|
1716 In Music
The year 1716 in music involved some significant events. Events * July 1 – Domenico Zipoli joins the Society of Jesus. Soon afterwards he is sent on a mission to Paraguay. *Georg Philipp Telemann visits Eisenach, resulting in an appointment as visiting Kapellmeister. *Antonio Stradivari – completes ''Le Messie'' violin (''The Messiah Stradivarius'') *Jonathan Swift conceives the idea for the Beggar's Opera. *Giuseppe Tartini hears Francesco Maria Veracini play the violin, and is inspired.{{Clarify, date=July 2017 Classical music * William Babell – ''The Fourth Book of the Ladys Entertainment'' *Johann Sebastian Bach **''Wachet, betet, seid bereit allezeit!'', Wachet! betet! betet! wachet! BWV 70, BWV 70a **Herz und Mund und Tat und Leben, BWV 147a, Herz und Mund und Tat und Leben, BWV 147a **''Mein Gott, wie lang, ach lange? BWV 155, Mein Gott, wie lang, ach lange'', BWV 155 **''Komm, du süße Todesstunde, BWV 161, Komm, du süsse Todesstunde'', BWV 161 **''Ärgre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
July 1
Events Pre-1600 * 69 – Tiberius Julius Alexander orders his Roman legions in Alexandria to swear allegiance to Vespasian as Emperor. * 552 – Battle of Taginae: Byzantine forces under Narses defeat the Ostrogoths in Italy, and the Ostrogoth king, Totila, is mortally wounded. *1097 – Battle of Dorylaeum: Crusaders led by prince Bohemond of Taranto defeat a Seljuk army led by sultan Kilij Arslan I. * 1431 – The Battle of La Higueruela takes place in Granada, leading to a modest advance of the Kingdom of Castile during the Reconquista. * 1520 – Spanish conquistadors led by Hernán Cortés fight their way out of Tenochtitlan after nightfall. * 1523 – Jan van Essen and Hendrik Vos become the first Lutheran martyrs, burned at the stake by Roman Catholic authorities in Brussels. * 1569 – Union of Lublin: The Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania confirm a real union; the united country is called the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ärgre Dich, O Seele, Nicht, BWV 186
(Do not be confounded, o soul), 186 is a church cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach. He composed it originally in Weimar in 1716 for Advent, , and expanded it in Leipzig in 1723 for the seventh Sunday after Trinity, where he first performed it on 11 July 1723. History and words Weimar The prescribed readings for the Third Sunday of Advent were from the First Epistle to the Corinthians, the ministry of faithful apostles (), and from the Gospel of Matthew, John the Baptist in prison (). The cantata is based on a cantata text written by Salomo Franck for the third Sunday of Advent, published in in 1717. His lyrics contained movements 1, 3, 5, 8, 10 of the later work and a different closing chorale of Ludwig Helmbold. Bach composed the music, BWV 186a, in 1716 in Weimar, where he first performed it on 13 December 1716. # Chorus: (movement 1 of BWV 186) # Aria 1: (3) # Aria 2: (5) # Aria 3: (8) # Aria 4: (10) # Chorale: A reconstruction of the cantata by Diethard Hellm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Baptiste Loeillet Of Ghent
Jean Baptiste Loeillet (6 July 1688 – c. 1720), who later styled himself Loeillet de Gant, was a Flemish composer, born in Ghent. He spent the largest part of his life in France in service to the archbishop of Lyon, Paul-François de Neufville de Villeroy. He wrote many works for recorder, including trio sonatas, unaccompanied sonatas for 2 recorders, and solo sonatas. He died in Lyon around 1720. Jean Baptiste Loeillet was a member of the large and musical Loeillet family, and the son of Pieter Loeillet and his first wife Marte (née Nortier). Loeillet added "de Ghent" to his surname to avoid confusion with his cousin, Jean-Baptiste Loeillet of London (1680–1730), who was a well-known musician and composer in London. The similar names have often caused confusion and mis-attribution of works, such as Alexandre Beón's arrangement of the C minor Piano trio for recorder, oboe, and basso continuo for modern instruments (the Piano Trio in B minor, now reprinted by International) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
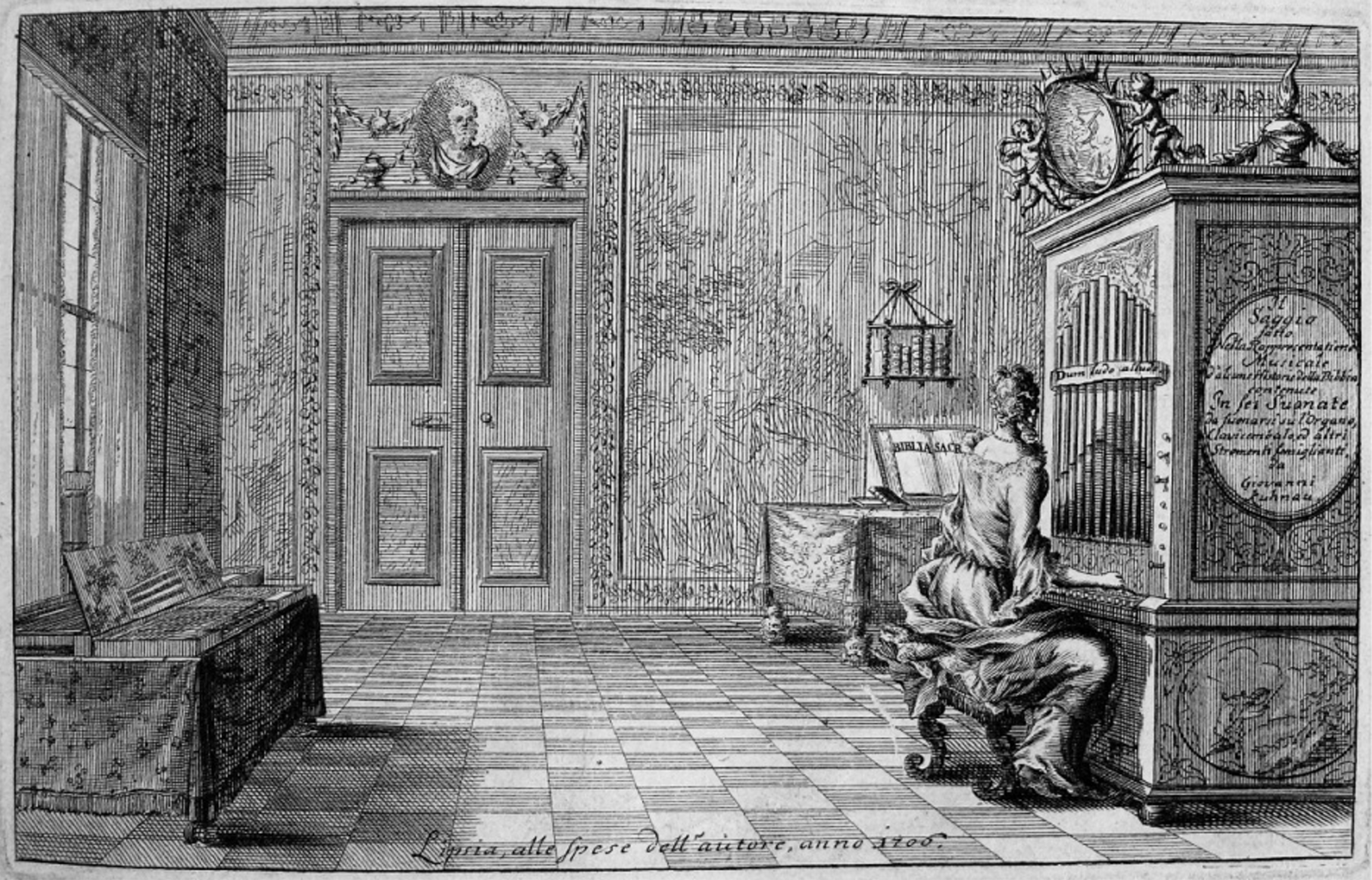
Johann Kuhnau
Johann Kuhnau (; 6 April 16605 June 1722) was a German polymath, known primarily as a composer today. He was also active as a novelist, translator, lawyer, and music theorist, and was able to combine these activities with his duties in his official post as Thomaskantor in Leipzig, which he occupied for 21 years. Much of his music, including operas, masses, and other large-scale vocal works, is lost. His reputation today rests on his ''Biblical Sonatas'', a set of programmatic keyboard sonatas published in 1700, in which each sonata depicted in detail a particular story from the Bible. After his death, Kuhnau was succeeded as Thomaskantor by Johann Sebastian Bach. Biography Much of the biographical information on Kuhnau is known from an autobiography published by Johann Mattheson in 1740 in his ''Grundlage einer Ehrenpforte''. Kuhnau's Protestant family was originally from Bohemia, and their name was Kuhn. Kuhnau was born in Geising, present-day Saxony. His musical talents we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Frideric Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel (; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque music, Baroque composer well known for his opera#Baroque era, operas, oratorios, anthems, concerto grosso, concerti grossi, and organ concertos. Handel received his training in Halle (Saale), Halle and worked as a composer in Hamburg and Italy before settling in London in 1712, where he spent the bulk of his career and Handel's Naturalisation Act 1727, became a naturalised British subject in 1727. He was strongly influenced both by the middle-German polyphony, polyphonic choral tradition and by composers of the Italian Baroque. In turn, Handel's music forms one of the peaks of the "high baroque" style, bringing Italian opera to its highest development, creating the genres of English oratorio and organ concerto, and introducing a new style into English church music. He is consistently recognized as one of the greatest composers of his age. Handel started three c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christoph Graupner
Christoph Graupner (13 January 1683 – 10 May 1760) was a German composer and harpsichordist of late Baroque music who was a contemporary of Johann Sebastian Bach, Georg Philipp Telemann and George Frideric Handel. Life Born in Hartmannsdorf near Kirchberg in Saxony, Graupner received his first musical instruction from his uncle, an organist named Nicolaus Kuester. Graupner went to the University of Leipzig where he studied law (as did many composers of the time) and then completed his musical studies with Johann Kuhnau, the cantor of the Thomasschule (St. Thomas School). In 1705, Graupner left Leipzig to play the harpsichord in the orchestra of the Hamburg Opera under the direction of Reinhard Keiser, alongside George Frideric Handel, then a young violinist. In addition to playing the harpsichord, Graupner composed six operas in Hamburg, some of them in collaboration with Keiser, a popular composer of operas in Germany. In 1709, Graupner accepted a post at the court of Hess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgio Gentili
{{disambig ...
Georgio is a variant of George. It may refer to: Mononyms *Georgio (singer) (born 1966), full name Georgio Alentini, born George Allen. American singer, songwriter, and musician *Georgio (rapper) (born 1993), birth name Georges Édouard Nicolo, French rapper and singer of Gudeloupean origin First name / Given name *Georgio Georgiades, from cast of TV series ''The Only Way Is Essex'' *Georgio Psychoundakis (1920–2006), Greek Resistance fighter on Crete during the Second World War) See also *George (name) * Georgios *Giorgio (other) Giorgio may refer to: * Castel Giorgio, ''comune'' in Umbria, Italy * Giorgio (name), an Italian given name and surname * Giorgio Moroder, or Giorgio, Italian record producer ** ''Giorgio'' (album), an album by Giorgio Moroder * "Giorgio" (song), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco Geminiani
230px Francesco Saverio Geminiani (baptised 5 December 1687 – 17 September 1762) was an Italian violinist, composer, and music theorist. BBC Radio 3 once described him as "now largely forgotten, but in his time considered almost a musical god, deemed to be the equal of Handel and Corelli." Life Born at Lucca, he received lessons in music from Alessandro Scarlatti, and studied the violin under Carlo Ambrogio Lonati in Milan and afterwards under Arcangelo Corelli. From 1707 he took the place of his father in the Cappella Palatina of Lucca. From 1711, he led the opera orchestra at Naples, as Leader of the Opera Orchestra and concertmaster, which gave him many opportunities for contact with Alessandro Scarlatti. After a brief return to Lucca, in 1714, he set off for London in the company of Francesco Barsanti, where he arrived with the reputation of a virtuoso violinist, and soon attracted attention and patrons, including William Capel, 3rd Earl of Essex, who remained a consiste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domenico Elmi
Domenico is an Italian given name for males and may refer to: People * Domenico Alfani, Italian painter * Domenico Allegri, Italian composer * Domenico Alvaro, Italian mobster * Domenico Ambrogi, Italian painter * Domenico Auria, Italian architect * Domenico del Barbieri, Florentine artist * Domenico di Bartolo, Italian painter * Domenico Bartolucci, Italian Roman Catholic cardinal * Domenico di Pace Beccafumi, Italian painter * Domenico Pignatelli di Belmonte, Italian Roman Catholic cardinal * Domenico Berardi, Italian footballer * Domenico Bernini, son of Gian Lorenzo Bernini * Domenico Bidognetti, Italian criminal * Domenico Bollani, Venetian diplomat and politician * Domenico Canale, Italian-American distributor * Domenico Caprioli, Italian painter * Domenico Caruso, Italian poet and writer * Domenico Cefalù, Italian-American mobster * Domenico Cimarosa, Italian composer * Domenico Cirillo, Italian physician and patriot * Domenico Colombo, father of Christopher Columb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaristo Felice Dall'Abaco
Evaristo Felice Dall'Abaco (12 July 1675, Verona, Italy — 12 July 1742, Munich, Bavaria) was an Italian composer, violinist, and cellist. Life Dall'Abaco was born in Verona to renowned guitarist Damiano dall'Abaco. He is thought to have been a pupil of Torelli's from whom he would have learned violin and cello. He became a violinist with Tommaso Antonio Vitali in Modena, and in 1704 joined the court of Maximilian II Emanuel, Elector of Bavaria in Munich as ''Kammermusiker''. After only a few months, he fled with the court to Brussels following Maximilian's defeat at the Battle of Blenheim. When he went into exile with the court, he spent time in France and absorbed some of the influences there. On Maximilian's restoration and return to Munich in 1715, Dall'Abaco was appointed ''Concert-meister''. He continued to compose chamber music at the French and Dutch courts until 1740, when he retired. Dall'Abaco's music is especially indebted to Vivaldi and Corelli. Dall'Abaco pass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L'art De Toucher Le Clavecin
''L'art de toucher le clavecin'' (English: ''The Art of Playing the Harpsichord'') is a didactic treatise by the French composer François Couperin. It was first published in 1716, and was followed by a revised edition in 1717. The treatise was written to instruct keyboard players in performance practice, particularly for Couperin's ''Pièces de Clavecin''; Couperin, upon its publication, noted that it was "absolutely indispensable for playing my ''Pièces'' in the style most suitable to them". With the early music revival, it became one of the primary sources for the keyboard fingering system which prevailed in Europe during the Baroque era. It also sheds light on the ornamentation used at the time. It is considered one of the most significant surviving treatises of the period. Publication history and contents There are no known autograph copies of the treatise, but copies survive of the two versions published during Couperin's lifetime. The 1716 edition of the work included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Couperin
François Couperin (; 10 November 1668 – 11 September 1733) was a French Baroque composer, organist and harpsichordist. He was known as ''Couperin le Grand'' ("Couperin the Great") to distinguish him from other members of the musically talented Couperin family. Life Couperin was born in Paris, into a prominent musical family. His father Charles was organist at the Church of Saint-Gervais in the city, a position previously held by Charles's brother Louis Couperin, the esteemed keyboard virtuoso and composer whose career was cut short by an early death. As a boy François must have received his first music lessons from his father, but Charles died in 1679 leaving the position at Saint-Gervais to his son, a common practice known as ''survivance'' that few churches ignored. With their hands tied, the churchwardens at Saint-Gervais hired Michel Richard Delalande to serve as new organist on the understanding that François would replace him at age 18. However, it is likely Couperin b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |