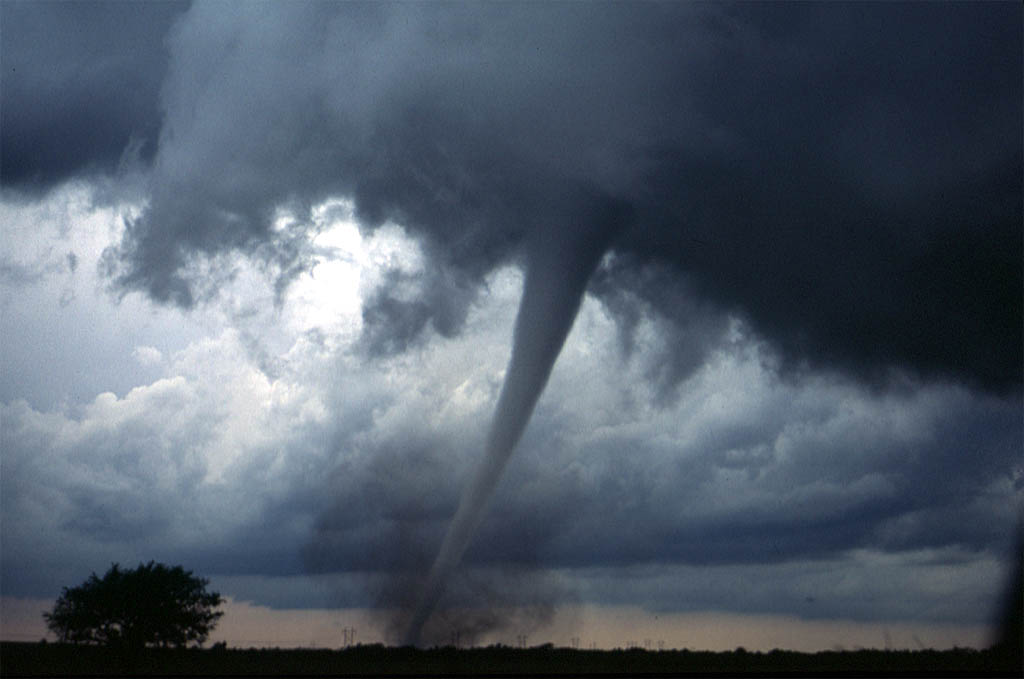
Tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the word cyclone is used in meteorology to name a weather system with a low-pressure area in the center around which, from an observer looking down toward the surface of the Earth, winds blow counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern. Tornadoes come in many shapes and sizes, and they are often visible in the form of a condensation funnel originating from the base of a cumulonimbus cloud, with a cloud of rotating debris and dust beneath it. Most tornadoes have wind speeds less than , are about across, and travel several kilometers (a few miles) before dissipating. The most extreme tornadoes can attain wind speeds of more than , are more than in diameter, and stay on the ground for more than 100 k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anderson County, Texas
Anderson County is a county in the U.S. state of Texas. Located within East Texas, its county seat is Palestine. As of the 2020 United States census, the population of Anderson County was 57,922. Anderson County comprises the Palestine micropolitan statistical area. Anderson County was organized in 1846, and was named for Kenneth Lewis Anderson (1805-1845), the last vice president of the Republic of Texas. History Native Americans Native Americans friendly to the settlers resided in East Texas before the Kiowa, Kickapoo, Kichai, Apache, and Comanche relocated to the territory. These tribes hunted, farmed the land, and were adept traders. By 1772, they had settled on the Brazos at Waco and on the Trinity upstream from present Palestine. The Tawakoni branch of Wichita Indians originated north of Texas, but migrated south into East Texas. From 1843 onward, the Tawakoni were part of treaties made by both the Republic of Texas and the United States. On May 19, 1836, an alliance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine, Texas
Palestine ( ) is a city in and the seat of Anderson County in the U.S. state of Texas. It was named for Palestine, Illinois, by preacher Daniel Parker, who had migrated from that town. The city had a 2020 U.S. census population of 18,544, making it the sixth-largest incorporated municipality in Northeast Texas by population. Palestine is a relatively small city located in the Piney Woods, equidistant from the major cities of Dallas, Houston, and Shreveport, Louisiana. It is notable for its natural environment, and has a notable dogwood blooming season. It has 23 historical sites on the National Register of Historic Places, and was the western terminus of the historic Texas State Railroad. Today this steam-and-diesel railroad museum operates tourist trains between Palestine and Rusk. History Indigenous groups such as the Coushatta Indians occupied this area for thousands of years before European encounter. During the years of Spanish and Mexican control of major parts of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee County, Texas
Cherokee County is a county located in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 50,412. The county seat is Rusk, which lies 130 miles southeast of Dallas and 160 miles north of Houston. The county was named for the Cherokee, who lived in the area before being expelled in 1839. Cherokee County comprises the Jacksonville micropolitan statistical area, which is also included in the Tyler–Jacksonville combined statistical area. History Native Americans The Hasinai group of the Caddo tribe built a village in the area in around AD 800 and continued to live in the area until the 1830s, when they migrated to the Brazos River. The federal government moved them to the Brazos Indian Reservation in 1855 and later to Oklahoma. The Cherokee, Delaware, Shawnee, and Kickapoo Native American peoples began settling in the area around 1820. The Texas Cherokee tried unsuccessfully to gain a grant to their own land from the Mexican government. Sam Houston, adopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico–United States Border
The Mexico–United States border ( es, frontera Estados Unidos–México) is an international border separating Mexico and the United States, extending from the Pacific Ocean in the west to the Gulf of Mexico in the east. The border traverses a variety of terrains, ranging from urban areas to deserts. The Mexico–United States border is the most frequently crossed border in the world, with approximately 350 million documented crossings annually. It is the tenth-longest border between two countries in the world. The total length of the continental border is . From the Gulf of Mexico, it follows the course of the Rio Grande (Río Bravo del Norte) to the border crossing at Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua, and El Paso, Texas. Westward from El Paso–Juárez, it crosses vast tracts of the Chihuahuan and Sonoran deserts to the Colorado River Delta and San Diego–Tijuana, before reaching the Pacific Ocean. Four American states border Mexico: California, Arizona, New Mexico, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico. The length of the Rio Grande is . It originates in south-central Colorado, in the United States, and flows to the Gulf of Mexico. The Rio Grande drainage basin (watershed) has an area of ; however, the endorheic basins that are adjacent to and within the greater drainage basin of the Rio Grande increase the total drainage-basin area to . The Rio Grande with Rio Grande Valley (landform), its fertile valley, along with its tributaries, is a vital watersource for seven US and Mexican states, and flows primarily through arid and semi-arid lands. After traversing the length of New Mexico, the Rio Grande becomes the Mexico–United States border, between the U.S. state of Texas and the northern Mexican states of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua and Coahuila, Nuevo León a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-pressure Area
In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possible rain or storms), while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis force, Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In Meteorology#Dynamic meteorology, meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places: * The first is in the area on the east side of upper Trough (meteorology), troughs, which form half of a Rossby wave within the Westerlies (a trough (meteorology), trough with la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Weather Service
The National Weather Service (NWS) is an Government agency, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weather-related products to organizations and the public for the purposes of protection, safety, and general information. It is a part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) branch of the United States Department of Commerce, Department of Commerce, and is headquartered in Silver Spring, Maryland, Silver Spring, Maryland, within the Washington metropolitan area. The agency was known as the United States Weather Bureau from 1890 until it adopted its current name in 1970. The NWS performs its primary task through a collection of national and regional centers, and 122 local List of National Weather Service Weather Forecast Offices, Weather Forecast Offices (WFOs). As the NWS is an agency of the U.S. federal government, most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |