|
1660 In Science
The year 1660 in science and technology involved some significant events. Events * November 28 – At Gresham College in London, twelve men, including Christopher Wren, Robert Boyle, John Wilkins, and Robert Moray, meet after a lecture by Wren and resolve to found "a College for the Promoting of Physico-Mathematicall Experimentall Learning", which will become the Royal Society. Botany * John Ray publishes ''Catalogus plantarum circa Cantabrigiam nascentium'' in Cambridge, the first flora of an English county. Mathematics * The popular English-language edition by Isaac Barrow of Euclid's ''Elements'' is published in London. Physics * Robert Boyle publishes ''New Experiments Physico-Mechanicall, Touching the Spring of the Air and its Effects'' (the second edition in 1662 will contain Boyle's Law). Births * February 19 – Friedrich Hoffmann, German physician and chemist (died 1742) * April 16 – Hans Sloane, Ulster Scots-born collector and physician (died 1753) * March 15 â ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
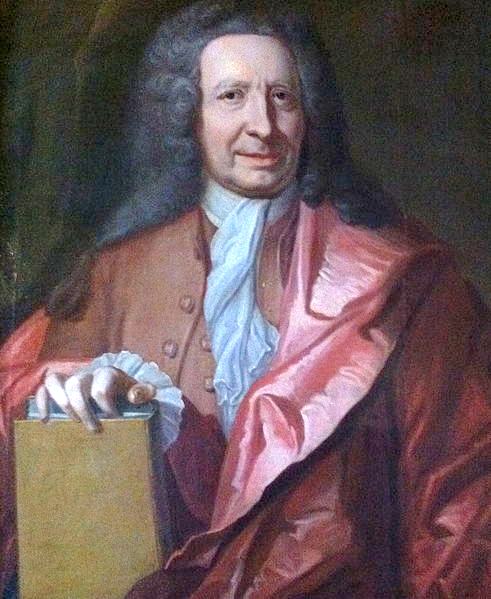
Friedrich Hoffmann
Friedrich Hoffmann or Hofmann (19 February 1660 – 12 November 1742) was a German physician and chemist. He is also sometimes known in English as Frederick Hoffmann. Life His family had been connected with medicine for 200 years before him. Born in Halle, he attended the local gymnasium where he acquired that taste for and skill in mathematics to which he attributed much of his later success. Beginning at age 18, he studied medicine at the University of Jena. From there, in 1680, he went to Erfurt, to attend Kasper Cramer's lectures on chemistry. Next year, returning to Jena, he received his doctor's diploma, and, after publishing a thesis, was permitted to teach. Constant study then began to tell on his health, and in 1682, leaving his already numerous pupils, he opened a practice in Minden at the request of a relative who held a high position in that town. After practising at Minden for two years, Hoffmann made a journey to Holland and England, where he formed the acquaintan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English People
The English people are an ethnic group and nation native to England, who speak the English language in England, English language, a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language, and share a common history and culture. The English identity is of History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon origin, when they were known in Old English as the ('race or tribe of the Angles'). Their ethnonym is derived from the Angles, one of the Germanic peoples who migrated to Great Britain around the 5th century AD. The English largely descend from two main historical population groups the West Germanic tribes (the Angles, Saxons, Jutes and Frisians) who settled in southern Britain following the withdrawal of the Ancient Rome, Romans, and the Romano-British culture, partially Romanised Celtic Britons already living there.Martiniano, R., Caffell, A., Holst, M. et al. Genomic signals of migration and continuity in Britain before the Anglo-Saxons. Nat Commun 7, 10326 (2016). https://doi.org/10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Hauksbee
Francis Hauksbee the Elder FRS (1660–1713), also known as Francis Hawksbee, was an 18th-century English scientist best known for his work on electricity and electrostatic repulsion. Biography Francis Hauksbee was the son of draper and common councillor Richard Hauksbee and his wife Mary. He was baptized on 27 May 1660 in the parish of St Mary-at-the-Walls, Colchester. He was the fifth of five sons. In 1673 Hauksbee entered Colchester Royal Grammar School. From 1678 to at least 1685 he apprenticed as a draper in the City of London, initially to his eldest brother. He was married no later than May 1687, when a daughter was born. Five of his eight children survived infancy. From 1687 to 1703, he may have run his own drapery shop. From at least March 1701, he lived at Giltspur Street, where he made air-pumps and pneumatic engines. The transition from drapery to scientific instrumentation and experimentation is not well documented. Historians have had to speculate about the events ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1740 In Science
The year 1740 in science and technology involved some significant events. Mathematics * Jean Paul de Gua de Malves publishes his work of analytic geometry, . Metallurgy * Benjamin Huntsman develops the technique of crucible steel production at Handsworth, South Yorkshire, England. Physics * Jacques-Barthélemy Micheli du Crest creates a spirit thermometer, making use of two fixed points, 0 for "Temperature of earth" based on a cave at Paris Observatory and 100 for the heat of boiling water. * Émilie du Châtelet publishes ''Institutions de Physique'', including a demonstration that the energy of a moving object is proportional to the square of its velocity (Ek = mv²). * Louis Bertrand Castel publishes ''L'Optique des couleurs'' in Paris, including the observation that the colours of white light split by a prism depend on distance from the prism. Technology * Henry Hindley of Yorkshire invents a device to cut the teeth of clock wheels. Awards * Copley Medal: Alexander Stuart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
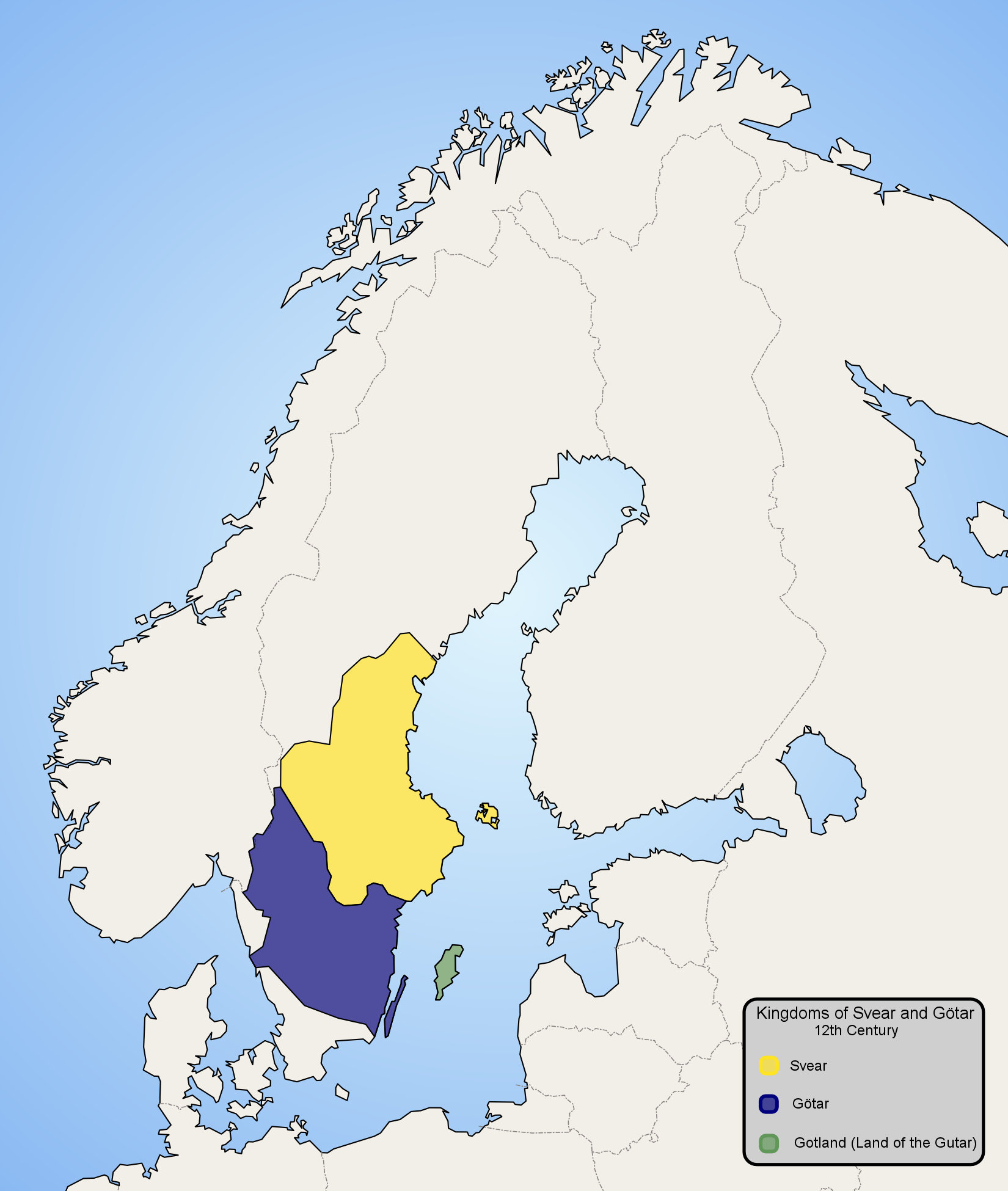
Swedes
Swedes ( sv, svenskar) are a North Germanic ethnic group native to the Nordic region, primarily their nation state of Sweden, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countries, in particular Finland where they are an officially recognized minority, with a substantial diaspora in other countries, especially the United States. Etymology The English term "Swede" has been attested in English since the late 16th century and is of Middle Dutch or Middle Low German origin. In Swedish, the term is ''svensk'', which is from the name of '' svear'' (or Swedes), the people who inhabited Svealand in eastern central Sweden, and were listed as ''Suiones'' in Tacitus' history '' Germania'' from the first century AD. The term is believed to have been derived from the Proto-Indo-European reflexive pronominal root, , as the Latin ''suus''. The word must have meant "one's own (tribesmen)". The same root and original mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olof Rudbeck The Younger
Olof Rudbeck the Younger or Olaus Rudbeckius d.y. (15 March 1660 – 23 March 1740) was a Swedish explorer, scientist, botanist, ornithologist and rector of Uppsala University. Biography Olof Rudbeck was born in Uppsala, Sweden, the son of Olaus Rudbeck Sr. (1630–1702), a professor of medicine at Uppsala University. He travelled to England, Holland and Germany in 1687 to study botany. Rudbeck took a medical degree at the Utrecht University in 1690. Returning to his home country in 1692, he succeeded his father as professor of medicine at Uppsala University. Serving alongside Lars Roberg (1664–1742), he specialized in anatomy, botany, zoology, and pharmacology, while Roberg gave lectures in medicine, surgery, physiology and chemistry. He travelled to Lapland in 1695, joining an expedition commissioned by the King Charles XI of Sweden (1655–1697), for which his mission was to study nature, the mountainous region in particular. He returned and published ''Lapponia illustrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1753 In Science
The year 1753 in science and technology involved some significant events. Astronomy * Ruđer Bošković's ''De lunae atmosphaera'' demonstrates the lack of atmosphere on the Moon. Botany * May 1 – Publication of Linnaeus' ''Species Plantarum'', the start of formal scientific classification of plants. * June – Establishment in Florence of the ''Accademia dei Georgofili'', the world's oldest society devoted to agronomy and scientific agriculture. Chemistry * Claude François Geoffroy demonstrates that bismuth is distinct from lead and tin. Computer science * January 1 – Retrospectively, the minimum date value for a datetime field in an SQL Server (up to version 2005) due to this being the first full year since Britain's adoption of the Gregorian calendar. Medicine * James Lind publishes the first edition of ''A Treatise on the Scurvy'' (although it is little noticed at this time). Physics * November 25 – The Russian Academy of Sciences announces a competition among che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulster Scots People
The Ulster Scots ( Ulster-Scots: ''Ulstèr-Scotch''; ga, Albanaigh Ultach), also called Ulster Scots people (''Ulstèr-Scotch fowk'') or (in North America) Scotch-Irish (''Scotch-Airisch''), are an ethnic group in Ireland, who speak an Ulster Scots dialect of the Scots language, a West Germanic language, and share a common history, culture and ancestry. As an ethnicity, they diverged from largely the same ancestors as those of modern English people, and Lowland Scots people, native to Northern England, and Lowland Scotland, respectively. Found mostly in the province of Ulster, and to a lesser extent in the rest of Ireland, their ancestors were Protestant, mainly Presbyterian, settlers who migrated from the Scottish Lowlands and Northern England during the Plantation of Ulster. The largest numbers came from Dumfries and Galloway, Lanarkshire, Renfrewshire, Ayrshire, Scottish Borders, Northumberland, Cumbria, Yorkshire, and to a much lesser extent, from the Scottish Highlands. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Sloane
Sir Hans Sloane, 1st Baronet (16 April 1660 – 11 January 1753), was an Irish physician, naturalist, and collector, with a collection of 71,000 items which he bequeathed to the British nation, thus providing the foundation of the British Museum, the British Library, and the Natural History Museum, London. He was elected to the Royal Society at the age of 24. Sloane travelled to the Caribbean in 1687 and documented his travels and findings with extensive publications years later. Sloane was a renowned medical doctor among the aristocracy, and was elected to the Royal College of Physicians at age 27. Though he is credited with the invention of chocolate milk, it is more likely that he learned the practice of adding milk to drinking chocolate while living and working in Jamaica. Streets and places were later named after him, including Hans Place, Hans Crescent, and Sloane Square in and around Chelsea, London – the area of his final residence – and also Sir Hans Sloane Square ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1742 In Science
The year 1742 in science and technology involved some significant events. Astronomy * January 14 – Death of Edmond Halley; James Bradley succeeds him as Astronomer Royal in Great Britain. Mathematics * June – Christian Goldbach produces Goldbach's conjecture. * Colin Maclaurin publishes his ''Treatise on Fluxions'' in Great Britain, the first systematic exposition of Newton's methods. Metrology * Anders Celsius publishes his proposal for a centigrade temperature scale originated in 1741. Physiology and medicine * Surgeon Joseph Hurlock publishes his ''A Practical Treatise upon Dentition, or The breeding of teeth in children'' in London, the first treatise in English on dentition. Technology * Benjamin Robins publishes his ''New Principles of Gunnery, containing the determination of the force of gun-powder and an investigation of the difference in the resisting power of the air to swift and slow motions'' in London, containing a description of his ballistic pendulum and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |